Glucosamine is a naturally occurring molecule in your body, but it is also a substance that needs to be supplemented. Nowadays, there are many products and supplements containing glucosamine available on the market, used in the treatment of joint diseases. Because it is produced in the form of dietary supplements, people can easily purchase and use it, often without needing a doctor's advice. However, not everyone knows whether to take glucosamine before or after meals, or when is the best time to take it.
1. What is Glucosamine?
Glucosamine is a naturally occurring chemical compound in our bodies, classified as an amino sugar. There are two main types of glucosamine: glucosamine sulfate and glucosamine hydrochloride.
Glucosamine acts as a building block for functional molecules in our bodies, primarily for the development and maintenance of cartilage in joints, which cushions the bones. However, as you age, the amount of this substance begins to decrease, leading to the gradual breakdown of joints. There is evidence that supplementing with glucosamine sulfate can help combat this condition.
Additionally, glucosamine is found in some animals and non-human tissues such as shellfish, animal bones, and fungi. Glucosamine supplements are often made from these natural sources.
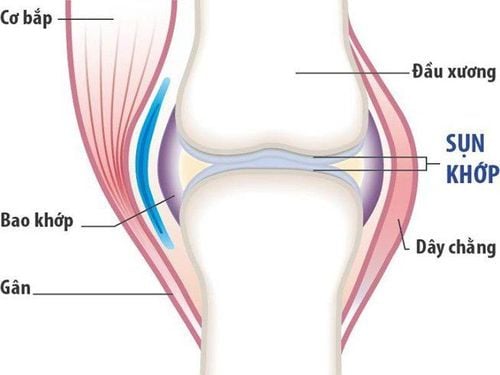
2. Benefits of Glucosamine
Most people know that glucosamine is used to support the treatment of joint diseases, especially osteoarthritis. However, not everyone understands all its benefits. Here are some key benefits of glucosamine:
- Reduces Inflammation: The exact mechanism of how glucosamine works in treating diseases is not fully understood. However, some studies have shown that it can reduce inflammation, especially when used with chondroitin, a compound also involved in the production and maintenance of healthy cartilage.
- Supports Joint Health: Cartilage is a smooth tissue that covers the ends of bones, forming joints. Synovial fluid helps bones move freely, reducing friction and allowing pain-free movement at the joints. Glucosamine is involved in forming several chemical compounds related to the creation of cartilage and synovial fluid. Some studies have shown that glucosamine supplements can protect joint tissue by preventing cartilage breakdown.
- Treats Bone and Joint Disorders: Although glucosamine is commonly used to treat various bone and joint conditions, more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness. Most studies show that using glucosamine sulfate can help control symptoms of osteoarthritis.
3. Forms and Supplements of Glucosamine
Supplemental glucosamine is made from natural sources such as shellfish, fungi, or produced synthetically in laboratories. The typical dosage of glucosamine is 1,500mg per day, which can be taken all at once or divided into multiple doses throughout the day.
There are two forms of glucosamine supplements:
- Glucosamine sulfate
- Glucosamine hydrochloride
- Additionally, some products combine glucosamine sulfate with chondroitin sulfate.
Most scientific data suggest that glucosamine sulfate supplements or glucosamine sulfate combined with chondroitin provide the best results.
4. When Is the Best Time to Take Glucosamine?
Many people have questions about the best time to take glucosamine, such as:
When is the best time to take glucosamine?
Should glucosamine be taken before or after meals?
Is it better to take glucosamine in the morning or evening?
Should glucosamine be taken daily?
You can take glucosamine whenever it is most convenient for you. Some people believe that taking it in the morning is best. Others prefer to take it with meals. Some people like to take it on an empty stomach with one or two glasses of water. However, some people experience side effects from oral use, so to reduce symptoms, you should take glucosamine during or after meals.
In many countries around the world, glucosamine is classified as a slow-acting drug for osteoarthritis symptoms and a disease-modifying osteoarthritis drug. Currently, glucosamine and chondroitin are the most commonly used supplements to improve osteoarthritis symptoms. Because the drug acts slowly, its effects may be seen after 2-3 months of continuous use.

To achieve the best results of glucosamine, you should follow the instructions on the product packaging or as directed by your doctor or pharmacist. Do not use this product more than the recommended dosage on the label. Avoid using different products containing glucosamine at the same time without your doctor's advice, as this may increase the risk of glucosamine overdose.
5. Can Taking Glucosamine Cause Side Effects?
Supplemental glucosamine is generally safe for most people. However, you may experience some side effects, such as:
- Nausea
- Heartburn
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Allergic reactions: hives, difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
You should not use glucosamine if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, as there is currently insufficient evidence to show it is safe in these cases.
Glucosamine may also worsen blood sugar control in people with diabetes, although this risk is relatively low. Therefore, if you are taking diabetes medication, consult your doctor before using glucosamine.
If you are looking for a medication to relieve joint pain, glucosamine supplements may be worth considering. However, it is best to consult your doctor before deciding to use glucosamine for specific advice and guidance.