This is an automatically translated article.
Hematuria is a common symptom of glomerulonephritis - inflammation of the kidney's filtering system. Glomerulonephritis may be part of a systemic disease or may occur alone. The disease can be caused by viral infections, blood vessel diseases, immune problems ... affecting the small capillaries that play a role in filtering blood in the kidneys.
1.Definition of acute glomerulonephritis
Acute glomerulonephritis syndrome is an acute inflammatory lesion of the glomeruli. The disease is characterized by the sudden appearance of red blood cells in urine, also known as gross hematuria, proteinuria, edema and hypertension.
Currently with scientific and technical advances, it has been agreed that: acute glomerulonephritis is not just a disease but a syndrome, or called acute glomerular syndrome. Acute glomerulonephritis arises not only from streptococci but also after staphylococcal, pneumococcal, viral infections. A modern, but still common in tropical countries, developing countries. The disease appears as sporadic or may form epidemics, especially in areas where sanitation is poor. The disease is very rare before 2 years of age, usually in children from 3 to 8 years old, boys are more common than girls (male/female ratio = 2/1). Acute glomerulonephritis is less common in adults than in children.
2. Symptoms of acute glomerulonephritis
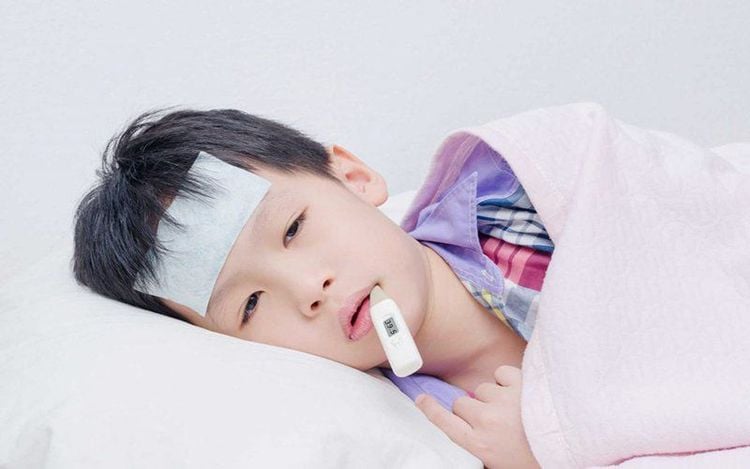
Trẻ bị viêm cầu thận cấp sẽ có triệu chứng mệt mỏi toàn thân và sốt 38-39 độ C hoặc nhẹ hơn
The disease is common in children after an episode of throat infection or skin infection from 7 to 15 days.
The disease has a sudden onset but there may be warning signs such as: Whole body fatigue, fever 38 - 39 degrees Celsius or less. Pain in the lumbar region on both sides, digestive disorders, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, nausea.
Initially appearing on the face, causing heavy eyelids, edema can heal quickly but can also cause generalized edema. Edema in acute glomerulonephritis is characterized by: soft, white, concave and finger prints, edema around the ankle, anterior tibia, instep. Possible severe edema: generalized edema such as pleural effusion, peritoneum, acute pulmonary edema, cerebral edema.
Oliguria or anuria: urine output is only 500-600ml/24 hours, oliguria (less than 500ml/24 hours) or anuria (less than 100ml/24 hours). Hematuria often occurs early along with edema.
Hypertension is usually evident in the first two weeks, more than 60% of cases of acute glomerulonephritis have hypertension. Acute pulmonary edema in acute glomerulonephritis is a common complication due to hypertension, edema and left heart failure.
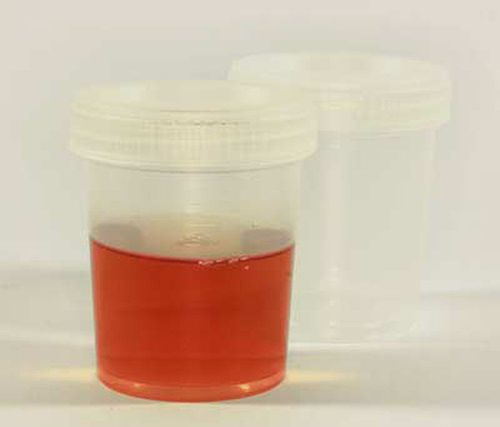
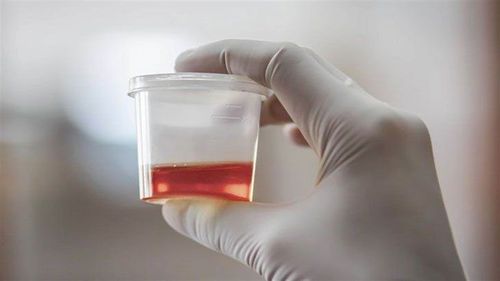
3. Macroscopic hematuria in acute glomerulonephritis

hình ảnh phân biệt đái máu đại thể và đái máu vi thể
Hematuria is blood in the urine. There are two types of hematuria: gross hematuria and microscopic hematuria. Gross hematuria is defined as when the urine is dark red in color, recognizable to the naked eye. Accordingly, the characteristics of gross hematuria in acute glomerulonephritis are as follows:
Macroscopic or microscopic hematuria, if present, often appears early along with edema, red or dark urine (red blood cells over 300,000// minutes), red blood cells are easily broken. May be accompanied by dysuria, dysuria, urinary frequency, urinary retention. Gross hematuria usually resolves early (7-10 days) but microscopic hematuria is prolonged, erythrocyteuria sometimes after 3-6 the month is over. Gross hematuria: urine color like meat wash. Addis residue test: Red blood cells 100,000 - 500,000/min, white blood cells 20,000/min. The red blood cell cast is a test with high diagnostic value, but it also has an uncommon rate. In practice, only two tests for erythrocytosis (for hematuria) and proteinuria are sufficient to identify acute glomerulonephritis. Acute glomerulonephritis with hematuria alone: Common in children, hematuria may be isolated, with no edema, no oliguria, anuria. Progress is generally good but recurrence is possible. About 60-80% of cases will resolve on their own with acute glomerulonephritis, however, in the remaining 20-40%, about 10-30% become chronic glomerulonephritis (after 10 to 25 years). There are about 1-2% of immediate deaths due to acute pulmonary edema, cerebrovascular accident. In the remaining 11%, glomerulonephritis progresses rapidly, leading to death within a few months. Therefore, when you see the symptoms of the disease, you should go to the medical center for examination and treatment.
Patients can visit and treat or screen for urological diseases and urological diseases at Vinmec International General Hospital. With comprehensive medical quality, a system of modern equipment, a team of qualified medical professionals will provide the best treatment regimen for patients.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE