This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Quoc Vinh - Emergency Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Goiter is a common thyroid disease, the prevalence is higher in women than in men. Most goiters are benign diseases, when detected and treated in time, the cure rate is quite high.
1. What is goiter?
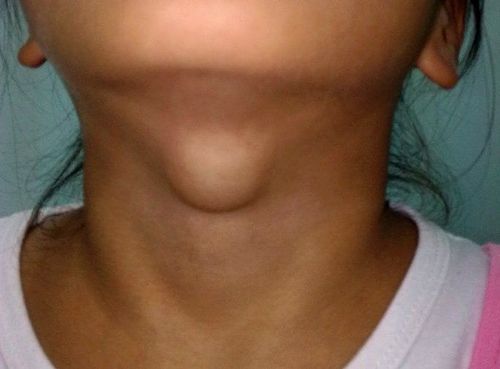
Goiter is a common noun to refer to a tumor arising from the thyroid gland, medically called a goiter, including many types such as diffuse or granular thyroid enlargement, thyroiditis, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, benign goiter, cancer . All were grouped into three groups: Benign tumors, cancer, and thyroid dysfunction, each with multiple types.2. How does goiter affect health?
Up to 70% of the population has goiter, but most goiters do not affect health. A few cases of large goiter causing compression, or cancer invading the surrounding or metastasized, or having thyroid dysfunction such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, then this affects health.Tumor compresses or invades causing difficulty breathing, swallowing, hoarseness, pain. When the tumor causes dysfunction leading to weight gain or loss, fatigue, chest palpitations, arrhythmia, hand tremors, sweating...
3. Causes of goiter
Causes of goiter include:Deficiency of iodine in the body is the main cause of goiter. Congenital thyroid disorders can cause goiter, which runs in families. Due to the use of drugs and food, due to prolonged use of some drugs such as: Lithium salt used in psychiatric specialties; synthetic antithyroid drugs; Iodine-containing drugs such as contrast agents; asthma medicine; rheumatic drugs; antiarrhythmic drugs or by eating foods that inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis such as: cruciferous vegetables, bamboo shoots, tapioca... In addition, women with nervous stimulation during development growing or pregnant and breastfeeding are also prone to goiter.
4. Symptoms of goiter
The size of goiter varies from person to person, in most cases it is small in size and hardly causes any symptoms.Some more severe cases can cause symptoms such as:
Cough Voice change (hoarseness) Difficulty swallowing, feeling like a tight throat Difficulty breathing may be accompanied by a wheezing sound when breath.

5. Diagnosis of goiter
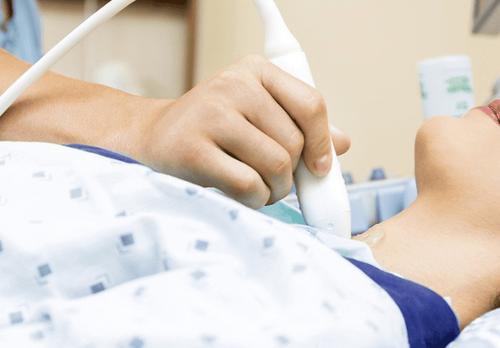
To determine if you have a goiter, your doctor will directly examine your neck to check for any abnormalities in the neck area. Large tumors can be directly seen or palpated, small tumors can be detected by palpation through swallowing saliva. Some tumors are small, cannot be examined, and require imaging studies to detect.Subclinical indications such as:
Thyroid ultrasound to evaluate the size and shape of the thyroid gland. Doppler ultrasound can detect vascular proliferation in the thyroid gland. Thyroid function tests aim to evaluate the levels of certain hormones in your blood. If this level is low or higher than normal, it can be related to goiter. Standard blood tests to check thyroid function include: Measure the activity of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), thyroid hormone (T3, T4, FT3, FT4). If the numbers are high or lower than average, it means that you have thyroid dysfunction or warn of your risk of developing a goiter in the future. In case of necessity, doctors can prescribe specialized tests to accurately diagnose goiter conditions such as TRAb (in Basedow), pituitary MRI (in TSH-secreting pituitary tumor), scintigraphy and concentration measurement. Iodine concentration (increasing the concentration of diffuse iodine in the Graves, increasing the concentration in the thyrotoxic nodules), .. and tests to check for complications such as: Measurement of osteoporosis, electrocardiogram (to detect complications) arrhythmia in hyperthyroidism), blood lipids, blood calcium..
6. Treatment methods for goiter
Treatment of goiter includes the following methods: Oral medicine, radiotherapy, surgery or just monitoring without any treatment.Take medicine: Depending on the cause of the disease, there are different types. Radiotherapy is a form of radioactive iodine that destroys thyroid cells. Surgery is the removal of part or all of the thyroid gland, depending on the type of goiter, one of the methods of lobectomy, near-total thyroidectomy, total thyroidectomy, and isthmusectomy is selected depending on the type of goiter. Follow-up: When the tumor is benign, small, does not cause discomfort, it is often chosen for follow-up, does not need any treatment and over time most of the time does not cause complications. The follow-up method is periodic re-examination, once every 1-2 years if you do not see any changes in your body.
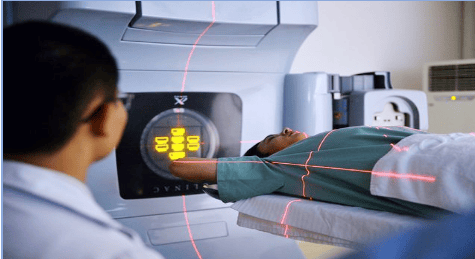
7. When to treat goiter?
7.1 Cases requiring treatment of Hypothyroidism TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) > 10 mIU/ml (Chronic, subacute, replacement thyroiditis). Clinical hyperthyroidism/thyrotoxicosis (hyperthyroidism, subacute/chronic thyroiditis, granulomatous thyroid nodules, adenomas). Cancer, suspected cancer ≥ 1 cm. Cancer < 1 cm with metastasis. Benign tumor shows signs of compression. 7.2 Cases to consider for treatment of Hyperthyroidism/subclinical thyrotoxicosis. Cancer, suspected small cancer <1cm. Large benign tumor with no sign of compression. 7.3 Cases not requiring treatment Mild hypothyroidism TSH < 10 mIU/mL. Small benign tumor.
Benign tumors cause difficulty breathing, swallowing, or cause cosmetic loss. Cancer or suspected cancer. Thyroid dysfunction type hyperthyroidism: Surgery is an option with 2 methods of taking drugs or radioactive iodine. Do not operate in the following cases:
Small benign tumor. The tumor is large but not oppressive, difficult to breathe, difficult to swallow, not uncomfortable in the neck area. The benign tumor does not cause loss of aesthetics, the aesthetics are decided by the patient.
8. Methods of disease prevention
Preventive measures are introduced to limit the cases of benign goiter and detect other types of goiter early to improve treatment results. Including the following methodsEnsure adequate supply of iodine for the body by eating foods rich in iodine such as: sea fish, shrimp paste, fish sauce. Using iodized salt is a simple and easy way to reduce the risk of iodine deficiency. For subjects with thyroid diseases, after treatment for mental diseases, digestive diseases and chronic kidney diseases with high risk of goiter, they need to be periodically examined for early detection of the disease. When you have symptoms of the disease, you should immediately go to the nearest medical facility for treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.