This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by a doctor from the Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Esophageal spasm is a rare disorder associated with increased muscle spasms of the esophagus. The pathogenesis is unclear, diagnosis and treatment options are still difficult.
1. What is esophageal spasm?
Esophageal spasm is a disorder of the smooth muscle contraction in the esophagus - the tube connecting the mouth and stomach - that makes it difficult to move food down to the stomach. When you have an esophageal spasm, the muscle between the esophagus and the stomach or the lower esophageal sphincter will not work and prevent food from flowing down.2. Symptoms of esophageal spasm
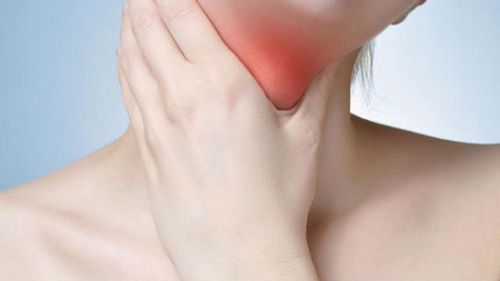
The main symptoms of esophageal spasm are difficulty swallowing solid, liquid, sensation of food stuck in the chest, reflux or chest pain when swallowing Chest pain can occur at rest, when swallowing or under stress, chest pain often posterior to the sternum but may radiate to the back, ribcage, arms and jaw, pain may range from seconds to minutes and may resemble angina The patient may also lose weight because of difficulty eating or pain .
Triệu chứng chính của co thắt thực quản là khó nuốt hoặc đau tức ngực khi nuốt
3. Causes of disease
The cause of esophageal spasm is unknown. However, many physicians hypothesize that it may be due to damage to the inner inhibitory nervous system in the esophagus, causing the inability to relax the esophageal smooth muscle in the esophageal body or the lower esophageal sphincter, the amplitude of contraction variable, this lesion may be secondary to autoimmune or infectious.Risk factors for the onset can be encountered such as high blood pressure, stress, depression, drinking alcohol or foods that are too hot and cold, older age and gastroesophageal reflux..
4. Diagnostic techniques
To make a diagnosis, your doctor may order a barium swallow X-ray (before the X-ray, you'll drink a white liquid called barite or swallow a reflective liquid that's visible on the X-ray). optical). A barium swallow x-ray will show the narrowing of the lower esophagus and the width of the upper esophagus. This procedure is also called a contrast-enhanced upper gastrointestinal X-ray.Doctors also use manometry to determine if the muscles in the esophagus are working and the pressure in the esophageal sphincter.
Endoscopy (using a small lighted tube with a small camera on the end) can check for other abnormalities of the esophagus such as esophageal stricture, sphincter, esophageal ulcers or internal or external tumor insertion, diverticulum.. besides that the doctor may order a biopsy, i.e. take a tissue sample and examine it under a microscope.
5. Treatment
Esophageal spasm has no cure, but therapy can improve the condition and help prevent complications.If you have esophageal spasm, the patient should be relieved of pressure in the lower esophageal sphincter by means of muscle dilation or balloon dilation surgery. However, once it has been dilated, the esophagus is at risk of not fully functioning again. Stretching may need to be repeated several times if symptoms recur.
Drugs such as nitrates or calcium channel blockers (which block the flow of calcium), which decompress the sphincter are often used if the patient is unable to perform sphincter dilation.
Your doctor may inject Botox (botulinum toxin) into the sphincter that stretches the esophagus.
If other treatments fail, your doctor may perform surgery to relieve pressure on the sphincter, called a lower esophageal sphincterotomy. The surgery can be performed laparoscopically. During laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon only needs to make a small incision instead of the large incision in conventional surgery, so there is no scar or only a faint scar.
If the disease is not treated in time, it can lead to complications such as tearing (perforation) of the esophagus, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and pneumonia. The most serious is leading to esophageal cancer.

Co thắt thực quản không có thuốc chữa, tuy nhiên liệu pháp điều trị có thể cải thiện tình trạng bệnh và giúp ngăn ngừa biến chứng
6. Habits to help limit esophageal spasms
Lifestyle habits that help limit symptoms of esophageal spasm include:Choose foods that are less likely to cause esophageal spasms Do not eat foods that are too hot or too cold Manage stress Follow up with scheduled appointments monitor the progress of symptoms and health status Listen to your doctor's instructions, do not arbitrarily take drugs not prescribed or arbitrarily quit prescribed drugs Call your doctor if you have difficulty swallowing for a while. for a long time, have pain when swallowing, or have symptoms that persist after treatment Call your doctor if you vomit blood or have new symptoms. Diffuse esophageal spasm can be treated medically or surgically, and can be combined with psychological treatment. Patients with choking should avoid straining during meals. If there are signs of gastroesophageal reflux or there is evidence of esophageal function test, gastroesophageal reflux should be treated, paying attention to using soft and liquid foods and dividing them into small pieces to help the patient. easier to swallow.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination, consulting and service services. comprehensive and professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.