This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Gastroenterologist, Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalEpigastric pain often has many causes, which can be gastrointestinal or extra-digestive. The information about epigastric pain below will provide some necessary knowledge about this issue, helping to orientate to deal with discomfort for yourself and your loved ones.
1. What is epigastric pain?
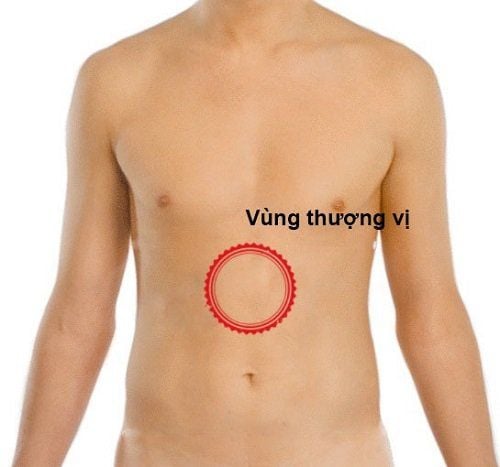
The upper epigastrium is limited below the nose of the sternum, below the umbilicus, and on both sides are the flanks.Epigastric pain is a very common symptom, sometimes it is just pain alone, but there are also epigastric pain combined with other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, belching, heartburn. However, not only gastrointestinal symptoms, epigastric pain can also be accompanied by cardiovascular symptoms such as shortness of breath, heaviness in the chest, leg edema, dry cough. Therefore, the causes of epigastric pain are very diverse and difficult to determine, depending on the accompanying symptoms and the patient's history to determine which is the main cause.
Vị trí vùng thượng vị trên cơ thể
2. What diseases can cause epigastric pain?
Depending on the characteristics of the pain, the location of the pain, the direction of spread, the progression, other accompanying symptoms and the ability to respond to the drug, it is possible to partially identify the pathology causing the epigastric pain.2.1. Stomach pain
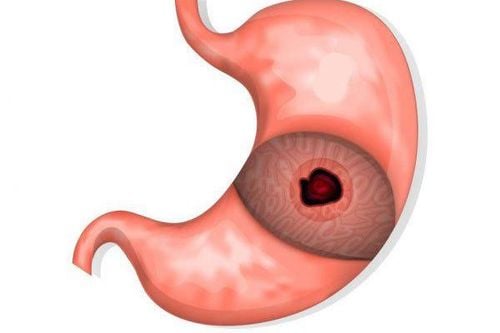
The most common is stomach pain in particular, digestive diseases in general. At this time, epigastric pain is of a meal-related nature, the pain will start and increase with hunger or after eating. People with this type of pain often have a habit of skipping meals, eating irregularly, eating a diet rich in sour and spicy substances, as well as regularly drinking alcohol, pain relievers, or experiencing stress and anxiety. In addition to the feeling of writhing pain in the area below the breastbone, they are accompanied by belching, heartburn, nausea, vomiting or nausea, discomfort.When the patient has a stomach ulcer (prepyloric), and chronic duodenal bulb can lead to pyloric stenosis, the dull pain often appears after eating, making the patient feel that he is not hungry. , indigestion, thereby adding anorexia, anorexia. The pain is only relieved if the patient vomits old food or it will last for a long time, causing discomfort, making the patient irritable, the face is always depressed and pessimistic.
2.2. Stomach perforation
Another complication of peptic ulcer is perforation of the stomach: epigastric pain is like a stabbing knife, the abdomen becomes hard as wood. The patient must lie down with his legs bent or sit with his back stooped. If punctured into a blood vessel, causing blood loss, shock and death can occur if not promptly operated.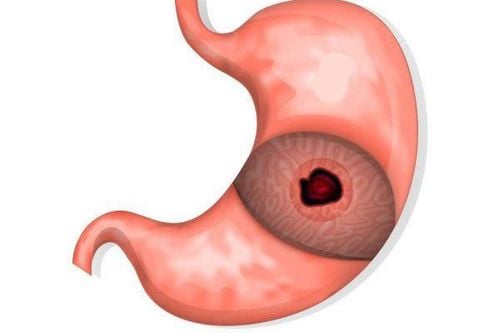
Thủng dạ dày có thể gây cơn đau thượng vị đột ngột
2.3. Diseases of the liver - bile
- Biliary colic: Pain in the right upper quadrant, or epigastrium spreading to the shoulder or to the back, may be accompanied by vomiting.- Acute cholecystitis or cholangitis: Fever, pain, jaundice...
- Liver abscess: Fever, pain, liver may be enlarged, liver fibrillation, painful intercostal pressure, possible sepsis, shock infection...
2.4. Acute pancreatitis
Continuous, severe pain in the epigastrium with vomiting, abdominal distension, possibly with fever.2.5 Chronic pancreatitis
Pain persists dull, the patient shows malabsorption syndrome, malnutrition.2.6. Other digestive diseases
- Food poisoning: sudden onset epigastric pain, pain relief after vomiting or defecation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension, accompanied by diarrhea. Previous eating history.- Food poisoning infection: Epigastric pain spreads throughout the abdomen, accompanied by high fever, loose stools with blood and mucus, can cause sepsis, septic shock.
- Appendicitis: may first be epigastric pain with mild fever before moving to the right iliac fossa. This is also a very often overlooked diagnosis.
2.7. Extra-digestive diseases
In addition, the viscera above the abdomen also cause epigastric pain such as the heart, lungs, pleura, mediastinum, aorta and even the diaphragm, the muscular layer separating the thorax and abdomen. Patients with severe heart failure, enlarged liver, and blood stasis also cause pain and tension in the epigastrium. Patients with posterior inferior myocardial infarction will present with epigastric pain with dyspnea, sometimes fainting instead of the usual left chest. If the patient has lower lobe pneumonia, lung abscess, diaphragmatic pleuritis, inflammation or mediastinal abscess, the diaphragm will also manifest with epigastric pain...However, with pain caused by Other organs are easy to miss, easily leading to serious complications if the patient has symptoms of belching, heartburn, nausea, and vomiting because of confusion with pain caused by digestive diseases. Even when damaged in the adjacent organs, the inflammatory response, the nerve pathway that stimulates pain also causes the patient to show similar gastrointestinal symptoms.
3. What to do when having epigastric pain?
Because the causes of epigastric pain are so diverse and rich that even doctors have to ask about the disease, examine it, and combine many factors, it is necessary to undergo a laboratory test to properly diagnose the disease, so it should not be subjective. . Because there are diseases that can be benign, repeated often, but there are also acute diseases that need intervention, if left late, there will be a risk of life.Accordingly, patients should come to be examined by a doctor, especially in cases where the pain first appears or the pain is severe or accompanied by fever, difficulty breathing, fainting. If the diagnosis is still in doubt or dangerous diseases need to be confirmed, the doctor will order appropriate tests and imaging, thereby helping to determine the cause and guide treatment.
4. How to prevent epigastric pain?
Although epigastric pain has many different causes, the most common treatment principle is to follow the instructions and treatment of the doctor. In addition, each individual needs to develop a balanced diet, correct diet, eat cooked and drink hot, limit hot spicy foods as well as quit smoking, limit alcohol. These things, if followed well, will be highly effective for the causes of epigastric pain, which are digestive pathologies.On the other hand, a reasonable lifestyle and rest, regular exercise and an optimistic lifestyle, reducing anxiety, reducing stress not only helps relieve symptoms of epigastric pain, but also good for heart health, general health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.