This is an automatically translated article.
ECMO is an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation method that uses a circulatory system to carry out oxygen exchange outside the body to support and maintain vital functions in patients with circulatory failure or heart failure. severe breathing.1. What is extracorporeal circulation?
Extracorporeal circulation is a technique to temporarily replace heart and lung function when surgical repair or replacement is needed to repair or replace major cardiovascular or vascular structures in the body. Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is performed by artificial heart-lung machines and must be controlled by highly qualified doctors and technicians.CPB is a semi-enclosed system that can completely replace the patient's cardiopulmonary function thanks to a pump system that coordinates with a gas exchange system connected to the duct, cannula, and heart of the patient. This system will induce physiological changes in the body that are actively controlled such as arterial blood pressure, systemic venous pressure, pulmonary venous pressure, blood components. , partial pressure CO2, O2, N2 and body temperature. This leads to self-regulating and self-protective responses of the patient.
Extracorporeal circulation can completely replace or partially support the functioning of the cardiopulmonary system, or it can be a complete replacement, but at the same time placing multiple cannula in different positions combined with cardiac arrest temporary refund.
ECMO is also one of the methods to support oxygen exchange through the extracorporeal circulatory system.
2. Overview of ECMO
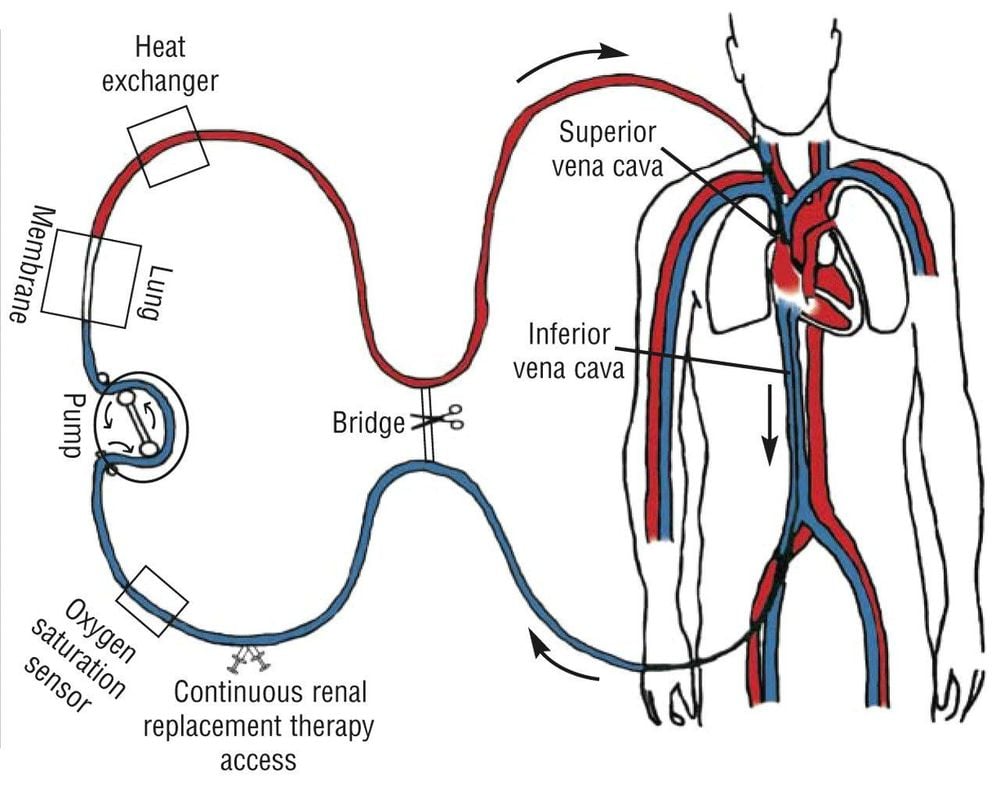
ECMO là phương pháp oxy hóa qua màng ngoài cơ thể
Subjects who need to use ECMO are patients with serious medical conditions, at risk of respiratory or circulatory arrest, which are life-threatening.
