This is an automatically translated article.
The most important health care for women aged 40 - 49 is to perform screening tests to detect possible health problems or diseases in those who do not yet have any symptoms. In addition, women aged 40 - 49 should also receive health advice from specialist doctors.
1. Screening test for women 40 - 49 years old
The most important consideration in the health care of a woman in her 40s is to perform important screening tests. That is:
1.1 Type 2 diabetes or pre-diabetes
Screened: All adults starting at age 45 and adults of all ages who are asymptomatic but are overweight or obese and have 1 or more additional diabetes risk factors Street; Frequency of screening: At least every 3 years.
1.2 Blood pressure
Screening target: All adults; Frequency of Screening: Check your health every year if your blood pressure is normal (less than 120/80 mmHg). If your blood pressure is higher than normal, follow your doctor's advice.
1.3 Breast cancer
Screening subjects: All women, especially those who are receiving health care for women aged 40 - 49; Frequency of screening: Annual mammograms should begin when a woman is 40 years old. You can talk to your doctor about the frequency of screening that's right for you (depending on your risk factors).
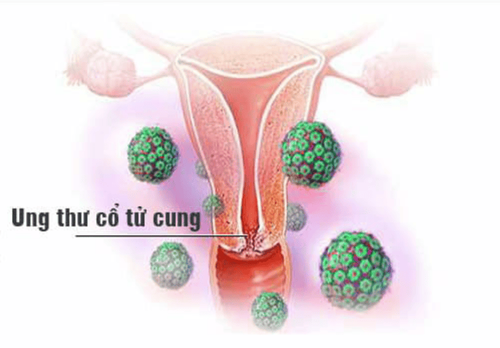
1.4 Cervical cancer
Screening subjects: All women, except those who have had a hysterectomy (removal of the cervix) for causes unrelated to cervical cancer and no history of cervical cancer/ severe precancerous; Frequency of screening: Women aged 30-65 should have a Pap test (Pap smear) combined with an HPV test every 5 years. Pap tests can be done every 3 years.
1.5 Colorectal cancer
Screening subjects: Women at average risk 45 years and older. This is a screening test to do when caring for a 45-year-old woman; Screening frequency: Several tests are available that will be performed at different times. These are: sigmoidoscopy every 5 years; Colonoscopy (virtual colonoscopy) every 5 years; Colonoscopy every 10 years; Annual fecal occult blood test; Check fecal immunochemicals annually; Stool DNA test every 3 years. If you choose a test other than endoscopy, you will need to have a repeat endoscopy if there are abnormal results. You can talk to your doctor about which test is best for you. In addition, some people may be considered for a different screening frequency because of their personal or family health history.

Kiểm soát huyết áp là điều cần thiết để chăm sóc sức khỏe phụ nữ tuổi 40
1.6 Other screening tests
A note when taking care of women's health in their 40s is that you need to perform other screening tests such as:
Alcohol abuse: All adults are screened for; screening frequency is during routine exams; Chlamydia: Screening subjects are women at higher risk of infection; frequency of screening is periodic examination if there is a risk of Chlamydia infection ; Anxiety: Screening subjects are all adults; screening frequency is during routine exams; Dermatological diseases: Screening subjects are sexually active women at higher risk of infection; The frequency of screening is periodic examination if there is a risk of dermatological disease. This is an important note when taking care of the skin for women aged 40; Hepatitis C: Screening subjects are adults with a higher risk of disease, performed once for people born between 1945 - 1965; frequency of screening is regular check-ups if at risk for hepatitis C; HIV: Subjects for screening are all women; screening frequency is during routine exams; Lipid disorders: Screening subjects are all women over 45 years of age at high risk of coronary heart disease. As for women aged 19 - 44 years, the screening should be based on risk factors for the disease (as prescribed by the doctor). The frequency of screening is at least every 5 years; Obesity: Screening subjects are all adults; screening frequency is during routine exams; Syphilis: Screening subjects are women at risk of infection; screening frequency is during routine exams; Tuberculosis : Screening subjects are adults at risk of infection; frequency of screening as prescribed by the doctor; Visual: All adults are screened; Screening frequency is the primary comprehensive screening at age 40. If you have a chronic medical condition, talk to your doctor about the appropriate screening frequency.
2. Health care consultation for women 40 - 49 years old
Health counseling for women aged 40 - 49 is very necessary. This includes:
Breast cancer, chemopreventive: For high-risk women, when risk is identified; BRCA mutation testing for breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility: For women at higher risk, when risk is determined; Diet and exercise: For adults who are overweight or obese, when diagnosed and periodically examined; Domestic violence: Counseling for women of childbearing age and older women (who are at higher risk), performed at regular health check-ups; Sexually Transmitted Diseases Prevention: Counseling for adults at higher risk of infection, performed at routine health screenings; Tobacco use and tobacco-related diseases: Counseling for all adults, performed at routine health screenings.

Tiêm ngừa cho phụ nữ tuổi 40 - 49
3. Vaccination for women aged 40 - 49
Among the goals to be achieved when taking care of the health of women aged 40 - 49, vaccination cannot be ignored. Specifically:
Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis: Vaccinate all adults every 10 years; Chickenpox: Vaccinate all adults ages 40 - 49 with no record of chickenpox infection or previous vaccinations. The injection dose is 2 doses, the 2nd dose is at least 4 weeks apart from the first dose; Measles, mumps, rubella: Vaccinate all adults aged 40 - 49 years with no record of chickenpox infection or previous immunizations. The injection dose is 1 or 2 doses; Influenza: Vaccinate all adults annually, when a vaccine is available in the community; Hepatitis A : Vaccinate people who are at risk for the disease. The injection dose is 2 doses 6 months apart; Hepatitis B: Vaccinate people who are at risk for the disease. The injection dose is 3 doses: 2nd dose 1 month after first dose, 3rd dose at least 2 months after 2nd dose (and at least 4 months after first dose); Haemophilus influenzae type B: Vaccinate people at risk for the disease. The injection dose is 1 - 3 doses; Meningococcal disease: Vaccinate people who are at risk for the disease. The injection dose is 1 or 2 doses; Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine: Immunization for people at risk. The injection dose is 1 or 2 doses. Screening tests, health counseling and reasonable vaccinations are essential when taking care of the health of women aged 40 - 49. Women in this age group should perform periodic screening to detect risks in a timely manner. disease and timely and effective treatment interventions.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.