This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor Ear - Nose - Throat Doctor - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International Hospital.
Hearing loss or hard of hearing are both common conditions in older adults. Hearing testing plays an extremely important role in detecting hearing problems early, so that measures can be taken to improve and correct them before they become more serious.
1. What is a hearing test?
Hearing tests can help assess your hearing. Normal hearing will have sound waves traveling into the ear, causing the eardrum to vibrate. This vibration helps the waves travel to your ears and activates nerve cells that send sound information to your brain. This information will be translated by the brain into the sounds you hear.
2. When does hearing loss happen?
Hearing loss occurs when you have problems with one or more parts of the ear, the nerves inside the ear, or the part of the brain that controls hearing.
Here are the 3 main types of hearing loss, including:
2.1 Neural Deafness This type of hearing loss occurs when there is a problem with the structure of the ear or the nerves that control hearing. It can appear as soon as you are born or later in life.
Neurological deafness is often a permanent condition, which can range from mild (hard of hearing) to severe (not able to hear any sounds).
2.2 Conduction This type of hearing loss can occur due to a blockage in the passage of sound into the ear. It tends to occur at any age, especially infants and young children, often due to fluid in the ear or an ear infection.
Conductive hearing loss is a health condition that is not worrisome and is treatable.
2.3 Mixed Mixed is a combination of both neuropathic deafness and conductive hearing loss.
Hard of hearing or hearing loss are common occurrences in the elderly. According to research, about one-third of adults aged 65 and older have hearing loss, often of the neuro-deaf type. If you've been diagnosed with hearing loss, talk to your doctor as soon as possible about steps to help treat or manage the condition.
3. Why do you need a hearing test?
Hearing tests for adults are now widely used to help identify hearing problems and their severity. There are many causes of hearing loss in adults, including:
Frequent work in loud noises Mowing the lawn or using power tools continuously Shooting guns or using loud noise weapons other Too much earwax Listening to music with loud speakers Getting hit in the head Infection Taking certain medications Having family members with hearing problems. Not everyone realizes they have a hearing problem. You may not even know you have hearing loss because it is often a gradual process. This is also why you should get a hearing test even if there are no noticeable hearing problems.
4. When to get a hearing test?
Hearing testing for the elderly plays an extremely important role in supporting early treatment of severe hearing loss or hearing loss. You may need a hearing test when you have the following symptoms:
Difficulty understanding what others are saying, especially in noisy environments Frequently asking others to repeat what they just said Difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds Need to turn up the volume when listening to the radio or watching TV Feeling of tinnitus.
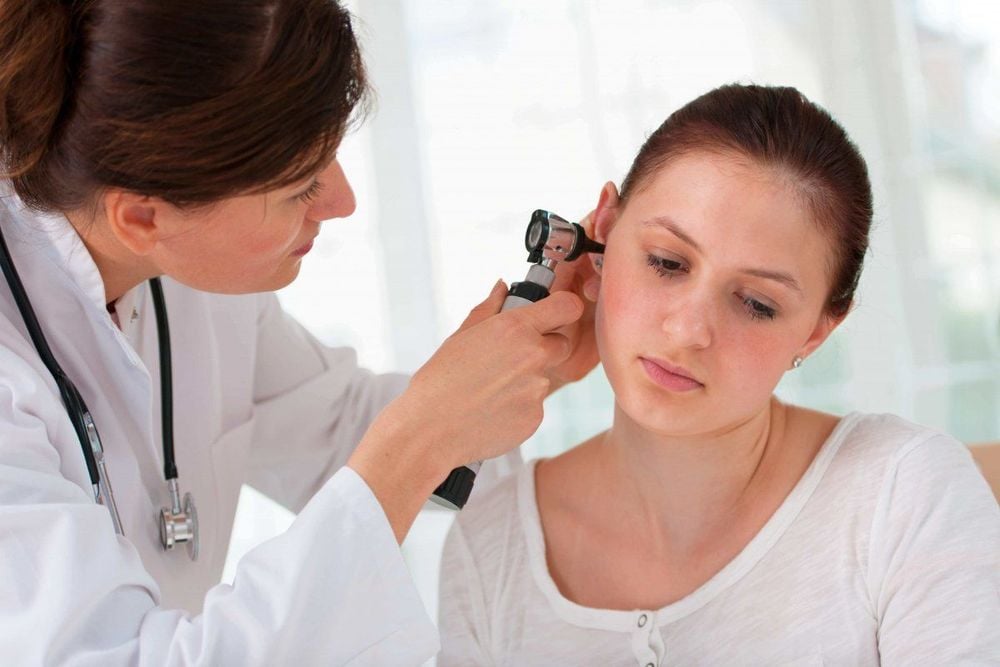
5. How is a hearing test done?
Hearing tests can be performed by the following professionals:
An audiologist, who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of hearing loss An ENT doctor, who specializes in treating hearing loss. for diseases or certain conditions of the ears, nose, and throat. Most hearing tests for adults aim to determine if a patient's response to sounds or words is distributed at different volumes, pitches, or noise environments. These are collectively known as acoustic tests, and include:
5.1 Sound reflex measurements Sound reflex measurements also known as middle ear muscle reflex (MEMR), help Test the ear's response to loud sounds.
For normal hearing, a small muscle inside the ear constricts when you hear loud noises, known collectively as the acoustic reflex. During acoustic reflexology, your doctor will place a soft rubber tip inside your ear.
Then a series of loud sounds are sent and recorded into the machine. The machine will display when the sound has activated the reflection. If you have severe hearing loss, very loud sounds will be needed to trigger the reflex.
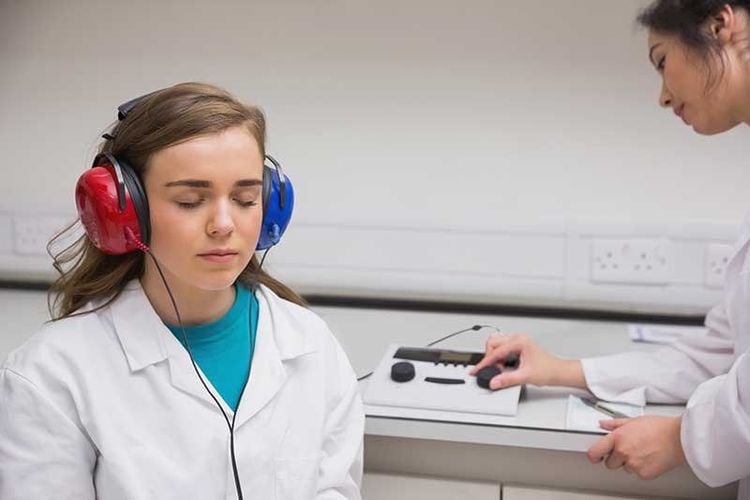
5.2 Audiometry During this hearing test, you will need to take the following steps:
Put on headphones and a series of tones will be sent to your headphones The audiologist will change the pitch. and loudness of sounds at various points during the hearing test. At certain points, sound can be difficult to hear. Your doctor may also ask you to answer whenever you hear a tone. You can react by pressing a button or raising your hand. Audiometry helps find the quietest sounds you can hear at different pitches. 5.3 Tuner A tuning fork is a metal device consisting of two ends and can produce sound when it vibrates. Here's the tuning fork hearing test:
An audiologist will place a tuning fork behind your ear or on top of your head, then tap it to produce sound. You will notify your doctor whenever you hear tones at different volumes or sounds in your left, right and both ears Depending on where the tuning fork is and how you react, This hearing test for adults can show if you have hearing loss in one or both ears. In addition, it also shows what type of hearing loss you have. 5.4 Speech and word recognition tests Speech and word recognition tests help assess your ability to hear language:
After you have put on the headset, your doctor will talk to you through headphones and ask to repeat a series of simple words spoken at different volumes. Your doctor will record the softest voice you can hear Some of these hearing tests can be done in a noisy environment, because many people with hearing loss or hearing loss often have difficulty hearing voices in such places. 5.5 Tympanometry Tympanometry is another type of hearing test. The audiologist will place a small device inside your ear canal. This device pushes air into the ear and causes the eardrum to move back and forth. Measuring the eardrum will help confirm if you have an ear infection or other problems such as a tear in the eardrum or a buildup of fluid in the eardrum.

6. Meaning of Hearing Test Results
The results of the hearing test will tell you if you have a hearing loss and help determine the type of hearing loss you have. If you've been diagnosed with neural deafness, the results will indicate grades of hearing loss, including:
Mild: You can't hear certain sounds, such as tones that are too low or low too high. Moderate: Can't hear a lot of sounds, such as voices, in a noisy environment. Severe: Can't hear most sounds Serious: You can't hear any sounds. The treatment and management of nerve deafness will depend on its severity. If you are diagnosed with conductive hearing loss, your doctor may recommend medication or surgery, based on the cause of your hearing loss.
7. Treatment of hearing loss
Many older adults with hearing loss tend to avoid social situations, leading to isolation and depression. Although hearing loss in older adults is often permanent, there are ways to help manage the condition, including:
Hearing aid: A device that is worn inside or behind the ear. Hearing aids amplify sounds so you can hear them. Cochlear implant: Your doctor may have you perform cochlear implant surgery. This treatment is often used for people with severe hearing loss and hearing aids are not effective. The cochlear implant can transmit sound directly to the auditory nerve. Surgery: Some forms of hearing loss can be treated with surgery, including problems with the eardrum or the small bones inside the ear.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Medlineplus.gov, webmd.com