2.2 Indications of ECMO Lungs are not able to supply oxygen to the body even with ventilatory support such as severe pneumonia with complications of respiratory failure, or patients diagnosed with pulmonary edema Acute with severe respiratory failure... The lungs cannot excrete carbon dioxide even with the help of a ventilator. The pumping action of the heart is not enough to supply blood to the body. Or it can be applied only to cases of cardiopulmonary disease and waiting time for organs to be transplanted. 2.3 Structure of the cardiopulmonary bypass system An ECMO system includes:
Cannula tube, which is a vascular access catheter Blood tube coated with heparin to prevent blood clotting during ECMO operation . Oxygen exchange membrane: composed of thousands of hollow fibers that allow red blood cells to enter and come into close contact with circulating gas. Blood pump: can be a roller pump or a centrifugal pump. Studies have shown that centrifugal pumps are preferable for extracorporeal circulation because they cause less hemolysis than roller pumps. The heat exchanger is intended to keep the blood warm as it passes through the extracorporeal circulatory system, avoiding heat loss when the extracorporeal blood flow is large. 2.4 Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation The ECMO system is connected to the patient's body through cannula tubes placed in large arteries and veins in the legs, neck, and chest.
ECMO machine system collects blood from the patient's body and pumps it through the oxygen exchange membrane of the artificial lung system. Here, the dialysate runs around the membrane, creating a difference in osmotic pressure and concentration, which is a condition for the exchange of fluids and solutes, and this process also increases the amount of oxygen. in the blood and help eliminate carbon dioxide out. Then, by using a pumping force equal to the force of the heart's contraction, ECMO helps return the exchange of blood and substances back to the body's circulatory system.
There are two configurations of oxygen exchange across the extracorporeal membrane: venous-venous and veno-arterial. The venous-arterial configuration is used to ensure both gas exchange and hemodynamic support. The venous-venous configuration is used mainly to ensure the body's oxygen and circulatory volume needs.
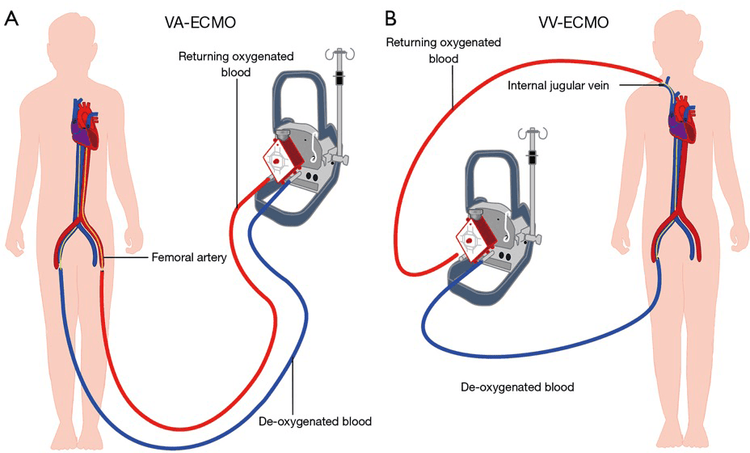
Quá trình trao đổi oxy qua màng ngoài cơ thể
Bleeding may occur in different organs in the body such as the brain, lungs and sometimes bleeding at catheter sites. This is due to the use of anticoagulants during ECMO use. Therefore, it is necessary to examine and test carefully before conducting ECMO and closely monitor the patient during the operation to ensure safety and timely detect complications. Infection: because it is an oxygen exchange system outside the body membrane and is directly connected to the blood vessels in the body, the risk of infection is very high and if not detected and handled promptly, it will lead to the risk of infection. sepsis affects the patient's life. Renal failure occurs when the ECMO system does not supply enough blood to the kidneys, usually acute renal failure. Stroke: caused by an embolism or because the system does not supply and distribute enough blood to certain areas of the brain. ECMO can also cause damage to the catheter sites. ECMO is a medical method that requires highly qualified doctors and technicians to perform.
Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital has successfully applied this method to the treatment process, helping to save the lives of many patients with severe respiratory and circulatory failure. The success rate of each case with indication to use this method is up to 85-90%.
The surgery at Vinmec Central Park was performed by MSc.BS. Khong Trong Thang - Head of the emergency resuscitation department. With 19 years of experience in medical examination and treatment and teaching of Emergency Resuscitation. Proficient in most techniques of Emergency Resuscitation, as well as having a lot of experience in new techniques (machine ventilation, continuous dialysis, MARS artificial liver, TPE, intensive hemodynamic monitoring).
In addition, the hospital has invested in modern machinery and equipment to support doctors during surgery and patient resuscitation, such as: Maquet's HR20 artificial cardiopulmonary system, Machine breathe GE's R860.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.