The article is professionally consulted by a doctor from the Department of Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Viral fever and dengue fever are both caused by different types of viruses. However, viral fever is usually quite benign and can heal after about 7 days, while dengue fever can leave many complications affecting the patient's life. Not everyone understands and distinguishes viral fever and dengue fever, the article below provides information to help distinguish viral fever and dengue fever.
1. Viral fever
1.1. Signs of viral fever
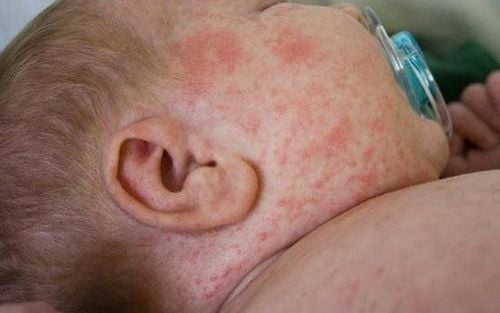
Viral fever is a general term for a disease caused by many viruses. Depending on the viral agent, the symptoms of the disease can be severe or mild. Usually, there are the following symptoms:
- Sudden high fever: 39-40C. During a viral fever, you are often tired and respond poorly to antipyretic drugs such as paracetamol.
- Upper respiratory tract infection: Accompanied by symptoms of rhinopharyngitis such as cough, runny nose, sore throat, etc.
- Digestive disorders: May appear with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, loose stools, etc.
- Lymph nodes: Lymph nodes appear in the head, face, and neck area, which may be painful and larger than normal.
- For adults: Muscle aches, headaches, fatigue, and children often cry.
- May be accompanied by conjunctivitis: Red eyes, clear tears
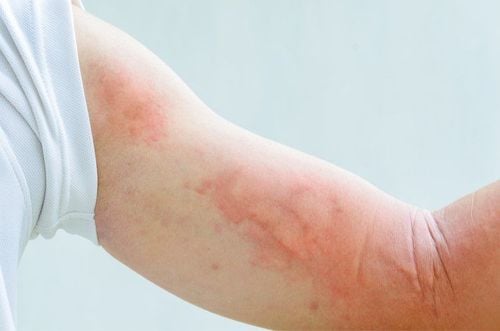
- Skin rash: Rash may appear 2-3 days after fever.
- In some cases, children may have convulsions due to high fever.
- The disease usually resolves spontaneously after about 7 days.
1.2. Instructions for treating viral fever
There is usually no specific treatment for viral fever, symptomatic treatment with nutrition support is most often indicated.
- Fever reduction: When fever is < 38.5 C use physical methods such as applying warm water to the forehead, armpits, and groin. When fever is 38.5 C apply warm compresses combined with Paracetamol at a dose of 10-15mg/kg, 4-6 times/day. Note that if the child has a history of convulsions, the drug should be used when the child has a fever of 38 C.
Anticonvulsants: If the child has a high fever or a history of convulsions, a combination of antipyretics and anticonvulsants should be used as prescribed. - Rehydration and electrolytes: When fever is high, the body loses water and electrolytes, leading to water and electrolyte imbalance. Electrolyte repletion with oresol according to the ratio on the package and drink as needed.
- Prevent secondary infection: Clean the body, eye drops with 0.9% saline solution.
Diet: Use liquid food, easy to digest, adequate nutrients, and increase vitamin C with fruits.
Note: Viral fever can become an epidemic so isolate to avoid contact with many people to spread to the community.
When the fever is high, does not respond to antipyretics and is accompanied by symptoms such as drowsiness, lethargy, convulsions, vomiting, headaches, that worsen over time, you should go to a medical facility for timely examination and treatment.
Some viruses can be prevented by vaccines such as: Measles, rubella, Japanese encephalitis, etc. Vaccination should be done on schedule to limit the disease.
Trắc nghiệm: Sự phát triển tinh thần, vận động của bé thế nào là đúng chuẩn?
Khi nào bé biết nói, biết hóng chuyện hay biết cầm cốc là "đúng chuẩn"? Điểm xem bạn biết được bao nhiêu mốc phát triển tinh thần, vận động "đúng chuẩn" của bé nhé!The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
2. Dengue fever
2.1. Signs of dengue fever
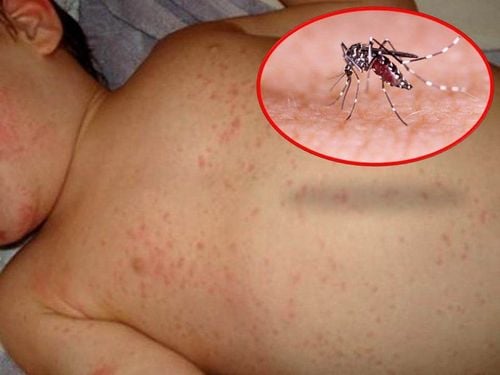
Dengue fever is caused by the Dengue virus, the disease is transmitted by mosquitoes carrying the virus and biting healthy people. The disease appears in 3 stages:
- Onset stage: Usually in the first 3 days of the disease. The patient has a sudden high fever of 39-40 degrees Celsius, fatigue, headache, eye pain, body aches, and may have upper respiratory tract inflammation. The symptoms are quite similar to viral fever.
