This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Doctor Phan Dinh Thuy Tien - General Internal Medicine - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.The human nervous system is a very perfect machine made up of neurons and glial cells. Nerve cells play a very important role in the body's response to the external environment. So, how many types of nerve cells are there and what are their characteristics?
1. Structure of human nerve cells
The human nervous system is a perfect structure, a collection of cells to perform various functions in the course of human life. The embryonic origin of the nervous system is the embryonic ectoderm. So how many types of nerve cells are there? The structure of the nervous system includes:Specialized nerve cells (called neurons) are responsible for conducting and performing nerve functions; Glial cells have a supporting function. According to the simple structure, there are 2 types of nerve cells, but each large type is divided into many small cell types. There is a different relationship between the two types of neurons in humans, depending on the central or peripheral nervous system. According to classification, glial cells are divided into many different types of cells such as:
Peripheral nervous system has 2 types of glial cells: sheath cells and Schwann cells; The central nervous system has four types of glial cells: endothelial epithelial cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglial cells.
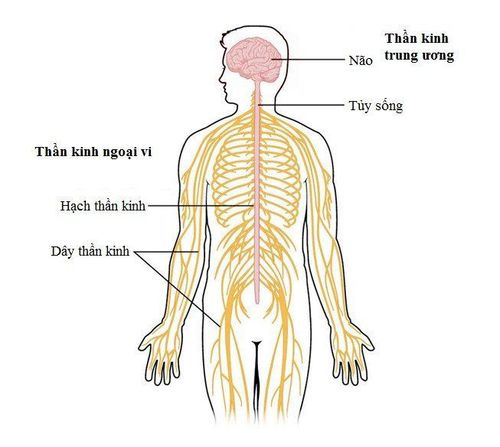
Hình ảnh hệ thần kinh trung ương
2. Characterization of human neurons (Neural)
Nerve cells (also known as neurons) are the basic units that make up the nervous system in the human body. Each neuron is composed of a main stem and many small branches.The nerve cell body is the site of major functions because it contains the nucleus and numerous cytoplasm. The rest of the neuron branches, usually consisting of one axon and many dendrites, whose main function is the transmission of nerve impulses. The human neuronal cell body has the following anatomical features:
The neuronal body has many different shapes and sizes, each neuron body usually has a variable number and arrangement of branches depending on the function cell. Normally, the neuron cell body is polygonal in shape, each corner will generate a branch; Inside the neuron body contains large size, light color and many large nuclei; The cytoplasm consists of Nissl bodies, which are essentially basophilic clusters. At the microscopic level, the Nissl body is a stack of parallel granulosa endoplasmic reticulum vesicles; In addition to the nucleus and cytoplasm, the neuronal cell body also contains a cell skeleton made up of supertubules and nerve fibers to connect with neuron branches. There are also other basic organelles of a cell such as mitochondria, golgi apparatus. Branches of neurons in humans have the following characteristics:
Branches of neurons are essentially extensions of the stem. These branches are divided into dendrites and axons. Each neuron usually consists of only one axon and many dendrites; The basic function of the dendrites is to participate in the transport of electrical impulses: The instructions in the dendrites are afferent, nerve impulses go from the end of the dendrites to the neuron body. In contrast, the centrifugal direction is the direction of movement of nerve impulses in the axons, that is, from the cell body to the axon terminal. The structural feature of dendrites is that they do not contain a nucleus, and the cytoplasm also contains many supertubules and nerve fibers similar to the cell body. In addition, dendrites also include granulosa endoplasmic reticulum, non-granular endoplasmic reticulum, free ribosomes, and mitochondria. The dendrites often divide into many smaller branches;
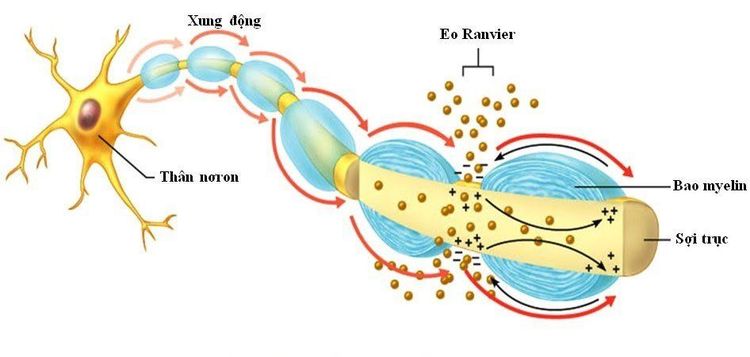
Các đặc điểm của nơron thần kinh
3. Synaptic
A synapse is a connection and transmission of electrical impulses between two different nerve cells or between a nerve cell and a muscle cell. Synaptic consists of 2 parts, pre-synaptic and post-synaptic, in the middle is a narrow synaptic cleft with a distance of 20-30 nm.Presynaptic is actually the terminal part of the axon composed of many synaptic vesicles; Postsynaptic is a specially modified region of neuronal or muscle cell membranes. Neural synapses are classified differently, including:
Based on the connection location between presynaptic and postsynaptic synapses divided into 3 main types: axial - branch synapses, axial - trunk synapses and axial - axis synapses. Some less common types such as branch - branch synapses, branch - trunk synapses, trunk - trunk synapses; Based on synaptic function, it is divided into excitatory synapse or inhibitory synapse; Based on the impulse conduction mechanism is a chemical or electrical mediator that is divided into chemical synapses, electrical synapses and mixed synapses.
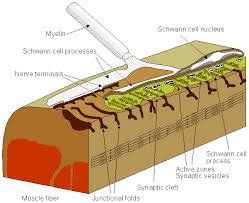
Khớp thần kinh còn có tên gọi khác là synap
4. Characteristics of glial cells
Glial cells are part of the nervous system, which do not have the function of conducting nerve impulses, but are closely related to neurons.Unlike specialized neurons, glial cells have the ability to reproduce throughout the cell life. At the same time, these cells also have an embryological origin, which is the embryonic ectoderm. There are many different types of glial cells, which divide depending on the central nervous system or the peripheral nervous system:
In the peripheral nervous system there are 2 types:
Sheath cells: Usually small in size, nucleated cells The cells are oval, dark, and have little cytoplasm and are difficult to see under the microscope. Sheath cells are usually found in the ganglia; Schwann cells: All nerve fibers of the peripheral nervous system are surrounded by Schwann cells. These cells fuse with branches of neurons to form myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers. In the central nervous system, there are 4 types of glial cells, including:
Astrocytes: The astrocytes often give off many cytoplasmic branches with the function of supporting the central nervous system; Undenatured cells: At the microscopic level, these cells are small, have dark nuclei, and have few cytoplasmic branches. The function of this glial cell is to produce myelin sheaths for neuronal branches similar to the Schwann cells of the peripheral nervous system; Intramedullary epithelial cells: Separating the lumen of the intramedullary canal from the ventricles; Microglial: The main function of this glial cell is phagocytosis, which is scattered throughout the white matter and gray nucleus of the central nervous system. Nerve cells are the basic units that make up the nervous system in the human body. Each neuron is composed of a main stem and many small branches, each of which plays an important role in human life.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.