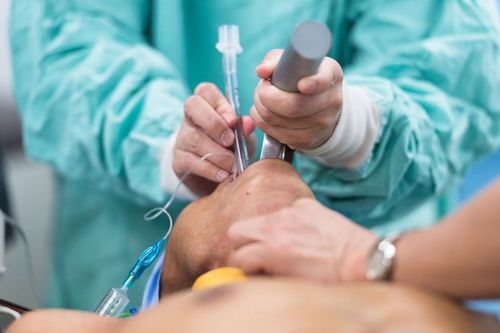
This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Le Duc Hoang - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.Bronchoscopy in mechanically ventilated patients is a difficult technique that can be of great help in the diagnosis and treatment of lung diseases.
1. Learn about bronchoscopy
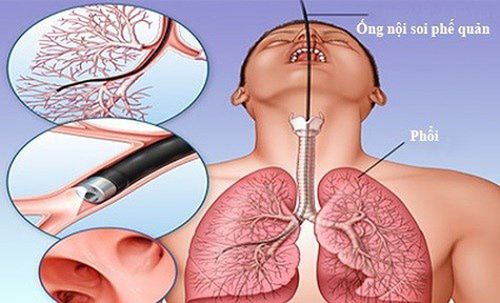
What is bronchoscopy? This is a procedure using the bronchoscope to examine the inside of the bronchial tree to help diagnose and treat lung related diseases such as:
Describe the anatomical damage to the inside of the bronchial tree. Take specimens to determine the cause, differentiate, and prognosticate the disease.
2. Indications for bronchoscopy
Malignant pathology:
Diagnosis of tracheobronchial cancer. Lung cancer staging. Follow-up after treatment for bronchial cancer. Evaluation of patients with malignant lesions of the head and neck. Evaluation in case of esophageal cancer. Infection:
Pneumonia relapsing or improving slowly, infection in immunocompromised patients, pleural effusion, lung abscess,... Other indications:
Atelectasis, interstitial lung disease, hemoptysis, persistent cough of unknown cause, aspiration of foreign body, chest trauma, pleural effusion with unexplained secretions, assessment of patients after lung surgery, accurate positioning of endotracheal tubes, evaluation lesions after intubation or tracheostomy, tracheal stenosis, hoarseness due to vocal cord paralysis, suspected tracheoesophageal or tracheobronchial-pleural fistula, prolonged pneumothorax, ....
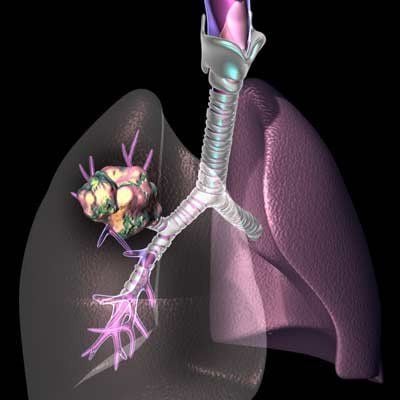
3. Contraindications
Cardiovascular disorders: severe arrhythmia, severe heart failure, myocardial infarction, recent or unstable angina,... Blood clotting disorder. The patient is uncooperative.
4. Bronchoscopy procedure
Step 1: Means, tools and consumables
Light source: halogen or xenon bulb, image processor Camera, video monitor, video recorder or polaroid photo printer. Flexible fiber bronchoscope. Biopsy pliers, foreign body clamps, brushes to take samples for bacteria and cells, aspiration needles. Ventilator wiring to L-shaped endotracheal tube. Suction machine, monitor, oxygen system, endotracheal intubation device, tracheostomy, other emergency medicine and equipment. Specialized bronchoscope cleaning tools, specialized bronchoscope holder. Step 2: Put artificial ventilation mode IPPV, 100% oxygen. Use sedatives and muscle relaxants if necessary.
Tracheostomy with 2% lidocaine injected through an endotracheal tube or a tracheostomy tube. Install an L-shaped flexible tube, connecting the ventilator tube and endotracheal tube or a tracheostomy cannula with a hole to pass the bronchoscope through to ensure artificial ventilation during the bronchoscopy. Use a flexible bronchoscope with an outside diameter of 2/3 of the inner diameter of the tube.
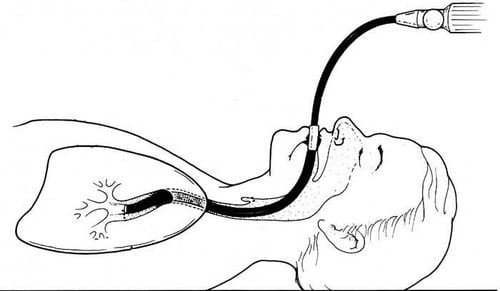
Step 3: Perform the technique
Patient position: supine. Mechanical ventilation with 100% FiO2. Bronchodilator with 2% xylocaine pumped through an endotracheal tube or a tracheostomy tube. When bronchoscopy in patients with mechanical ventilation through the endotracheal tube, the bronchoscope should be inserted into the endotracheal tube, when bronchoscopy in patients with mechanical ventilation through the tracheostomy, the bronchoscope should be passed through the nasal passage next to the cannula to go down the trachea to minimize the risk of injury. reduce endoscopic damage. When bronchoscopy, make sure the bronchoscope always goes between the bronchial tubes to limit damage to the tracheobronchial wall. The principle of bronchoscopy: bronchoscopy first to avoid infecting the healthy lung. If the patient is seriously ill, or if the patient is poorly cooperative, the prognosis is not enough for both sides, then the patient's side should be examined first. If the side of the lesion is unknown, or the lesion is diffuse on both sides, the right side should be examined first. During endoscopy, it is necessary to closely monitor parameters: SpO2, pulse, blood pressure. Pause endoscopy when SpO2 < 92%. Ventilate until SpO2 ≥ 98%, then start again. When endoscopic examination, it is necessary to carefully observe the lesions along the way, in turn from the top to bottom PQ holes to avoid missing lesions. After observing all the bilateral PQ holes, comprehensive assessment of the lesions began to conduct specimen collection techniques.
