This is an automatically translated article.
Evaluation of left ventricular systolic function as expressed by left ventricular ejection fraction is the most commonly used and validated measure of echocardiography. This parameter has an important position in the field of cardiology in general, in the diagnosis and treatment of daily patients in particular. There are different methods to evaluate left ventricular systolic function by echocardiography, with different advantages in each case.1. What is left ventricular systolic function assessment?
Measurements of left ventricular systolic function are used to determine how well the left ventricle can pump blood into the systemic circulation with each heartbeat. This is an extremely important parameter in echocardiography because it can vary in many different diseases, and correlates with many clinical symptoms such as the degree of dyspnea, the limitation of exercise that can be seen in other diseases. heart failure patients. Furthermore, left ventricular systolic function is also a major prognostic factor in the in-hospital and future acute MI.The way to evaluate left ventricular systolic function has the basic principle of measuring the difference between the end systolic value divided by the end diastolic value. There are many different ways to quantify and measure left ventricular function on echocardiography, with 2D or 3D images, each with its own advantages and limitations, which are identified and applied appropriately in each different situation. The quantitative parameters of left ventricular systolic function commonly used in clinical practice are presented in turn below.
2. Visually observing left ventricular systolic function
This is a visual assessment of left ventricular systolic function with the naked eye by experienced echocardiographers. The doctor will evaluate this criterion based on the observation of myocardial function in each area or in other words, wall thickening and inward movement of the endocardium of certain areas of the heart muscle according to the blood vessels of the extremities. distribute. Distortions that occur in each area, such as poor thickening or thinning, and abnormal displacement can be identified as an estimate of reduced left ventricular systolic function.Each region of the myocardium should be viewed from multiple planes so that motion abnormalities can be visually assessed accurately according to the following criteria:
1) Normal or hyperkinetic
2 2) Hypokinetic (decreased in contraction thickness)
3) Immobility (no or negligible thickening)
4) Dysmotility (systolic wall thinning or elongation)
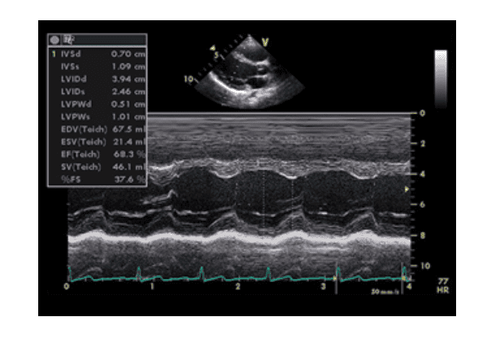
Các nhà siêu âm tim giàu kinh nghiệm có thể quan sát trực quan chức năng tâm thu thất trái bằng mắt thường
3. Shrinkage fraction
Fractional shortening (FS) is a parameter measured by echocardiography with the 2D M-Mode method. Using TM mode, the parameters of left ventricular end-systolic diameter and left ventricular end-diastolic diameter are directly measured by the sonographer. These parameters are the dimensions of the ventricles captured by M-Mode at the end of systole and diastole.Using the formula for the ratio of the difference between the left ventricular end-diastolic diameter and the left ventricular end-systolic diameter to the left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, the percentage difference in the size of the ventricles to the left during a cardiac cycle is the fraction of contraction that will be measured as the degree of contractility of the left ventricle. A shrink fraction value of 28% is considered normal. If it is lower than this value, the left ventricle is considered to be functionally impaired during systole.
Shrinkage fraction is a very common parameter although there are also some important confounding factors. In particular, the measurement of total left ventricular function is seen from linear imaging but if there is an abnormality of wall movement it can lead to false measurements, which will overestimate or underestimate the results. shrinkage fraction.
4. Ejection fraction
The ejection fraction (EF) is calculated from the end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume. This is the relationship between the amount of blood ejected during each cardiac cycle compared with the size of the left ventricle when filled with blood. This parameter is performed in echocardiography with 2D or 3D images. Currently, the Simpson method, which measures ejection fraction on 2D echocardiography, is the most commonly practiced with conventional echocardiographic indications.The formula used to calculate left ventricular ejection fraction is: EF(%) = (EDV-ESV) / EDV x 100 with:
EF = Radioactive fraction
EDV = End diastolic volume
ESV = End systolic volume
If left ventricular ejection fraction is lower than 52% in men and less than 54% in women, it is considered abnormal left ventricular systolic function.
