This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Nguyen Hong Tram - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the examination and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases, especially gastrointestinal - hepatobiliary diseases, gastrointestinal endoscopy and general internal diseases.1. Current status of liver disease caused by alcohol
When alcohol is consumed in large amounts, it can damage or even destroy liver cells. One of the liver's main functions is breaking down alcohol so it can be eliminated from the body. Although the liver has the ability to regenerate and repair itself, if we constantly load a lot of alcohol into the body, the liver's processing ability can decline leading to serious liver damage, gradually losing liver function. .Statistics also show that excessive alcohol consumption will cause fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis. Patients who drink 30ml or more of alcohol per day have a high risk of cirrhosis. However, Vietnam is still one of the countries with the highest alcohol consumption in the world. In 2005, Vietnam ranked 24th, by 2015 it jumped to 8th, while the volume of beer consumed in 2010 was 2.41 billion liters. By 2016, the consumption volume increased to 3.79 billion. liter.

The numbers related to fatty liver caused by alcohol are also not very positive. As recorded in 2010, nearly 500,000 deaths from cirrhosis and 81,000 deaths from liver cancer worldwide were related to alcohol, of which men accounted for four times more than women. An estimated 3.3 million people worldwide die from alcohol each year, more than AIDS, tuberculosis and violence combined.
2. Mechanism of alcoholic fatty liver
Lipids from food when entering the intestine will be absorbed in the form of fatty acids, monoglycerin and glycerol. Most of these fatty acids are transported to the liver and esterified into triglycerides. Some fatty acids are esterified in combination with cholesterol to form phospholipids, or oxidized to acetone and CO2. Trygliceride will then bind to lipoproteins that are produced by the liver for excretion from the liver. Therefore, fatty liver is mainly formed due to 3 reasons: increased fat production in the liver, decreased fat excretion from the liver and increased fat mobilization in body tissues.The participation of alcohol, alcoholic beverages has a strong impact on all the above stages:
Drinking alcohol increases the mobilization of fat from storage tissues, increases carbohydrates and acid glucurophosphate due to reduced liver function. , which leads to an increase in fatty acid esters, and ultimately to an increase in trygliceride generation. Alcohol reduces extrahepatic fatty acid oxidation. The decline in liver function combined with poor nutrition in alcohol drinkers will limit the synthesis of lipoproteins and inhibit the excretion of fat in the liver, increasing fatty deposits in the liver. Hepatocytes have cavities filled with fat that will push the cell nucleus to one side. Alcohol can cause acute or chronic fatty liver. In acute fatty liver, the patient may have acute abdominal pain due to hepatocellular distension. When the test shows increased transaminase enzymes, blood bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase... Some patients may have mental disorders. Chronic fatty liver disease will often depend on the extent and duration of alcohol consumption and the patient's comorbidities. When chronic fatty liver, patients may have anorexia, abdominal distension, pain in the liver, psychosis, tremors, liver function tests show a decline in liver function. The ultrasound results showed that the liver parenchyma was steadily hyperechoic. Progression can lead to chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis...
3. Fatty liver symptoms
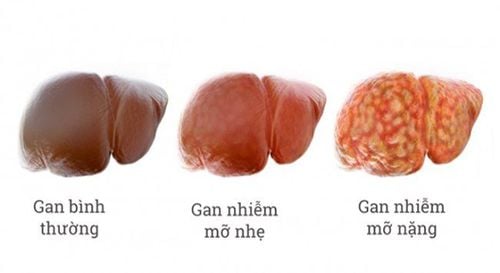
Often liver diseases will take place in silence, without any symptoms until the liver has been seriously damaged. Significant later symptoms may include: fatigue, weight loss, loss of appetite, yellowing of the eyes and skin, swelling in the ankles and abdomen, memory impairment, drowsiness, vomiting or bowel movements blood. This means that the liver is already at a significant stage of damage. The disease often progresses according to the trend: from normal liver - fatty liver - steatohepatitis - cirrhosis, and finally liver cancer.Stage 1: Fat accounts for 5-10% of liver weight. Clinically asymptomatic. Stage 2: Fat accounts for 10-30% of liver weight. Clinically, the liver is larger than normal, liver enzymes are increased, people are tired. Stage 3: Fat accounts for more than 30% of liver weight. This is a severe stage of hepatitis and cirrhosis, elevated liver enzymes, pain in the liver, patients feeling fatigued, possibly jaundiced, bleeding.
4. Prevention of fatty liver caused by alcohol
The simplest and most effective way to prevent alcoholic fatty liver disease is to stop drinking alcohol. According to WHO recommendations, people should not regularly drink more than 14 units of alcohol per week (each unit is equivalent to half a glass of beer or a 25ml glass of spirits).People who regularly drink alcohol should go for regular tests and ultrasounds to detect liver damage early. People who already have liver disease absolutely do not drink alcohol because it will make the liver disease worse. If you are a perfectly healthy person and have a habit of drinking alcohol, you should try to cut down on strong alcohol consumption, switch to wine and beer every day in moderation. If drinking correctly each week, using 7-14 units (1 unit of alcohol is equivalent to 25ml of 40% alcohol) of alcohol for women and 21 units for men, it is very good for the heart and digestive system. If women drink more than 3 units of alcohol/day, men drink more than 4 units of alcohol/day will cause liver damage leading to hepatitis, alcoholic fatty liver, cirrhosis and eventually liver cancer.
5. Measures to treat alcoholic fatty liver
Some ways to treat fatty liver caused by alcohol:The patient must consciously give up alcohol. After 4-6 weeks of quitting alcohol, if the liver damage is only in the fatty liver stage (fatty liver), the structure and function of the liver can gradually recover. Attention should be paid to enhancing nutrition and controlling comorbidities such as diabetes, obesity, and malnutrition. It is possible to use some additional vitamins such as vitamin C, E...in addition to the daily diet. Should limit eating foods rich in cholesterol such as viscera or animal fat, focus on eating more vegetables and fruits. If the patient is also overweight or obese, they should exercise to lose weight.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.