This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Pham Thieu Trung - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.
Peripheral nerve block regional anesthesia is a simple procedure for the management of multi-site pain that originates in relation to the nerve roots. Peripheral nerve blockade provides temporary pain relief, and can help doctors identify the cause of pain.
1. Peripheral Nerve Blockage
Peripheral nerve block regional anesthesia is used for surgical anesthesia, in addition to general anesthesia, and for postoperative analgesia. Nerve-selective anesthesia is used to diagnose and treat chronic pain syndromes. The peripheral nervous system is the part of the nervous system that includes the nerves and ganglia outside the spinal cord and brain. The peripheral nervous system functions to connect the central nervous system with the limbs and organs. Peripheral nerve blockade may include upper extremity peripheral nerve block or lower extremity peripheral nerve block
Peripheral nerve blockade has only temporary pain relief, no long-term effect. The procedure was performed in batches and was stopped to assess effectiveness. Each patient has a different response, some feel better after the injection, but there are also people who do not improve. Therefore, physicians will have to offer alternative treatment for patients who do not respond to nerve block. Peripheral nerve blockade only helps patients reduce pain without prolonging life and improving prognosis.
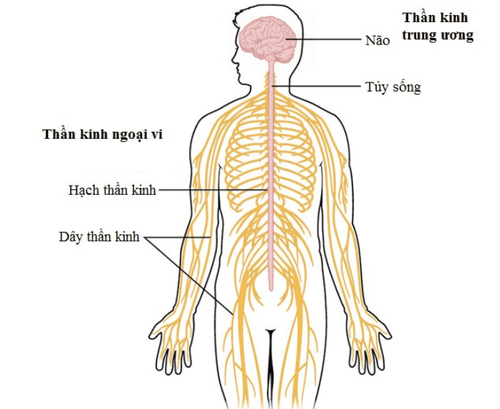
Vị trí các dây thần kinh ngoại vi trong cơ thể con người
2. Indications and contraindications
2.1 Indications
Peripheral nerve block regional anesthesia is indicated in the following cases:
Surgical anesthesia Combined with general anesthesia Pain relief during and after surgery 2.2 Contraindications
Absolute contraindications for patients:
Infection of the anesthetic site Severe hypotension Increased intracranial pressure Mitral stenosis, severe aortic valve Bleeding pathology
Relative contraindications for:
Patients with sepsis Uncooperative patients Spinal deformities

Phong bế thần kinh ngoại vi chống chỉ định với người bệnh dị dạng cột sống
3. Procedure for performing anesthesia of peripheral nerve block area
The doctor first needs to determine the area of anesthesia, then review the patient's history to see if there are any contraindications. Examine and identify nerve damage before administering anesthesia.
The doctor will inject the medicine with the same ampoule as a regular vaccine syringe. The drug is selected based on the condition of each patient. In most cases, to ensure the accuracy of the procedure, the doctor needs to use additional imaging equipment to guide the needle, be it a fluorescent screen or a tomography machine.
When the doctor inserts the needle, the patient may feel a stinging sensation. After the injection, the patient will feel more comfortable. Sometimes, the doctor can insert the needle quite deep into the area of the nerve to be blocked. The patient may feel some discomfort at this point, but will still need to try to stay still so the needle doesn't go out of its way.
If the injection site is close to a large nerve or a bundle of nerves such as the sciatic nerve, the doctor will check by asking the patient if there is a sudden sensation of pain. If the patient has sudden pain, it means that the needle has come close to this nerve and needs to be withdrawn and reoriented. This actually happens very rarely. After the injection, the patient will feel pain relief in the injected area.
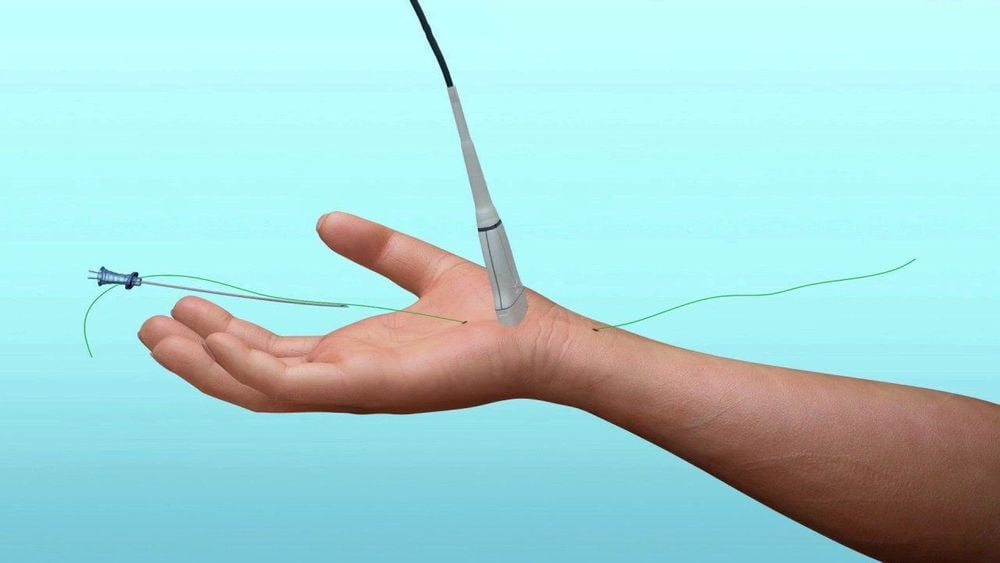
Kỹ thuật gây tê vùng phong bế thần kinh ngoại vi (vùng chi trên)
4. Complications of regional anesthesia of peripheral nerve block may be encountered
Anesthesia in the peripheral nerve block area can cause a number of complications such as:
Infection at the injection site Bleeding Wrong injection into a blood vessel Blocking the orchid to other nerves Blocking the wrong nerve if Nerves located too close to each other Mild radiation exposure if fluoroscopy or CT is used.
In addition, local anesthesia of peripheral nerve blockade can also cause serious complications such as paralysis or damage to the arteries supplying blood to the spinal cord. Other serious complications may include: low blood pressure, mistakenly punctured the lungs or kidneys, mistakenly injected alcohol into the artery, causing diarrhea, weakness in the limbs.
In summary, local anesthesia of peripheral nerve blockade provides quite effective pain relief, but only has a temporary effect and does not bring long-term effect. Contraindicated in patients with coagulopathy or on anticoagulants, and uncontrolled infection. Peripheral nerve blockade is usually done in batches to assess effectiveness, and if the patient does not respond, an appropriate alternative treatment plan must be changed.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
SEE MORE
Why does the incision heal, the patient still hurts? What is chronic pain? Causes and treatment Some common complications of anesthesia and anesthesia