This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by MSc.BS Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
The term ESD, which stands for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection, is translated as endoscopic submucosal dissection technique. This is a new technique used to treat early cancer of the gastrointestinal tract.
1. What is ESD technique?
Gastrointestinal cancer is one of the most common cancers, accounting for the largest percentage of cancers. According to the latest research, the rate of stomach cancer in Vietnam ranks 18th out of 20 countries with the highest rate of stomach cancer in the world. The alarming numbers above show that most of the patients are diagnosed at a late stage. While if detected early, with gastrointestinal mucosal resection, it is completely possible to cure gastrointestinal cancer for patients.
Currently, with the progress of endoscopic interventional submucosal dissection (ESD) to treat early gastrointestinal cancer, early diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancer plays a very important role. In the stage of gastrointestinal mucosal dysplasia, pre-cancer, or cancer is still localized in the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, if submucosal resection is removed, the disease can be completely cured, and the survival time of patients can stretch like other normal people.
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) is a minimally invasive procedure for early gastrointestinal cancer treatment to help patients preserve the entire stomach.
This method was developed and solved the limitations of conventional mucosal resection, with the advantage of minimal trauma; preservation of the gastrointestinal tract; improve the quality of life for patients; After only a few days, the patient can be discharged from the hospital and receive regular drug treatment, the endoscopic lesions will be cured.
2. Some basic structural and functional features of the gastrointestinal tract
The basic structure of the gastrointestinal tract wall consists of 4 layers, from the inside out including:mucosal layer Submucosa (submucosa) Muscle layer (inner sphincter and outer longitudinal muscle) Outer shell The alimentary canal functions both to transport and store food, as well as to digest and absorb nutrients in food. After that, the excess food residue will be concentrated, and then excreted through the anus. In the lining of the alimentary canal there are digestive glands. Depending on the specific structure and function of the alimentary canal (esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon and rectum), the surface mucosal cells along with the digestive gland at a particular site may own characteristics. The submucosa is a connective tissue with blood vessels, nerves and lymphatic systems that nourish and transport toxins out.
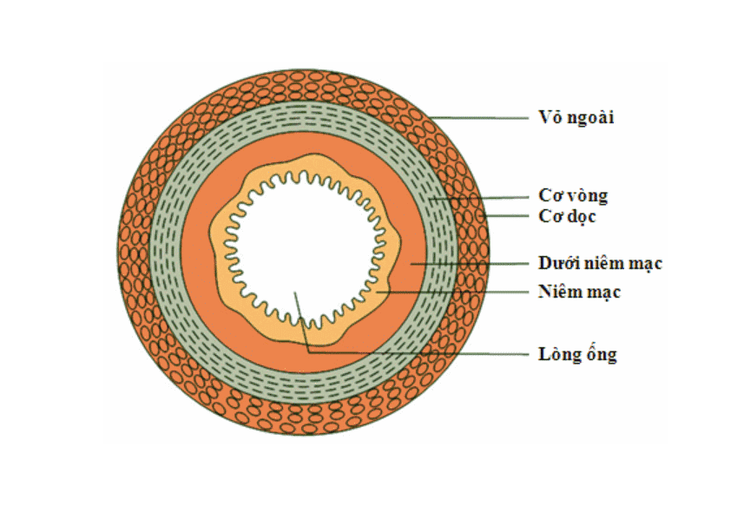
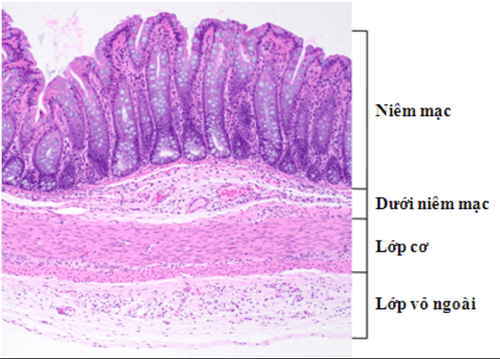
Hình 1: Cấu tạo thành ống tiêu hoá
3. Indications and contraindications
3.1 Indications According to the Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy of Japan, endoscopic treatment is recommended for the following cases:
Differentiated adenocarcinoma lesions, form without superficial ulceration and regardless of size, or adenocarcinoma with superficial ulceration, less than 3cm in diameter Undifferentiated cancer lesion, no superficial ulceration, less than 2cm in diameter 3.2 Contraindications Undifferentiated cancerous lesions, >2cm in diameter, or differentiated cancerous lesions, with superficial ulcers, >3cm in diameter Suspect acute coronary syndrome Uncontrolled hypertension Suspicion of hollow visceral perforation Suspicion of aneurysm or dissection Owner Patients with respiratory failure Patients with severe heart failure Patients with uncooperative mental disorders Relative contraindications: Decrease in systolic blood pressure <90mmHg.
4. Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
Advantages:
If submucosa is removed, the disease can be completely cured, and the patient's life time can be prolonged like other normal people. Minimal trauma; protect the gastrointestinal tract. Improve the quality of life for patients. The lesion can be used for pathology. Disadvantages:
Difficult technique, requires the endoscopist to be experienced and meticulous, precise in each operation.
