This is an automatically translated article.
Basedow's disease, commonly known as goiter, is a fairly common endocrine disease in women. The disease affects the metabolic disorders of the thyroid gland and causes permanent complications if not treated early. Therefore, basedow's disease and how to treat it are important information to know in order to achieve the best treatment effect.1. What is basedow's disease?
Grave's disease, also known as Grave's disease or goiter, is an immune system disorder that results in the overproduction of thyroid hormone. As a result, the patient presents with a syndrome of hyperthyroidism on all organ systems. Although there are many disorders that can lead to hyperthyroidism, basedow's disease is a common cause.
Because thyroid hormones are responsible for all metabolic processes in the body, the signs and symptoms associated with Graves' disease can be varied and varied, with a significant impact on overall health. patient's body. Epidemiology shows that basedow's disease can affect anyone, but it is more common in women than in men and usually has an onset before age 40.
Treatment of basedow's disease has the main goal of inhibiting the overproduction of thyroid hormone and reducing the severity of symptoms.
2. What are the causes of basedow's disease?
Graves' disease is usually caused by disorders in the autoimmune system's fight against the body's own tissues, the thyroid parenchyma, although the exact reason why this happens is unknown. clearly understood.
Hội chứng cường giáp ảnh hưởng xấu đến sức khỏe của người bệnh
Graves' disease is often caused by disorders in the autoimmune system's resistance to the body's own tissues, here the thyroid parenchyma, although the exact reason why this happens is unknown. clearly understood.
However, anyone can get Graves' disease and some factors that can increase the risk are:
Family history: There is a chance that a gene or genes inherited from one parent can predispose a person to the disease. People are more susceptible to thyroid disorders. Gender: Women are more likely to have Graves' disease than men. Age: Graves' disease is usually found in people under the age of 40. Other Comorbid Autoimmune Disorders: People with other disorders of the immune system, such as type 1 diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, are at increased risk. Emotional or physical stress. There are medical conditions or stressors in your life that can play a role in the onset of Graves' disease, especially in people who already have a genetic predisposition. Pregnancy: Recent pregnancy or childbirth can increase the risk of autoimmune disorders. Smoking: Cigarette smoke can affect the immune system, increasing the risk of Graves' disease.
3. What are the symptoms of basedow?
Patients may seek medical attention for the following reasons:Feelings of anxiety and irritability Tremors in the hands or fingertips Sensitivity to high temperatures Increased sweating, moist and warm skin Loss of weight despite habits eat normally
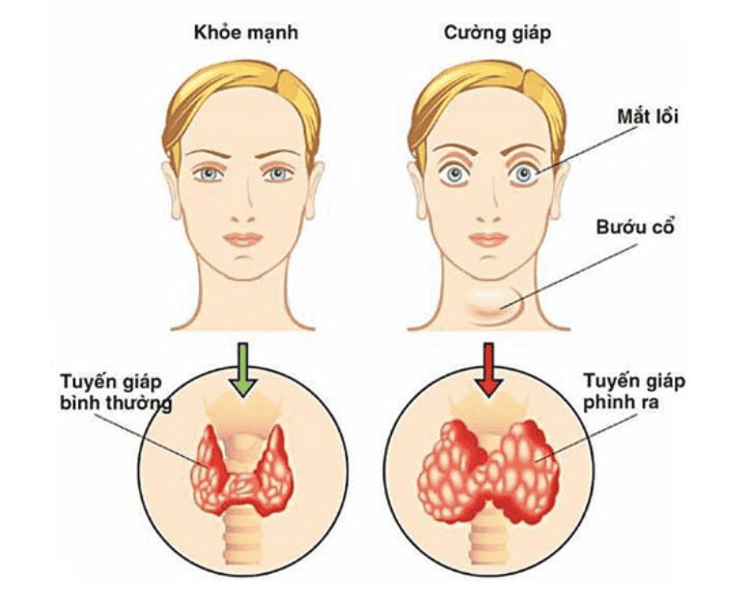
Một số triệu chứng thường gặp của bệnh basedow trên lâm sàng
Enlarged thyroid gland, appearance of goiter Changes in menstrual cycle Erectile dysfunction or decreased libido Frequent bowel movements Protruding eyes Fast or irregular heartbeat
4. What is the diagnosis of basedow's disease?
Diagnosis of basedow's disease in addition to the above symptoms may include the following tests:
Blood tests: Your doctor will order blood tests to determine the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) as well as levels of thyroid hormones (T3, T4) in the blood. People with basedow's disease often have lower-than-normal TSH levels and elevated thyroid hormone levels.
Another test measures the level of autoantibodies but is not usually necessary for diagnosis. However, a negative result may indicate another cause of hyperthyroidism.
Radioactive iodine absorption: The body needs iodine to make thyroid hormone. By delivering a small amount of radioactive iodine and then measuring it in the thyroid gland with a specialized scanner, a doctor can determine the rate at which the thyroid is taking up iodine above the normal rate.
Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of structures inside the body. Ultrasound can show an enlarged thyroid and is most useful in people who cannot measure radioactive iodine absorption, such as pregnant women.
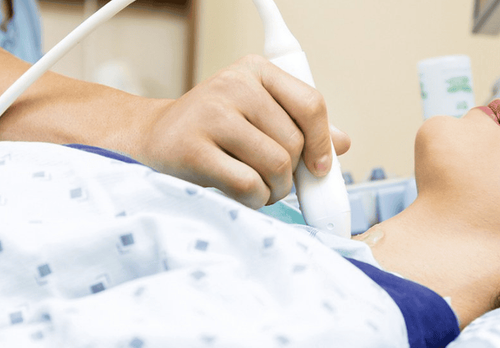
Siêu âm tuyến giáp giúp chẩn đoán bệnh basedow
5. How to treat basedow's disease
Treatments for basedow's disease are aimed at serving the treatment goal of inhibiting thyroid hormone production and blocking the hormone's effects on the body.
