This is an automatically translated article.
Being overweight and obese can increase the risk of a number of health problems and may be associated with a number of emotional and social problems. In this article, we will provide more useful information about the health risks of being overweight and obese.1. What is overweight and obesity?
Obesity is an abnormal or excessive accumulation of fat in adipose tissue that impairs health. In most cases, it is the result of energy consumption exceeding energy expenditure over a period of many years. It is defined in adults as a body mass index (BMI) over 30.Obesity is no longer a disease that only affects more developed, affluent nations. It is currently a worldwide public health problem, affecting all ages and socioeconomic groups. In 1995, it was estimated that worldwide 200 million adults were obese and 18 million children under the age of 5 were overweight. In 2000, the World Health Organization estimated that 1.2 billion people worldwide were overweight, of which at least 300 million adults were obese: about 130 million in developed countries and 170 million in other countries. Overall, the increase in obesity rates has been strongest among the wealthier populations living in less developed countries, which are thought to be developing.
Being overweight and obese can increase your risk of a number of health problems including the following: All causes of death (death); High blood pressure ( Hypertension ); High LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol or high triglyceride levels ( Dyslipidemia ); Type 2 diabetes ; Coronary heart disease; Stroke; Gallbladder disease; Osteoarthritis (the breakdown of cartilage and bone in joints); Sleep apnea and breathing problems; Low quality of life; Mental illness such as clinical depression, anxiety and other mental disorders; Body pain and difficulty with physical activity; Cancers. ..

Thừa cân và béo phì có thể làm tăng nguy cơ mắc một số vấn đề sức khỏe và có thể liên quan đến một số vấn đề về cảm xúc và xã hội
2. How does a doctor determine if you are overweight?
Healthcare professionals use a measurement called body mass index (BMI) to find out if a person is overweight. BMI is a calculation that uses your height and weight to estimate how much body fat you have.BMI = weight in kg / (height in meters) 2
After calculating your BMI, your doctor or nurse will plot the results on a BMI chart. This allows health professionals to compare your growth with other teenagers of the same age and sex to see where you fit in.
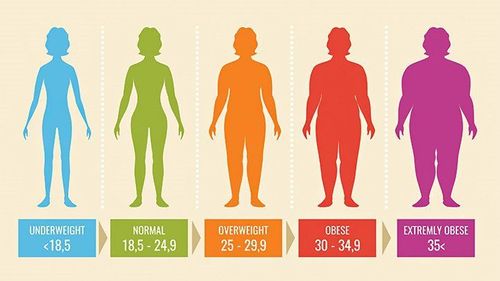
Under 18.5 - Underweight 18.5 to 25 - Desired or healthy level 25-30 - Overweight 30-35 - Obese (Type I) 35-40 - Obese (Type II) Over 40 - Fat Diseased or severe obesity (Grade III) BMI varies with age. That's why your doctor should plan and track your BMI over time. There are also different rankings for girls and boys.
When your BMI is compared to benchmarks, your doctor can compare it to teenagers your age and sex. Based on where your BMI number shows up, your doctor will decide if your BMI falls within the underweight, healthy weight, overweight, or obese ranges.
While BMI provides a general measure of obesity using height-adjusted weight, measuring waist circumference or waist-hip ratio can provide additional information about where distribution of body fat. Fat concentrated around the stomach is a higher risk factor for heart disease and type 2 diabetes than fat distributed around the hips. In general, men are more at risk of obesity-related diseases when their waist circumference reaches 94cm. For women, the risk rises to 80cm. The risk of the disease increased significantly with 102cm for men and 88cm for women. For people of Asian descent, the numbers are different: a waist measurement of 80cm in women and 90cm in men puts your health at risk.
3. Causes of obesity
In general, obesity is often the result of an individual consuming more energy than they need; This is called positive energy balance. This is common in today's society, where there is an abundance of cheap, high-energy foods, and in which both our work and leisure time becomes increasingly sedentary. While there are some negative effects around specific nutrients or foods, there is no single food or nutrient that causes obesity. Body weight is ultimately determined by a person's energy balance, which is the result of a balance between "energy in" as determined by general diet and physical activity levels. "energy out" substance.In addition to social influences, such as food availability and sedentary lifestyle, genetics also play a role. For example, there are good correlations between the obesity levels of parents and their children, and between siblings, especially twins. Genetic influences on body size and shape should not be used as an excuse to ignore active dietary and lifestyle advice to help maintain a healthy weight.

