This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Bui Thi Hong Khang - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Central Park International Hospital
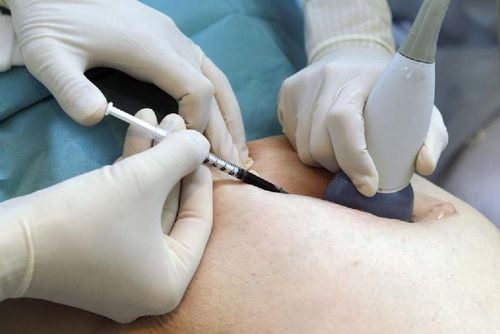
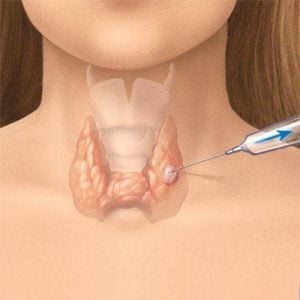
Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNA) is a minimally invasive technique with rapid, inexpensive results. The accuracy of FNA in the diagnosis of benign and malignant diseases of the lymph nodes is over 90%; However, the sensitivity of this method varies greatly between groups of benign and malignant, primary and secondary diseases.
1. Introduction
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) was first used in 1914, by an English physician named Gordon R. Ward, to diagnose lymphoma of the lymph nodes. However, the technique is still not widely available due to doubts in the medical community about its accuracy; It was not until the second half of the twentieth century, thanks to the research works of Swedish doctors, that the lymph node FNA was accepted in the diagnosis of lymph node diseases. FNA is a minimally invasive technique with quick and inexpensive results. The accuracy of FNA in the diagnosis of benign and malignant diseases of the lymph nodes is over 90%; However, the sensitivity of this method varies greatly between groups of benign and malignant, primary and secondary diseases. The diagnosis of carcinoma metastasized to the lymph nodes has the highest sensitivity (> 95%), the diagnosis of lymphoma has the lower sensitivity (80-90%). In recent years, cytology has made great strides in the diagnosis and classification of lymph node lymphomas, by combining cytomorphology, immunophenotypic techniques, cytogenetics, and cytogenetics. molecular biology.
Enlarged lymph nodes are a common symptom, due to many different causes, in which the cause of malignancy is the most concerned. The likelihood of lymphadenopathy due to malignancy varies with age, location, and size of the lymph node. For cases of peripheral lymphadenopathy, only 1% is due to malignancy; but this rate is much increased for enlarged lymph nodes occurring in the supraclavicular, retroperitoneal, intra-abdominal and mediastinal regions. Most cases of lymphadenopathy in children are reactive hyperplasia; but in people over 40 years of age, the likelihood of malignancy increases. Enlarged lymph nodes with a diameter of ≤ 1 cm are usually due to benign disease, and > 2 cm in diameter are usually due to granulomatous inflammation or malignancy; Therefore, a diameter of ≥ 1.5 cm is considered to be the limit for the size of the lymph node, which requires tests - including FNA - to determine the cause of lymphadenopathy.
2. In which cases is nodal FNA indicated?
Nodal FNA is indicated in the following cases”
In people with no history of malignancy, lymphadenopathy 1.5 cm in the periphery or in abnormal locations such as supraclavicular, retroperitoneal , intra-abdominal and mediastinal (in these locations, nodal FNA is performed under endoscopic-ultrasound guidance). The purpose of FNA is to determine the cause of lymphadenopathy. Enlarged lymph nodes in cancer patients have been identified. The purpose of FNA is to help with clinical staging and follow-up after treatment. For lymph node cytology, two complementary staining methods are available:
Romanowsky staining (May-Grunwald-Giemsa, Diff-Quick) to visualize the cytoplasmic characteristics of lymphocytes; and Papanicolaou staining to reveal the characteristics of the nucleus. If possible, both methods should be used at the same time.
3. Fine-needle aspiration cytology of lymphadenopathy
3.1 Result response system
The results of cytological diagnosis of lymph nodes, similar to other sites, are divided into large groups:
Do not meet diagnostic criteria Negative Atypical Suspect Malignancy A negative result does not completely exclude the possibility of malignancy, so it should always be compared with the clinical picture.