Some treatments for basedow's disease include:
5.1 Radioactive iodine therapy With this therapy, the person takes radioactive iodine by mouth. Because the thyroid gland needs iodine to produce hormones, when radioactive iodine enters thyroid cells, the radioactive energy destroys overactive thyroid cells over time. This causes the thyroid gland to shrink and symptoms to subside, usually over a few weeks to months.
However, radioactive iodine therapy may increase the risk of new or worsening symptoms of basedow ophthalmia. This side effect is usually mild and temporary, but this therapy may not be recommended if you already have moderate to severe eye problems.
Other possible side effects are neck pain and temporary increase in thyroid hormone. In addition, radioactive iodine therapy is not used to treat basedow's disease in pregnant women or women who are breastfeeding.
Besides, because this treatment causes the thyroid gland to underactive, you may need further treatment to give your body a normal amount of thyroid hormone.
5.2 Anti-thyroid drugs Anti-thyroid drugs interfere with the thyroid's use of iodine to produce hormones. These prescription drugs include propylthiouracil and methimazole. Because the risk of liver disease is more common with propylthiouracil, methimazole is considered the first choice when a doctor prescribes the drug. When these two drugs are used as monotherapy for basedow's disease, recurrence of hyperthyroidism occurs. Thyroid may occur later. Therefore, it is necessary to take the drug for a longer period of time than a year and will provide better long-term results. Antithyroid drugs may also be used before or after radioactive iodine treatment as an additional treatment.

Một số loại thuốc được sử dụng trong điều trị bệnh basedow
Side effects of both drugs include rash, joint pain, liver failure or a decrease in white blood cells that fight infection. Methimazole is not used to treat pregnant women during the first trimester because of the risk of mild birth defects. Therefore, propylthiouracil is the preferred antithyroid drug in the first trimester for pregnant women. After the first trimester, the use of methimazole is usually continued in lieu of propylthiouracil.
5.3 Beta Blockers These drugs do not inhibit thyroid hormone production but will help block the hormone's effects on the body. It can help reduce a fairly rapid heart rate, tremors, anxiety or irritability, temperature sensitivity, sweating, diarrhea, and muscle weakness.
Beta-blockers that can be used in basedow's disease such as propranolol, atenolol, metoprolol or nadolol.
It should be noted that beta-blockers are not usually prescribed for people with asthma, because they can trigger an acute asthma attack.
5.4 Surgery Surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid gland is also an option in the treatment of basedow 's disease . After total thyroidectomy, the patient will need lifelong thyroid hormone therapy.
The risks of surgery are possible damage to the vocal cords and the small glands located next to the thyroid gland called the parathyroid glands.
6. Complications of basedow's disease
If the disease is not treated or the treatment of basedow disease is not effective, the disease can cause complications as follows:
Abnormalities in pregnancy. Possible complications of basedow's disease during pregnancy include miscarriage, premature delivery, fetal thyroid dysfunction, poor fetal growth, heart failure, and preeclampsia. Heart rhythm disturbances. If left untreated, Graves' disease can lead to permanent arrhythmias, changes in the structure and function of the heart muscle,
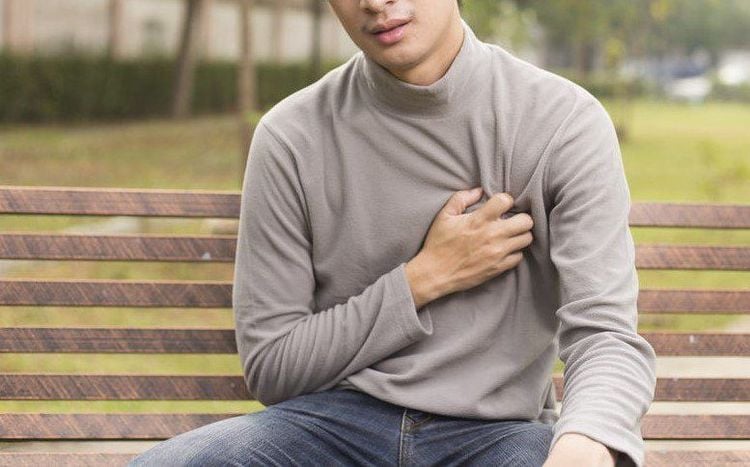

Một số người bệnh có thể gặp tình trạng rối loạn nhịp tim do biến chứng của bệnh basedow gây ra
Armor storm. This is a rare but life-threatening complication if not treated promptly. A sudden and drastic increase in the amount of thyroid hormone in the blood can cause a person to have a high fever, sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, delirium, severe weakness, seizures, irregular heartbeat, yellow skin, low blood pressure and even coma. Osteoporosis . Untreated hyperthyroidism can also lead to weak and brittle bones because too much thyroid hormone interferes with the body's ability to incorporate calcium into the bones. In summary, since this is a fairly common disease in the general population, the information you need to know about basedow's disease and its treatment is quite common and easily accessible. It is important to detect the disease early and actively adhere to goiter treatment, periodically check thyroid hormone levels to achieve the goal of good disease control and avoid unfortunate complications.
For detailed advice, please come directly to Vinmec health system or register online HERE.