This is an automatically translated article.
Flexible bronchoscopy is widely used to diagnose and detect respiratory diseases. Currently, the rate of people suffering from respiratory diseases is increasing, so early detection for timely treatment is very important.
1. Flexible bronchoscopy
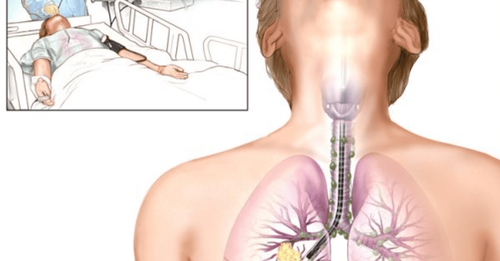
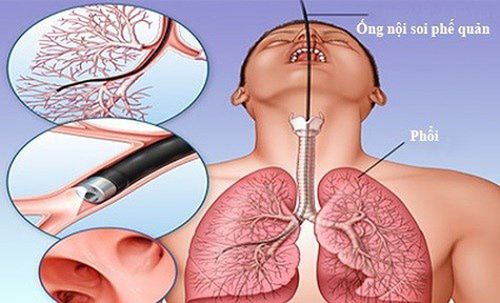
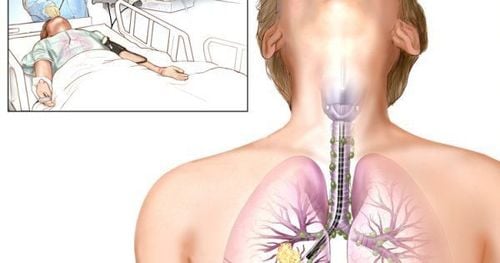
Flexible bronchoscopy is a medical procedure that uses a small, flexible endoscope with a light and camera attached to one end. The endoscope is inserted into the patient's airway through the nose or mouth. The images obtained from the camera will be displayed on a computer screen, allowing the doctor to assess the damage, along with abnormalities in the respiratory tract.
Flexible bronchoscopy is one of the methods of diagnosis and treatment of important respiratory diseases such as: pneumonia, lung cancer, bronchitis,... Endoscope with camera can High resolution, providing quality and clear images. Moreover, the flexible endoscope will help reduce pain and discomfort in the neck during and after the endoscopy procedure than using the rigid endoscope.
Especially for bronchoscopy in children, the use of a flexible tube can reduce the damage to the child's respiratory tract. In some cases, because the patient is too scared or coughing, a lot of stimulation can perform bronchoscopy pre-anesthesia.
2. Indications and contraindications
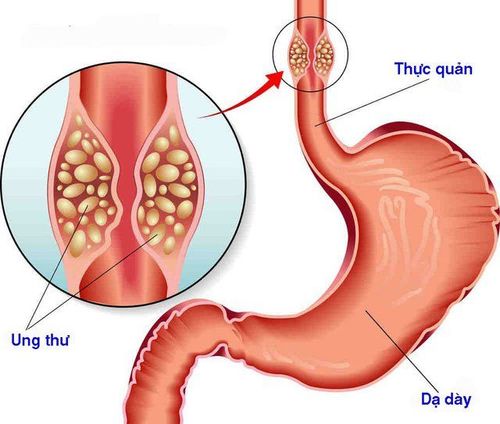
Chỉ định nội soi phế quản ống mềm với ung thư thực quản
2.1 Indications Indications for bronchoscopy in the following cases:
Diagnosis of bronchial cancer; Staging of bronchial cancer; Follow-up after treatment for bronchial cancer; Evaluation of patients with malignant lesions of the head and neck; Evaluation in case of esophageal cancer; Infections: recurrent pneumonia, infections in people with immunocompromised diseases, lung abscesses, pleural empyema,...; Other respiratory diseases: atelectasis, pleural effusion, unexplained prolonged cough, chest trauma, foreign body aspiration,... 2.2 Contraindication Cases contraindicated bronchoscopy Management:
Cardiovascular disorders: heart failure, myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, angina, uncontrolled hypertension,...; Acute respiratory failure, uncontrolled bronchial asthma, pneumothorax without drainage,...; Blood clotting disorder.