5. Parameters of cardiac output, cardiac index and stroke volume
Doppler echocardiography and 2D imaging can be used to calculate a number of hemodynamic parameters such as cardiac output, cardiac index, and stroke volume. These parameters are important for the assessment of left ventricular systolic function.However, these parameters have the limitation that they cannot be calculated accurately if the patient has left ventricular outflow tract obstruction. Also, since most echocardiographic devices calculate these parameters on the basis of either the Simpson method or the TM mode, an additional limitation is that it cannot be applied in the presence of mitral regurgitation. Due to the disadvantages mentioned above, these parameters are rarely used in clinical practice.
Siêu âm tim Doppler và hình ảnh 2D có thể được sử dụng để tính toán một số thông số huyết động như cung lượng tim (cardiac output), chỉ số tim (cardiac index) và thể tích nhát bóp (stroke volume)
6. Spherical longitudinal strain ratio
Global longitudinal strain (GLS) is the change in the length of the left ventricle in a given direction relative to the baseline length. Thereby, this parameter will help provide the ability to assess myocardial function by area and will directly assess the contractile function of the heart.The advantage of this parameter is that it is an early and highly sensitive predictor of regional LV dysfunction. This is particularly important because regional inotropic dysfunction is often present before the ejection fraction officially declines. The commonly used formula to calculate the spherical longitudinal strain ratio is: GLS (%) = (MLs-MLd) / MLd with:
MLs = myocardial length during systole MLd = myocardial length in diastole Since the length of the myocardium during systole is smaller than during diastole, the value of the longitudinal strain ratio is usually negative. In other words, a negative longitudinal strain ratio indicates contraction activity while a positive value relates to relaxation. One drawback in measuring the longitudinal strain ratio is the need to depend on the measuring angle.
7. Tissue Marked Echocardiogram
Tissue-marked echocardiography is a new technique. By tracking the change of each blob on the 2D image, myocardial velocity and deformation parameters such as strain length and strain rate can be calculated. Therefore, tissue-marked echocardiography will help measure the different components of myocardial contractility and provide information on global contractility by assessing not only longitudinal tension, but also circumferential strain. and radial.The principle of tissue-marking echocardiography is an offline method. Digital loops are recorded and processed by a software as the myocardium is monitored throughout the cardiac cycle. The software will then calculate the amount of distortion and the results will be displayed in various forms.
The advantage of tissue-marking echocardiography is that it solves the limitations caused by measuring angle error. Therefore, this tool to evaluate left ventricular systolic function has become an established prognostic value in a number of clinical conditions that require high accuracy.
8. Elasticity
Elasticity is a parameter that indicates the contractility of the myocardium through a measurement of the rate at which pressure increases in the left ventricle during systole. In short, the faster the left ventricle is able to pressurize, the better the contractile function of the left ventricle will be judged. The increase in pressure in the atrioventricular chamber can be recorded with a reflux chart measured at the location of the mitral orifice.However, this method also has some limitations. For example, in some arrhythmias, elasticity may be reduced due to dyssynchrony rather than decreased contractility. In addition, the regurgitation signal at the mitral valve is a necessary criterion to calculate this parameter, but it may depend on the image quality or be affected by the disease at the valve.
9. 3D . Echocardiography
Có rất nhiều chỉ dẫn để đánh giá chức năng tâm thu thất trái với công cụ siêu âm tim
However, to date, the limitation of 3D echocardiography is its dependence on image quality and, as the new medium, there are few published data on normal values. Therefore, the evaluation of left ventricular systolic function on 3D echocardiography has only been initially performed in laboratories experienced in this technique and under feasible image quality conditions.
In summary, there are many indications for assessing left ventricular systolic function with echocardiography. This parameter is especially necessary in different clinical situations, when it is necessary to distinguish whether the patient's shock, hemodynamic instability is cardiac or noncardiac. However, it is necessary to understand the principles, advantages and limitations of each method in order to know how to apply the appropriate measurement.
Vinmec International General Hospital is equipped with a modern echocardiogram system with machinery and equipment on par with the most prestigious hospitals in the world to support doctors in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases for patients. core. Along with that is a team of experts including experienced professors and doctors who have successfully performed many surgeries for patients with heart disease.
Vinmec International General Hospital is equipped with 4D ultrasound machine with modern features, high resolution, probe size, thickness, ability to pump blood, heart activities,... As a result, it helps to detect and diagnose abnormalities or complex pathologies of the heart in the most accurate way.
Accompanying the most modern ultrasound machine today is a system of facilities with a dedicated ultrasound room, computer software connected to the machine allowing accurate signal transmission. Especially, the 4D ultrasound technique is performed by a team of professionally trained doctors, with absolute respect for technical rules. Therefore, the results obtained have very high accuracy, which is the basis for the doctor to give the best solution for the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to sources: NCBI, 123sonography.com, jeccm.amegroups.com, mayoclinicproceedings.org, Vietnam Cardiology Association