This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor, Specialist II Le Thi Na - Doctor of Hematology - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
The HbA1c test is a blood test used to check the amount of glucose bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells. People with diabetes or diseases that raise blood sugar have more glucose bound to hemoglobin. So what HbA1c test methods are there and does the HbA1c test require fasting?
1. What is the process of testing for HbA1c?
HbA1c is a test index to diagnose and monitor the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Glucose is bound to hemoglobin continuously and almost irreversibly throughout the life of the red blood cell, averaging 120 days in a normal person. When blood glucose levels rise above normal for long enough, glucose reacts with Hb without enzyme catalysis to form glycosylated hemoglobin.
Red blood cells have 3 types of Hb: HbA1 accounts for 97-99%, HbA2 accounts for 1-3%, HbF <1%. HbA1 includes 3 groups HbA1a, HbA1b and HbA1c, of which HbA1c accounts for 80%. To express glycosylated hemoglobin, the glycosylated portion of HbA1c is quantified, referred to as HbA1c, in units of %.
The HbA1c concentration will be positively correlated with the mean plasma glucose concentration over the previous 3 months. Therefore, by quantifying HbA1c, it is possible to identify the average blood glucose concentration in the previous 2-3 months of the patient, allowing to evaluate the effectiveness of the diabetes treatment process.
2. Current HbA1c testing methods
Analysis of HbA1c currently can be divided into 2 main groups of methods, based on:
Chemical reactions and separation and quantification of components.
Chemical analysis requires two independent tests for HbA1c and total hemoglobin. HbA1c is measured on the basis of a specific chemical reaction with the N-valine terminator glycate of the β chain. Simultaneously measuring Hemoglobin by photometric method, combining the results of the two tests will allow HbA1c to be calculated. In fact, combining the results of the two tests can reduce the accuracy of the HbA1c test. This is the disadvantage of the chemical method. However, the advantage of the method is that it can be performed on most conventional biochemistry machines
2.1. Immunoassays (Immunoassays) Mix patient plasma with an excess of anti-HbA1c antibodies. HbA1c in the patient's plasma then acts as an antigen, which will combine with the added antibody, forming an immune complex that changes the turbidity of the medium. Rely on turbidimetric methods or spectrophotometer to determine. Total hemoglobin was measured at 2 wavelengths before incubation, at the same cuvette.
Hemoglobin variants will not be detected and will hardly affect the measurement method, as long as suitable specific antibodies are present. When a patient has HbF, HbA2 (lack of a β chain) will artificially decrease the measurement of HbA1c. As with other immunoassays, there will be no linear relationship between concentration and signal, multipoint calibration is a requirement, so that HbA1c measurement results are not biased beyond the appropriate range.
2.2. Enzyme analysis (Enzymatic Assays) In enzyme technology, the enzyme fructosyl peptide protease is used to cleave the β chain, releasing fructosyl peptide. The resulting peptide chains, mostly dipeptides, can combine with fructosyl peptide oxidase to produce hydrogen peroxide of a characteristic colour. Measure the concentration of HbA1c through determining the density of the formed color. In parallel, the total hemoglobin was determined by photometric method. Testing will be affected if the patient carries HbF or HbA2 because of the lack of the β chain. High levels of bilirubin also affect test results.
In the separation method glycated hemoglobin (A1c, glucose bound) and non-glycated hemoglobin (A0, unbound) have different characteristics, which allows the separation of the two and the individual quantification of A1c as well as total A1c + A0.