3. Implementation steps
Xét nghiệm máu chẩn đoán các rối loạn về đông máu
3.1 Preparation for endoscopy The patient is carried out blood tests to diagnose whether there are clotting disorders or not; Patients are asked to fast for at least 6 hours before the endoscopy and stop drinking water 2 hours before; The doctor will conduct a clinical examination with the patient to know the health status, medical history or drugs being used. In case the patient does not meet the requirements to perform endoscopy, the doctor will advise and give a more appropriate diagnostic method. 3.2 Carrying out endoscopy The patient is anesthetized with drugs before performing the endoscopy. After anesthesia, the patient remains conscious; The patient sits or lies in the most appropriate position for the flexible bronchoscopy process to take place easily and quickly. Usually having a higher head position or leaning back; The doctor proceeds to insert the endoscope through the mouth or nose and deep down to different locations of the tracheobronchial branch. At this time, the doctor will easily observe and evaluate signs of injury or abnormal state inside the respiratory tract thanks to the images captured from the camera. For cases that need an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will perform a biopsy to take samples to perform related tests or pump a volume of fluid into the lungs, after endoscopy this amount of fluid will also be aspirated. . Flexible bronchoscopy usually takes 5 to 10 minutes or so.
3.3 Monitoring and managing complications Bronchoscopy does not affect health, so patients can be discharged from the hospital within the same day. Patients may experience basic conditions such as pain in the neck area, hoarseness of voice, coughing up light blood in the case of biopsy samples,... However, if they feel signs like continuous shortness of breath, , arrhythmia, heavy bleeding,... the patient needs to report to the doctor for timely treatment. Some complications may occur after bronchoscopy:
Lack of blood oxygen: During bronchoscopy In a flexible tube, the oxygen pressure in arterial blood PaO2 can be reduced by 10 mmHg, SaO2 is reduced by 2%-5% or more. If there is acute respiratory failure, stop the bronchoscopy immediately, increase oxygen flow, use bronchodilators by inhalation or infusion if necessary.
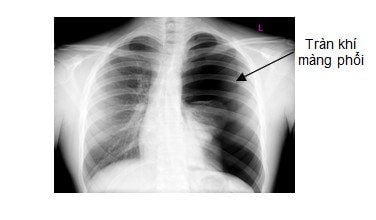
Nội soi phế quản có thể gặp biến chứng tràn khí màng phổi
Bleeding: Bleeding complications often occur during biopsies. To prevent serious complications of hemoptysis when doing bronchial biopsies and transbronchial biopsies, the first biopsy should be done with a small and shallow press to see the extent of bleeding, if not dangerous, then biopsy. really. When there is bleeding, injecting 0.01% adrenaline solution has the effect of reducing bleeding at the bronchial biopsy site, injecting morphine intramuscularly, using the bronchoscope tip to close the bleeding PQ hole. If the bleeding cannot be stopped, the endotracheal tube must be removed, and emergency embolization should be contacted. Infection: If after endoscopy, the patient has fever, cough and cloudy sputum, the sputum culture should be cultured to look for pathogenic bacteria. Bronchospasm: This complication often occurs due to inadequate anesthesia to inhibit the sensory stimulation causing bronchospasm through the parasympathetic nerve. Care should be taken to prevent this complication in people with a predisposition to increased bronchial reactivity such as bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pneumothorax: occurs in 5%-5.5% during transbronchial biopsies, bronchial brushing or in patients with severe alveolar dilatation. If the pneumothorax is small, you can only need to breathe oxygen, take a follow-up film, if the pneumothorax is large, you need to open the pleura to drain the air. Other complications and complications: Allergy to lidocaine local anesthetic, so it is necessary to test with local anesthetic before examination in people with a history of allergy: intravenous methylprednisolone. In summary, flexible bronchoscopy is a diagnostic method that is being widely performed, to detect respiratory diseases. Flexible bronchoscopy gives patients, especially children, less pain and discomfort in the throat than rigid bronchoscopy.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, flexible bronchoscopy is performed on modern machinery, this technique does not make patients uncomfortable when conducting endoscopy: Choking, feeling Asphyxiation... Before the procedure, the patient will be anesthetized and carefully controlled the airway to ensure safety and minimize irritation or discomfort for the patient, then the doctor will perform perform endoscopic techniques, remove foreign bodies and then check and control to ensure there are no complications for the patient.
For consultation and registration for bronchoscopy with anesthesia at Vinmec International Hospital, you can contact HERE, or register online HERE.