Depending on the lesions on the lung film and bronchoscopy images, the technique of taking samples can be performed: bronchoalveolar lavage, bronchial tumor biopsy, transbronchial aspiration, no birth bronchoscopy during bronchoscopy in mechanically ventilated patients. After the endoscopy is completed, the ventilator indicators are gradually returned to the parameters before the endoscopy.
5. Follow up
During the scan, monitor pulse status, blood pressure, blood oxygen saturation, electrocardiogram. The doctor continuously observes the general condition of the patient to detect and treat complications immediately.
6. Accidents and handling
6.1. Hypoxemia During flexible bronchoscopy, the arterial blood oxygen pressure PaO2 can be reduced by 10 mmHg, SaO2 decreased by 2%-5% or more. If there is acute respiratory failure, immediately stop the bronchoscopy, increase the oxygen flow, use bronchodilators by inhalation or infusion when showing signs of bronchospasm.
6.2. Bleeding Bleeding complications often occur during biopsies. To prevent serious bleeding complications when doing a biopsy of the tumor or bronchial mucosa, the first biopsy should be done with a small and shallow press to see the extent of bleeding, if not dangerous, then the actual biopsy. When there is bleeding, inject 0.01% adrenaline solution to reduce bleeding at the bronchial biopsy site, inject morphine intramuscularly, use the bronchoscope tip to close the bleeding PQ hole, otherwise the tube must be removed. endotracheal intubation, contact emergency embolization.
6.3. Bacterial infection If the patient has fever, cough, and cloudy sputum, sputum culture should be cultured to look for pathogenic bacteria.
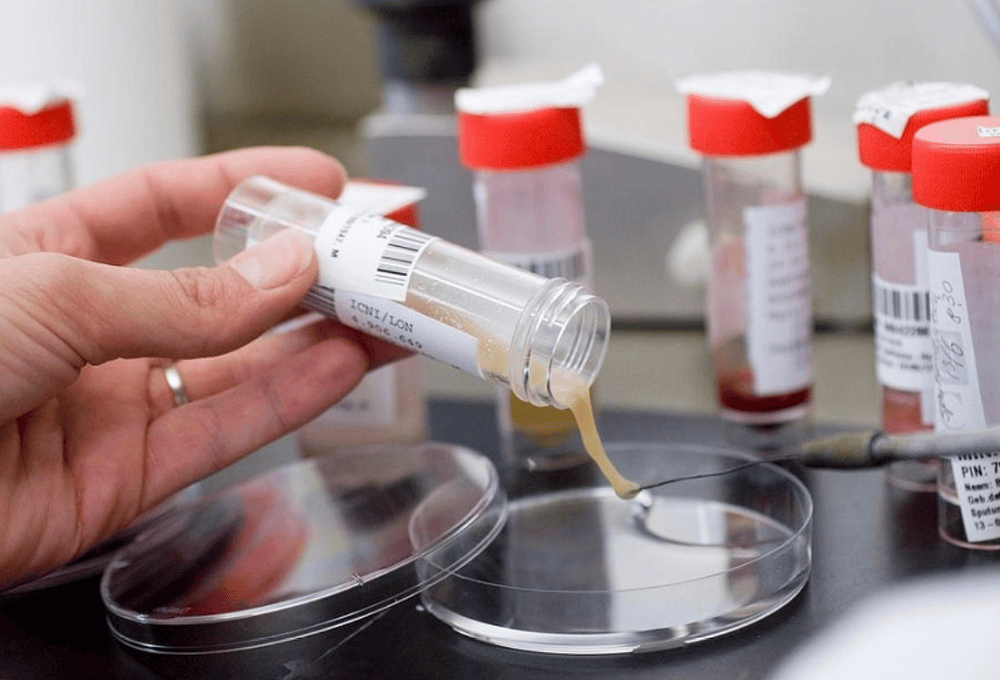
6.4. Pneumothorax Transbronchial biopsy should not be performed in patients on mechanical ventilation because of the very high risk of pneumothorax.
When there is pneumothorax: reduce ventilator pressure. Open the pleura for continuous air drainage.
6.5. Other complications and complications Allergy to lidocaine local anesthetic: need to test with local anesthetic before bronchoscopy. When signs of lidocaine allergy appear: IM dimedrol 10mg x 1 tube, methylprednisolone 40mg x 1 vial (intravenous). Broken brush or intrabronchial biopsy forceps: Use other biopsy pliers to remove the broken tip. Ventilator patients need to be regularly monitored by an emergency physician, otherwise it will lead to sputum congestion, pneumonia, worsening of the patient's condition, leading to the risk of respiratory failure and death.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.