3.2 Normal lymph node cytology
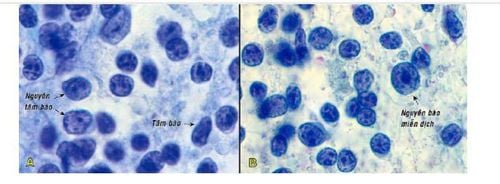
Normal lymph nodes are very small in size, not palpable, so they are hardly aspirated. The term "normal cytology" here refers to cells aspirated from a ganglion that are enlarged by reactive hyperplasia, when the normal cellular components of the node are all increased in numbers. Aspiration smears from normal high-density reactive hyperplastic lymph nodes. The cellular component is mainly lymphocytes (90%). In addition, there are other types of cells such as plasma cells, histiocytosis, chromogenic macrophages, dendritic cells, interstitial dendritic cells, and polymorphonuclear leukocytes.
Lymphoglandular bodies, which are cytoplasmic fragments of lymphocytes, globose, 2-7 ìm in size, uniformly gray-green or sometimes present in the background of the lymph node smear vacuoles (Pap staining). Lymphoma is characteristic of lymphoid tissue, when the count in a large field of view is more than 20, it can be confirmed that the smear has been aspirated from the lymphoid tissue.
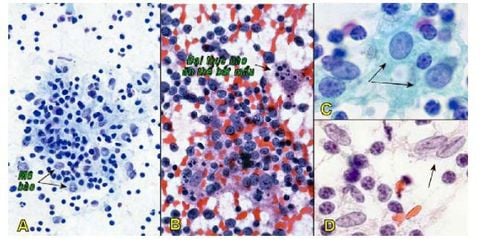
3.3 Inflammatory lymph nodes - reactive hyperplasia
3.4 Cancer of lymph node metastasis
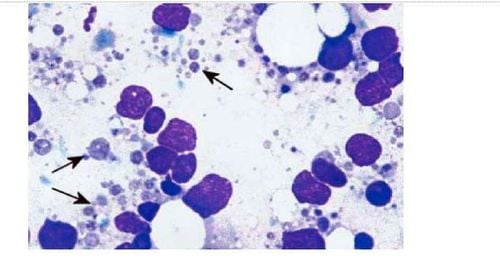
Lymph nodes are common metastatic sites of cancers, mainly carcinomas or melanomas; Sarcomas rarely metastasize to lymph nodes. The ability to quickly and accurately diagnose lymph node metastases is an outstanding advantage of the FNA technique. FNA can identify carcinoma of the lymph node, which in many cases can suggest the location of the primary tumor (Figure 4).
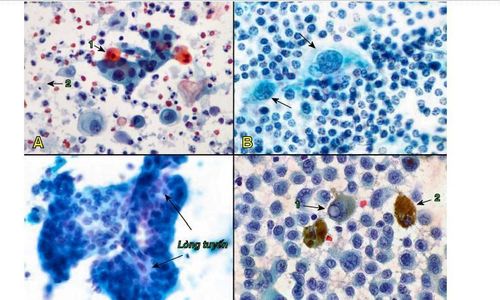
4.5 Primary cancer of the vessels
Primary cancer of the lymph nodes or lymphoma (lymphoma) is a malignant neoplasm of cells derived from the lymphoid tissue, presenting as solid tumors. Lymphoma includes many types, divided into two main groups: Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, according to the World Health Organization's 2008 classification.
According to the 2001 summary report at the Ho Chi Minh City Oncology Hospital. In Ho Chi Minh City, FNA has low sensitivity in diagnosing lymphomas; Therefore, if the clinical picture suggests lymphoma (eg, generalized lymphadenopathy), it is best to perform a biopsy to obtain a histopathological diagnosis and to easily perform additional immunohistochemical techniques when needed. necessary, rather than using FNA as a first-line diagnostic approach. However, nodal FNA remains valuable in clinical staging of a confirmed lymphoma or in monitoring for recurrence after treatment.
Recently, with the development of modern techniques (cytochemical immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, molecular genetic techniques such as PCR and FISH), specialized cytogenetics laboratories in European-American countries have sought to accurately diagnose different types of lymphoma, based solely on cells aspirated from lymph node tissue. In Vietnam at present, the diagnosis of lymphoma by FNA technique is still based solely on morphological analysis of cells, so it needs to be confirmed later by biopsy and histopathological diagnosis.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: GPB Textbook GPB Department of Medical University Pham Ngoc Thach HCMC.