Béo phì thường là kết quả của việc một cá nhân tiêu thụ nhiều năng lượng hơn mức họ cần
4. Health effects of overweight and obesity
4.1. Nervous system Being overweight or obese greatly increases the risk of stroke, where blood stops circulating to the brain. Obesity can also have a profound effect on your mental health. This includes a higher risk of depression, low self-esteem and body image problems.4.2. Respiratory system Fat around the neck can make the airways too small, making it difficult to breathe at night. This is called sleep apnea. Breathing can actually stop for a short time in people with sleep apnea.
4.3. Digestive system Obesity is associated with a higher risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Gastroesophageal reflux disease occurs when stomach acid leaks into the esophagus.
Additionally, obesity increases the risk of developing gallstones - which is when bile builds up and hardens in the gallbladder. Requires surgical intervention
Fat can also accumulate around the liver and lead to liver damage, scar tissue, and even liver failure.
4.4. Cardiovascular and endocrine system In people with obesity, the heart needs to work harder to pump blood around the body. This leads to metabolic cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, or hypertension. High blood pressure is the leading cause of stroke.
Obesity can also make the body's cells resistant to insulin. Insulin is a hormone that carries sugar from your blood to the cells in your body, where it is used for energy. If you are resistant to insulin, the sugar cannot be absorbed by the cells, resulting in high blood sugar.
This increases your risk of type 2 diabetes, a condition where your blood sugar is too high. Type 2 diabetes is linked to a host of other health problems, including heart disease, kidney disease, stroke, amputation, and blindness.
High blood pressure, high cholesterol and high blood sugar along with excess body fat can cause the blood vessels that carry blood to the heart to become stiff and narrow. Hardened arteries, also known as atherosclerosis, can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Diabetes and high blood pressure are also common causes of chronic kidney disease.

Béo phì làm tăng nguy cơ mắc bệnh tiểu đường tuýp 2
4.6. Skeletal and muscular system Obesity can reduce bone density and muscle mass. This is called bone loss obesity. Skeletal obesity can lead to a higher risk of fractures, physical disability, insulin resistance, and poorer overall health.
The extra weight can also put too much pressure on the joints, leading to pain and stiffness.
4.7. Skin system Rash can occur in places where there are fatty skin folds on the body. A condition called acanthosis nigricans may also occur. Acanthosis nigricans is characterized by discoloration and thickening of the skin in the folds and wrinkles of your body.
4.8. Other effects on the body Obesity is associated with an increased risk of many different types of cancer, including endometrial cancer, liver cancer, kidney cancer, cervical cancer, and cancer. colon, esophageal and pancreatic cancers, and several other cancers.
As your body mass index (BMI) increases, so does your risk of developing cancer.
Khi chỉ số khối cơ thể (BMI) của bạn tăng lên, thì nguy cơ phát triển ung thư cũng tăng theo
5. How to reduce the risk of obesity?
To reduce your risk of obesity-related metabolic abnormalities, you should make sure to maintain your body weight within a healthy BMI range; Eat a healthy varied diet and engage in regular physical activity.In case the individual is already overweight or obese, weight loss can provide many health benefits. This can be achieved by reducing energy intake, or increasing the duration and intensity of physical activity. In fact, a combination of each of these approaches can produce the best results. For sustainable weight loss, individuals should aim to lose no more than 1 kg a week. This gradual weight loss will increase your ability to maintain weight loss while maintaining muscle mass.
It is very important to prevent obesity in the first place, and “dieting” can be challenging, especially because dietary changes cannot be easily maintained as part of a healthy lifestyle. a person's life in the long run. "Fat diets" often fail, because you don't persevere enough and go back to old eating habits instead of making life changes.
In many countries, there are cultural pressures that make people slim. Also, some people try to lose weight even though they are within the normal weight range for their height. Fat loss should not be done unless absolutely necessary, as this can lead to a person becoming underweight or not absorbing enough essential nutrients, and in severe cases, it can be a factor. development of an eating disorder, such as anorexia nervosa.
Periodic health check-ups help to detect diseases early, so that there are treatment plans for optimal results. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy, including:
Health checkup package general Standard 2020 General health check-up package VIP 2020 General health check-up package Special 2020 General health check-up package Children 2020 General health examination package Work permit - Issuance of work permits Examination results of people sick will be returned home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: nutrition.org.uk; healthline.com