5. Implementation process
The patient lies on the procedure table, is monitored with a monitor, according to the doctor's instructions , start marking the area to be cut and dissect the mucosa about 3-5mm from the lesion boundary Step 2: Injecting submucosa to inflate the mucosa containing the cancerous lesion Step 3: Create a cutting area around the lesion Step 4 : Cut off the submucosa, remove the lesion from the gastrointestinal tract Send the specimen to the pathology department to re-evaluate the entire lesion
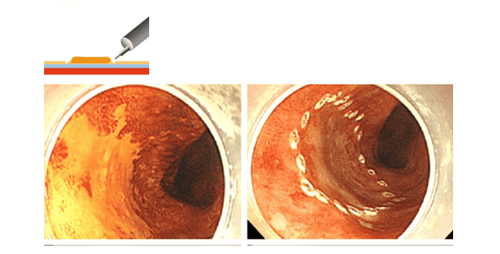
Hình 2: Đánh dấu quanh tổn thương để tạo ranh giới đường cắt giữa mô lành và mô ung thư
Hình 3: Tiêm dung dịch ưu trương vào lớp dưới niêm mạc để nâng tổn thương lên
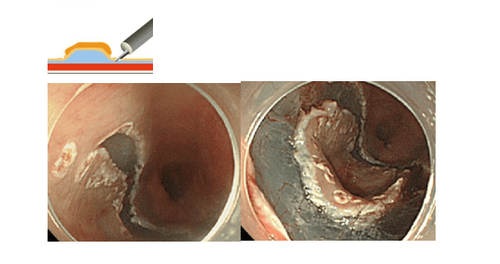
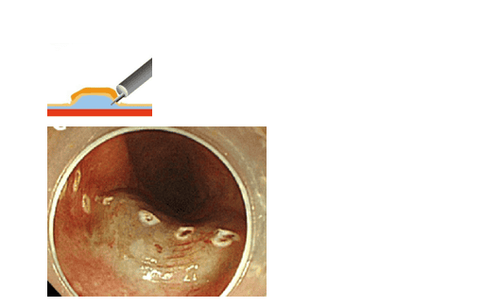
Hình 4: Tạo diện cắt vòng quanh tổn thương
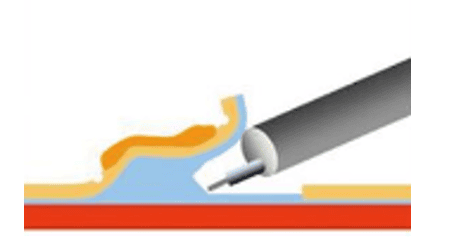
Cắt bóc tách lớp dưới niêm mạc để tách lớp dưới niêm ra khỏi tổn thương
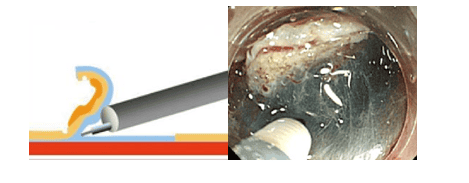
Hình 5: Việc cắt bóc tách đã gần hoàn thiện
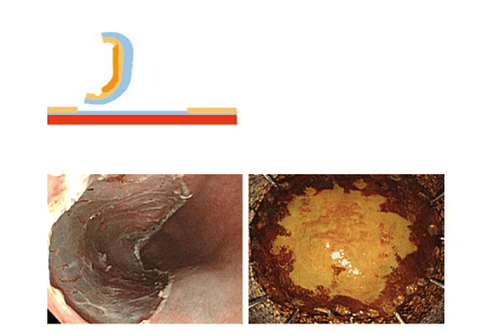
Hình 6: Hoàn thành việc cắt bóc tách lớp dưới niêm mạc
Source: Asano M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection and surgical treatment for gastrointestinal cancer. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2012; 4(10): 438-447
6. Can all early cancerous lesions be treated with this method?
Not all early cancer lesions to be treated with ESD method, according to the study of Japanese authors, for early gastric cancer, do not perform ESD with undifferentiated cancer lesions, >2cm in diameter, or differentiated cancerous lesions, with superficial ulcers, >3cm in diameter. But this case requires surgery to cure the radical.
Along with a team of well-trained doctors in early gastrointestinal cancer diagnosis and treatment, Vinmec Central Park Hospital is equipped with the most modern gastrointestinal endoscopy system of Olympus, one of the best The best machine companies today, including those being treated like the Olympus CLV 190 endoscope.
The advantage of endoscopes is that they have a narrow band of light (NBI), NBI endoscopic images have high resolution and contrast, making it easier to detect, screen and diagnose gastrointestinal cancer in early stage. Once the cancer is detected at an early stage, depending on the nature of the lesion, it will be cut by mucosal resection (EMR), or submucosal dissection (ESD) through flexible bronchoscopy, without having to undergo surgery.
Not only that, to ensure sterility of endoscopes, the hospital is also equipped with an automatic endoscope washing machine and RO water filtration system.
Customers can go directly to Vinmec Central Park to visit or contact hotline 0283 6221 166 for support.