This is an automatically translated article.
The urinary system of children has similar components to the urinary system of adults, but the characteristics of each part of the urinary system are different. Therefore, sometimes the symptoms of urinary tract disease in children are slightly different from those of adults.1. Structure of urinary system in children
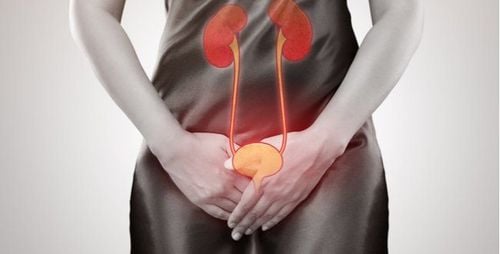
The urinary system of a child is similar to that of an adult, consisting of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra and paraglomerular organs. Some anatomical and structural features of the components of the urinary system of children are as follows:1.1 Kidney The position of the kidney in young children is lower than in older children and adults. The lower pole of the kidney is at the level of the IV-V lumbar vertebrae. Shape: The kidneys in young children are bean-shaped and cusp-shaped. Weight: The weight of the kidney increases gradually with age, like a newborn baby, the kidney weighs about 11 -12g; 6 months 24-25g; 1 year old 36-37g; Puberty weighs about 115-120g. Structure: The kidney consists of the cortex and the medulla, the ratio between the cortex and the medulla is 1: 4 in infants, 1: 3 in breastfed infants, and 1: 2 in adults. Therefore, when renal ultrasound is performed. In young children, the kidneys are less sound than in adults. The structure of the nephron renal unit is similar to that of an adult, including the glomerulus, the proximal tubule, the loop of Henle, the distal tubule, the collecting duct, and the paraglomerular organization. Renal calyces: Each kidney has about 9 to 12 calyces, divided into 3 groups including upper, middle, and lower. The shape of the renal calyx system is different at different ages, because in the calyx, there is a peristaltic contraction to push urine downwards. 1.2 Ureterus The ureter in children is relatively large and long, so it is easier to bend. The ureter connects to the kidney and exits to form a right angle, while in older children and adults, it is an obtuse angle, so urine is easy. stagnation in the kidney causes water retention in the renal calyces.
1.3 Bladder Location: The bladder in children is located high above the pelvis, so when it is filled with urine, the bladder bridge is easy to feel.
Bladder capacity: This capacity increases with age.
Newborns: 30 - 60 ml Breastfed babies: 60 - 100 ml Children over 5 years old: 100 - 200 ml Children over 10 years old: 150 - 350 Children 15 years old: 200 - 400 ml 1.4 Urethra The urethra is the passageway urine from the bladder out of the body, in young children the size of the urethra depends on age and sex.
Girls: The urethra is wide but short, about 2 - 4 cm. Because of their short and wide structure, they are more susceptible to infection upstream than boys. Boys: The urethra is narrow but about 6-15 cm long.

Hệ tiết niệu ở trẻ em cũng có những thành phần tương tự như hệ tiết niệu của người lớn
2. Functional characteristics of the urinary system in children
2.1 Glomerular Filtration Function Dialysis is the most important function of the glomerulus and the first step in urine formation. Through the membrane at the glomerulus, the substances with large molecular weight are retained and the substances of low weight are eliminated. The glomerular filtration rate is an indicator of kidney function or kidney function.The glomerular filtration rate in newborns is still low, only reaching about 25% of the average value of older children and increasing with age until about 2-3 years old, the index is similar to that of adults.
2.2 Reabsorption function of the renal tubules After the blood is filtered in the glomerulus, the first urine is formed and then followed by the renal tubules to the renal calyces. However, the composition of the first urine is full of substances such as amino acids, glucose, salts Ca, Mg, K, Na, Cl... Therefore, when the first urine passes through the renal tubules, it will be reabsorbed. substances needed by the body only waste products are almost not absorbed or very little.
Children < 2 years old: The renal tubular reabsorption function is still poor, so the urine density is low. Due to the poor concentration, if the child is dehydrated, the body is not able to retain water.
Children > 2 years old: The reabsorption function is similar to that of adults.
2.3 Excretion function of renal tubules Substances that are not necessary for the body, but have a large molecular weight or have a structure that links molecules together to form a network that will not be able to be eliminated through the membrane through the filter. glomerulus can. They will be eliminated via secretion in the distal tubule and part of the collecting duct.
The renal tubular secretion function in children under 2 years old is worse than in children over 2 years old and adults.
2.4 Endocrine function is an important function of the paraglomerular organization. The paraglomerular organization works well from the moment the baby is born and produces two substances: Erythropoietin: A substance that stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells. Renin: Has the effect of activating vasoconstrictor chemicals, causing an increase in blood pressure.
Trong hệ tiết niệu ở trẻ em thì thận có chức năng quan trọng nhất là lọc máu
3. Normal urine output in children
In the first days after birth, babies often urinate very little, sometimes anuria due to physiological dehydration and because the baby is breastfed late, but often urinate more often later because of the small bladder capacity and ability to control the bladder. Central nervous system control is poor.After 1 year of age, the number of urinations of children is greatly reduced due to the better storage capacity of the bladder and better reabsorption capacity of the renal tubules.
Children's urine output depends on many factors such as age, weight, diet, hot and cold weather and kidney function.
Normal urine output in children is between 2-2.5ml/kg/h.
Oliguria in children when urine output is less than 1 ml/kg/h. Anuria in children when urine output is less than 0.5 ml/kg/h. When children have oliguria or anuria, it is necessary to find the cause, which may be due to the child drinking less water, dehydration or kidney disease.
The structure of the urinary system of children is different from that of adults, so there are also some other pathological characteristics. In addition, the function of the urinary system is not quite as good as that of adults, so children are more susceptible to diseases, as well as the ability to retain water for the body is less.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.