This is an automatically translated article.
Genotropin is used to treat growth retardation or short bowel syndrome in children. The main active ingredient of the drug is somatropin. So what is Genotropin and how is it used?
1. What is Genotropin?
What does Genotropin do? Genotropin is a medicine used to treat certain conditions such as growth retardation, GH deficiency, intestinal disorders (short bowel syndrome) or weight loss and emaciation caused by HIV. Somatropin - the main active ingredient of Genotropin is also used to increase height in children with certain syndromes (such as Noonan syndrome, Turner syndrome or idiopathic short stature).
2. How to use Genotropin
Drug users need to carefully read the drug information from the manufacturer or from the pharmacist before starting to use Genotropin. Some brands of Genotropin are used by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection. Besides, some other brands are only used subcutaneously. Therefore, how Genotropin is used will depend on the brand the patient is taking. Talk to your pharmacist to make sure that the patient is injecting the medicine correctly. Another important thing is to change the injection site of Genotropin to avoid abnormal skin problems.
To bring the best effect, Genotropin must be used exactly as prescribed by the doctor, the patient must understand the therapy and strictly follow the doctor's instructions. The dose of Genotropin depends on the age, weight, medical condition and response to treatment of each patient.
If you are taking Genotropin at home, you should learn all the instructions on how to use the medicine from your healthcare provider. Some other notes when using Genotropin such as:
Do not shake while mixing, because shaking can make the drug not work properly; Before use, inspect the product with the naked eye for precipitation or drug discoloration, if any, do not use; Learn how to safely store and dispose of medical supplies. If you are using Genotropin as an injection, you should not share the pen with others, even if the needles have been changed. Sharing can cause cross-infection.
If Genotropin is used to treat short bowel syndrome, the patient should consult with their doctor about a special diet (high in carbohydrates / low in fat) or the need for additional nutrients. necessary, needs.
If Genotropin is used for weight loss/muscle loss, it can take up to 2 weeks for the drug to work. Patients should not use Genotropin more, more often than prescribed by the doctor because the risk of side effects will increase.
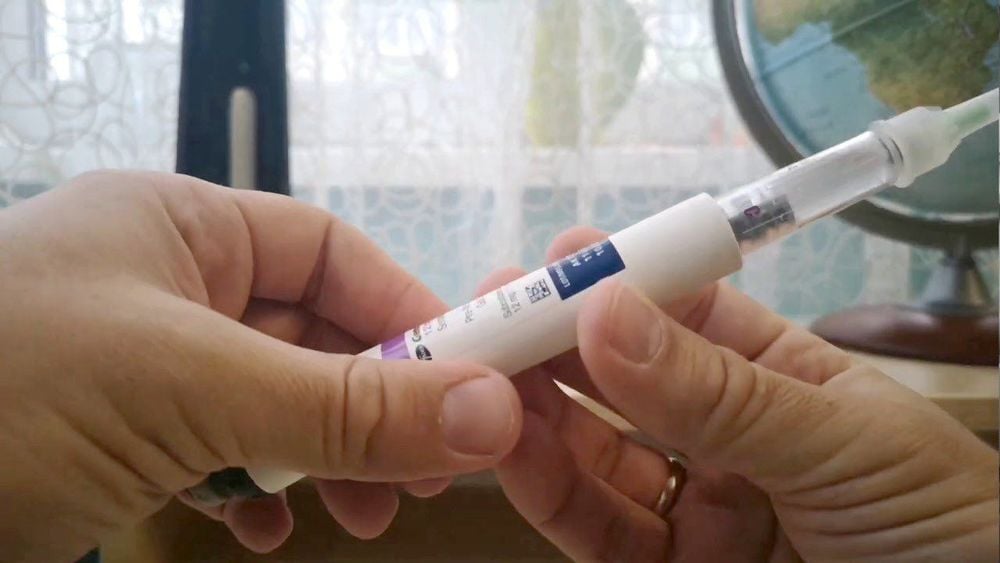
Thuốc Genotropin được dùng bằng đường tiêm theo hướng dẫn của bác sĩ
3. Genotropin side effects
Common side effects of Genotropin include:
Headache; Nausea, vomiting; Tired; Muscle pain; Asthenia . If these symptoms persist or become more bothersome while taking Genotropin, inform your doctor or pharmacist immediately. Tell your doctor promptly if you have any of the following serious side effects of Genotropin:
Persistent fatigue; Unusual/unexplained weight gain; Does not tolerate cold; Persistent bradycardia; Fast heart beat ; Ear pain/itching; Hearing problems; Joint pain, knee pain; Numbness/tingling sensation; unusually increased thirst or urination; Swollen hands/ankles/feet; Change the shape or size of any moles; Persistent nausea, vomiting; Stomach pain, severe abdominal pain; Vision changes; Convulsions ; Severe headache. Genotropin-related lung or breathing problems that may occur in children are known as Prader-Willi syndrome. Some risk factors include being male, being overweight or having serious lung/respiratory problems (sleep apnea, lung infections, lung disease).
Children should be checked for certain breathing problems (upper airway obstruction) before and during treatment, where loud snoring or sleep apnea is a common sign of airway obstruction. It is important to notify the doctor promptly when the patient develops these signs or any signs of lung infection such as fever, persistent cough or difficulty breathing. Genotropin may increase your risk of developing a tumor or cancer. Discuss the risks and benefits of Genotropin with your doctor before using it.

Thuốc Genotropin có thể gây ra một số tác dụng phụ ngoài ý muốn
4. Precautions when using Genotropin
Before using Genotropin, tell your doctor about a history of allergy to somatropin or any other allergic condition. The doctor or pharmacist should be concerned about the patient's medical history, especially of:
Adrenal gland problems; eye problems (such as diabetic retinopathy); Recent major trauma/surgery; severe breathing problems (acute respiratory failure); Diabetes or a family history of diabetes; Fat; Kidney disease; Tumor (cancer, especially of the head/neck); Thyroid problems; Curved spine. If you have diabetes, Genotropin can increase your blood sugar, so check your blood sugar as often as directed and share the results with your doctor. Notify your doctor if you have symptoms of hyperglycemia such as increased thirst, increased frequency of urination when taking Genotropin.
When giving Genotropin to an infant, mix Genotropin with distilled water for injection that does not contain preservatives. The preservative (benzyl alcohol) in Genotropin solution for injection can (rarely) cause serious problems (sometimes fatal) when given to infants during the first months of life. This risk is higher in low birth weight infants. Recognizing symptoms include rapid breathing, low blood pressure, or a very slow heart rate. These symptoms should then be reported to the doctor immediately.
The elderly are a group of people who are more sensitive to the side effects of Genotropin, especially the effect on blood sugar and swelling of the ankles and feet.
Genotropin should only be used when clearly needed during pregnancy after the risks and benefits have been discussed. There have been no studies on whether Genotropin passes into breast milk, so nursing women should consult their doctor before taking the medicine.
5. Genotropin drug interactions
Drug interactions can change the way Genotropin works or increase your risk of serious side effects. Products that may interact with Genotropin drugs include estrogen supplements/replacements.
Symptoms of Genotropin overdose include: severe headache, nausea or vomiting; sudden sweating, fatigue, tremors, confusion (hypoglycemia), or persistent swelling of the hands and feet.
Tests such as eye exam, thyroid function test, blood sugar level, growth hormone level... will be done regularly to monitor the body's response to the drug or check for side effects.
It is important to get optimal results that Genotropin is taken on schedule. If a dose is missed, a patient should ask a doctor or pharmacist immediately to establish a new dosing schedule. Do not arbitrarily double the dose of Genotropin.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com