- Critical stage (hemorrhagic stage): The fever may decrease, and signs of bleeding from mild to severe (due to a decrease in platelets in the blood) appear, which is the stage where many complications occur.
- Subcutaneous bleeding: The patient sees bleeding spots under the skin, accompanied by itchy skin symptoms.
- There may be nosebleeds and bleeding gums, and women may have bleeding unrelated to the menstrual cycle.
- Digestive tract bleeding with symptoms of black stools, bloody stools, or vomiting blood.
- More severe bleeding can manifest as cerebral hemorrhage, or intra-abdominal hemorrhage, which is life-threatening.
- Due to the phenomenon of blood concentration, if the patient does not receive enough fluids, he or she may have low blood pressure, and more severe shock due to reduced circulating volume.
- Convalescent phase: The patient has no fever, is less tired, and platelets begin to increase.
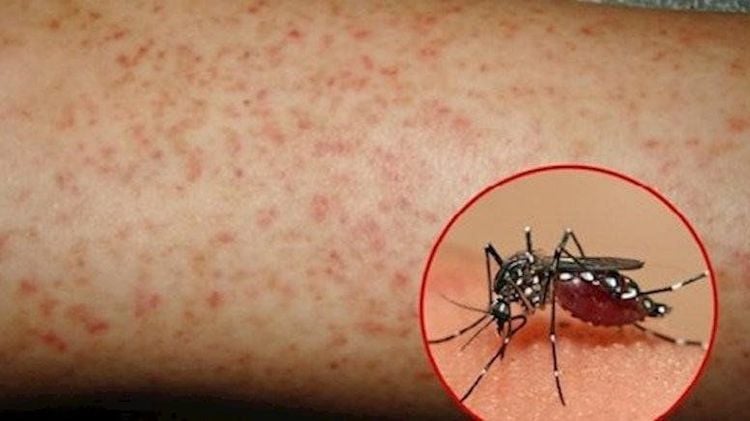
2.2. Instructions for treating dengue fever
As it is also a disease caused by a virus, there is no specific treatment, treatment is mainly symptomatic treatment combined with diet and rest:
- Limit physical activity and rest in bed.
- Fever reduction: When the fever is <38.5 degrees Celsius, use methods such as applying warm water compresses to the forehead, armpits, and groin. When the fever is 38.5 degrees Celsius, apply warm compresses combined with Paracetamol (do not use ibuprofen or aspirin to reduce fever) at a dose of 10-15mg/kg, every 4-6 hours. Note that if the child has a history of seizures, use medication when the child has a fever of 38 degrees Celsius or more.
- Replenish water and electrolytes: Drink plenty of water, and use oresol or hydrate to replenish water and electrolytes.
- Eat liquids that are easy to digest, and increase vitamin C with fruits.
- Regularly monitor the progression of the disease: if severe symptoms appear such as high fever that does not respond to antipyretics, lethargy, drowsiness, vomiting a lot and inability to drink, severe abdominal pain, abnormal bleeding such as black stools, vomiting blood, menorrhagia, nosebleeds, uncontrollable bleeding gums, etc., go to a medical facility immediately for timely treatment to avoid complications.
3. How to distinguish viral fever and dengue fever
To distinguish viral fever and dengue fever based on:
- Epidemiology: Viral fever and dengue fever can both be epidemics, so this factor can be used to guide the disease.
- Distinguishing dengue fever in the early stages must be based on paraclinical tests. If it is dengue fever, then the tests are: Dengue Test (+), Blood formula (decreased platelet count, increased red blood cell volume Hct). If it is viral fever, the above indicators are normal.
- For dengue fever in the critical stage: Dengue fever begins to appear bleeding in many forms, while viral fever does not have symptoms of bleeding. The way to distinguish between a rash in viral fever and subcutaneous bleeding in dengue fever is that if the rash appears when we stretch the skin, the rash will disappear, but if it is a hemorrhage, it will not disappear.
Dengue fever and viral fever have quite similar symptoms in the early stages, but they can still be distinguished by paraclinical tests. Distinguishing between dengue fever and viral fever is necessary to orient and promptly monitor complications caused by dengue fever.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.