This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Nhat - Infectious Specialist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalHepatitis C is a type of hepatitis caused by a virus, which can be transmitted when the blood of a person infected with the hepatitis C virus enters the body of an uninfected person. About 70-80% of people with hepatitis C do not have any symptoms.
1. Symptoms of Hepatitis C
After the hepatitis C virus enters the body, they have a rather long incubation period (about 6-8 weeks), followed by this period of onset. Most cases of hepatitis C have no clinical symptoms until cirrhosis manifests, sometimes with fatigue, anorexia, bloating, mild right upper quadrant pain, gastrointestinal disturbances, muscle pain. Mild, subtle jaundice may occur. There may be extra-hepatic manifestations such as: joint pain, arthritis, easy hair loss......
However, the above symptoms are sometimes only mild, the patient does not pay attention, so it is easy to ignore even The liver is in a very severe inflammatory phase. The full-blown disease stage can last about 6-8 weeks and then the disease will go away on its own without treatment. However, cure cases account for only 15 to 30% of cases. The rest will become healthy carriers of the hepatitis C virus (that is, after 6 months the body cannot eliminate the hepatitis C virus) or become chronic hepatitis C sufferers.

2. Is hepatitis C contagious?
Hepatitis C is usually transmitted when the blood of a person infected with the hepatitis C virus enters the body of an uninfected person. Today, most people get this infection by sharing needles or other items to inject drugs.
Hepatitis C virus can be transmitted in the following ways:
Sharing needles, or other items used to inject drugs with a carrier of hepatitis C virus; Medical staff who are stabbed by a needle while working; The child is born to a mother who carries the hepatitis C virus; Sharing certain items with someone who carries the hepatitis C virus (such as razors, toothbrushes,...); Having sex with someone who carries the hepatitis C virus. However, there is currently no evidence of infection with the hepatitis C virus from mosquito bites or other insect bites. Because the disease has no obvious symptoms, most people do not realize they have been infected and may unknowingly allow the disease to spread in the community.
Although it is very contagious and has many dangerous complications, but hepatitis C can be cured if detected early, with the right medicine and right treatment. The current popular treatment method is antiviral drugs combined with new generation interferon.
2. Harm of Hepatitis C
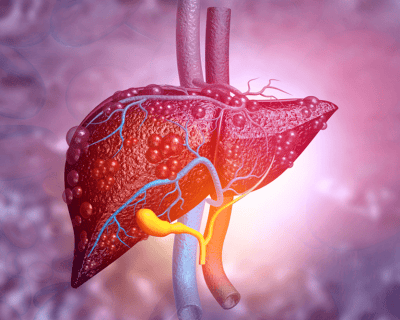
Cirrhosis The first complication of hepatitis C is cirrhosis. Many people think that cirrhosis is caused by alcohol, but any condition that damages the liver over many years can cause cirrhosis and the formation of scar tissue. Scar tissue will take a long time, about 20–30 years for liver damage to lead to cirrhosis. If cirrhosis is not treated properly, the risk of liver failure is very high.
When the liver is cirrhosis, caused by the hepatitis C virus, it damages healthy cells, causing scars and forming fibrous tissue. They slow the flow of blood through the liver, causing blood to pool in the veins of the digestive system. In the early stages of cirrhosis, there are often only vague symptoms such as fatigue, loss of appetite or mild pain in the right abdomen, but sometimes there are no symptoms. A common complication of cirrhosis is portal hypertension, in which there is an increase in pressure in the portal vein, which helps transport blood between the organs of the digestive system and the liver.
Liver failure When cirrhosis is caused by hepatitis C, if not treated, the disease will progress more and more seriously, because scar tissue caused by the virus continues to grow, making liver function worse. , eventually leading to liver failure. Liver failure is manifested by very serious signs such as: jaundice, yellow eyes, decreased urination, swollen limbs, ascites, personality changes.
Cirrhosis and liver failure caused by hepatitis C virus are very serious complications and antiretroviral therapy is extremely necessary and important to clear the virus to prevent complications and when cirrhosis is present. , liver failure, liver transplantation is the recommended method to use.
Liver cancer In addition to complications of cirrhosis and liver failure, hepatitis C virus also causes liver cancer. This is the late and most dangerous complication of hepatobiliary diseases. When infected with the hepatitis C virus, the risk of liver cancer is 12 times higher than that of people who are not infected and in fact liver cancer often occurs in people with cirrhosis. In addition, factors that increase the risk of liver cancer caused by hepatitis C include alcohol abuse, smoking, HIV infection, obesity, and high levels of iron in the liver.
Other complications Hepatitis C virus in addition to attacking and destroying the liver, the complications of the disease also affect other parts and systems in the body. Because while infected with hepatitis C virus, the body forms antibodies to fight, it is this antibody that creates reactions that cause harmful effects to other organs of the body such as kidney damage, numbness, itching and pain due to nerve damage, joint pain, skin redness, ulcers. In addition, hepatitis C can also increase the risk of developing other diseases including diabetes, depression...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.