This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Doctor Nguyen Xuan Ninh - Emergency Doctor, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
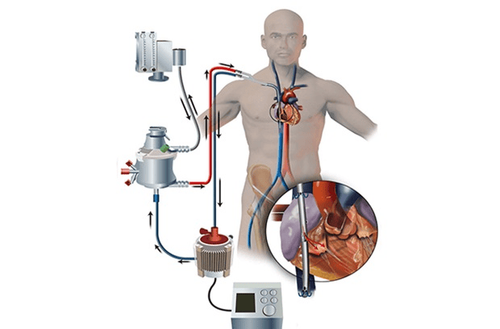
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) or extracorporeal life support (ECLS) is a method of circulatory and respiratory support when the heart or lungs or both cannot function normally. This method helps to replace the heart or lungs or both in the short term.
1. Overview of ECMO
ECMO machine helps to bring blood out of the body, then removes CO2 and adds oxygen to red blood cells. This method provides temporary supportive treatment for patients with severe respiratory failure (ARDS), cardiogenic shock that does not improve with other measures to maintain life while waiting for lung or heart disease to recover.
In addition, ECMO is also used for patients with end-stage pulmonary fibrosis, or end-stage heart failure while waiting for a lung or heart transplant. More recently, ECMO has also been used to resuscitate patients with cardiac arrest who have not responded to traditional CPR. Then ECMO will be the last resort solution, temporarily restoring circulation to the victim.
2. Classification
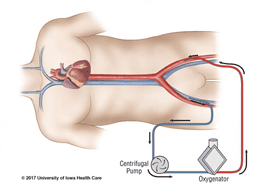
The two most common types are venous-arterial ECMO (V-A ECMO) and venous-venous ECMO (V-V-ECMO). In both methods, blood is drawn outside the body from the venous system. Venous blood will be passed through the ECMO membrane. Here, venous blood will be supplemented with oxygen and CO2 removed, then the blood is returned to the body. In V-A ECMO, blood is returned to the arterial system and in V-V ECMO the blood is returned to the venous system. VV ECMO only supports the respiratory system, not the heart, and V-A ECMO can support both heart and respiration.
2.1. V-V ECMO In this procedure, in most cases, the doctor will place a catheter into the femoral vein to drain blood and a tube into the right internal jugular vein to return blood. V-V ECMO is commonly used for respiratory failure.
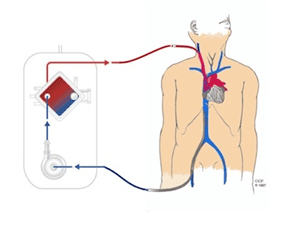
2.2. V-A ECMO In this procedure, in most cases, the doctor will place an intravenous catheter into the left or right femoral vein to drain blood and an arterial catheter into the left or right femoral artery. to return blood to the body. The position of the right femoral vein catheter tip was kept immediately near the junction of the inferior vena cava and the right atrium, while the tip of the right femoral artery catheter was in the iliac artery. V-A ECMO is commonly used in heart failure
3. Specify ECMO
Mainly patients with severe respiratory failure or cardiogenic shock as mentioned above. In addition, ECMO may be considered in the following specific situations:
Severe acute respiratory failure (PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 100 mmHg) has been optimally mechanically ventilated but has not been effective.
Severe respiratory failure on optimal mechanical ventilation but still has elevated CO2 with pH < 7.2 Cardiogenic shock Cardiogenic arrest Cardiogenic shock, cardiac arrest after cardiac surgery Used to maintain life while waiting for a heart transplant or waiting to be placed ventricular assist device or waiting for a lung transplant
4. Contraindications
Majority are relative contraindications such as:
Severe pre-existing medical conditions that reduce quality of life such as CNS disease, advanced cancer, coagulopathy or high risk of cardiovascular disease. bleeding during anticoagulation. Old age, obesity. Prolonged mechanical ventilation or death has been diagnosed.
5. Possible complications of ECMO
ECMO helps maintain life while waiting for root cause treatment, has been shown to reduce mortality in the group of patients with acute respiratory failure, cardiogenic shock. However, ECMO also causes many complications. There are two main groups of complications: procedure-related complications during catheterization and complications related to anticoagulants administered while operating the ECMO system Complications related to catheterization procedures such as human The disease carries the risk of puncture, tearing of the artery or vein, the risk of serious bleeding, and possibly even death. Patients are also at increased risk of amputation due to lack of blood supply to the leg in the V-A ECMO V-A ECMO Complications related to anticoagulation: studies show a bleeding risk of 30-40% due to heparin-containing anticoagulation given during ECMO. The most serious bleeding complication is cerebral hemorrhage. In addition, patients using ECMO machines are also at risk of other complications such as infections, ulcers, cerebral ischemia, etc. Currently, ECMO technology has been deployed at Vinmec Central Park hospital. ECMO technique is considered a lifesaving technique for severe pneumonia and acute myocarditis that do not respond to conventional treatments and need more time to recover. ECMO is also a bridge for seriously ill patients waiting for a heart or lung transplant.
In addition, the hospital has invested in modern machinery and equipment to support doctors during surgery and patient resuscitation, such as: Maquet's HR20 artificial cardiopulmonary system, Machine breathe GE's R860.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
The article references the source:
Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. Retrieved
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
The Manual of Clinical Perfusion