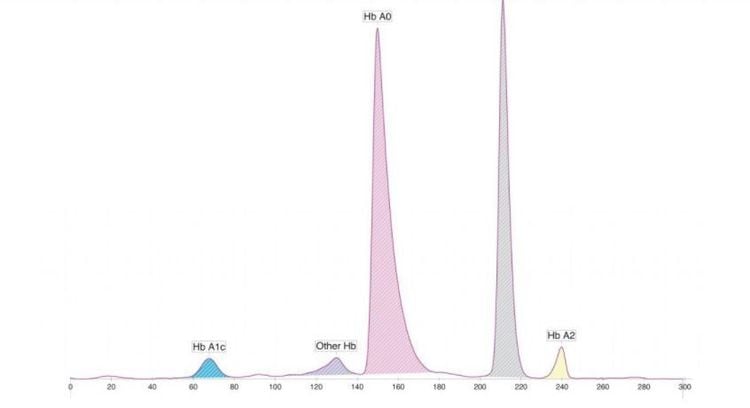
2.3. High pressure liquid chromatography is based on the differences in the affinities of the hemoglobin components resulting in migration rates in different chromatographic columns. Because glucose binds to the β-valine site, the isoelectric point of A1c differs from A0 by 0.02 pI, a difference that allows separation by ion exchange chromatography (IEC). However, the isoelectric difference between A1c and A0 is so small that only high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) equipment can perform their separation. When analyzing HbA1c with an HPLC instrument, each sample is analyzed one by one, forcing manufacturers to strike a balance between machine performance and analysis quality. The split time is short, so the peaks are not clear.
In addition to A1c and A0 quantification, other abnormal hemoglobin can be detected on the chromatogram such as: HbF (fetal hemoglobin), HbA1a/b (auxiliary hemoglobin), CarHb (carbamylated Hb). ), HbS (sickle cell). This is an outstanding advantage of analysis of HbA1c by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), because in the presence of hemoglobin variations, HbA1c results do not reflect average blood glucose levels. In 2010, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) announced that HbA1c determined by HPLC was considered the standard for the diagnosis of diabetes. However, this method is subject to interference by hemoglobin variation.
Because HbA1 c laboratories use different methods, the results obtained will not be the same. Therefore, it is extremely important to standardize the method of measuring HbA1c. Accordingly, HPLC is considered the gold standard, the reference method of other methods, used in the studies of the British Diabetes Research Institute (UKPDS) and the Trial of Complications and Control. diabetes mellitus (DCCT).
2.4. Capillary electrophoresis Capillary electrophoresis is a separation technique based on the differential movement of differently charged hemoglobin in a capillary column, under the influence of an electric field generated by a high voltage. position. This method has good separation, good accuracy and precision. Separation of most variants, no analytical noise, biological noise warning. Standardized according to the IFCC reference method.
2.5. Affinity Chromatography Affinity chromatography analyzes glycated hemoglobin (GHb, not just HbA1c) and non-glycated hemoglobin (NGHb, not just HbA0). HbA1c containing glucose binds to M-aminophenylboronic acid and is separated from hemoglobin when it passes through a cartridge containing boronate. Based on structural differences. This method is not affected by normal hemoglobin variation. However, it is not possible to detect hemoglobin variants, which can cause erroneous results if the variant is glucose-bound (eg, high HbF).
3. Some factors affect HbA1c . test results
Confounding factors: increased bilirubin, hypertriglyceridemia, leukocyte destruction, hemoglobin variation
Biological variations and some physiological characteristics of the patient; pregnancy, age, race, malaria, iron deficiency, bleeding, blood transfusion, kidney failure, splenectomy, alcoholism.
Certain drugs affect outcome interpretation: antivirals, anticonvulsants, antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics...
HbA1c is widely recognized as an important marker for management diabetes. HbA1c has many advantages but still has limitations, mainly as a biological confounding factor, by affecting erythrocyte survival, which can cause confusion when interpreting results. Methods of measuring HbA1c should be used that are capable of detecting and warning of conditions that may confound the results. If you have any of the above medical conditions, HbA1c should not be used to diagnose diabetes.
It is because of the values of HbA1C that now the HbA1c test is one of the tests performed in the Cardiovascular and Diabetes Screening Package at Vinmec, helping to detect and screen for diabetes early and from there timely and effective treatment plan.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.