This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by BSCK I Nguyen Duc Tho - Anesthesiologist - Anesthesiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International HospitalAnd Specialist I Ho Quoc Tuan - Anesthesiologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
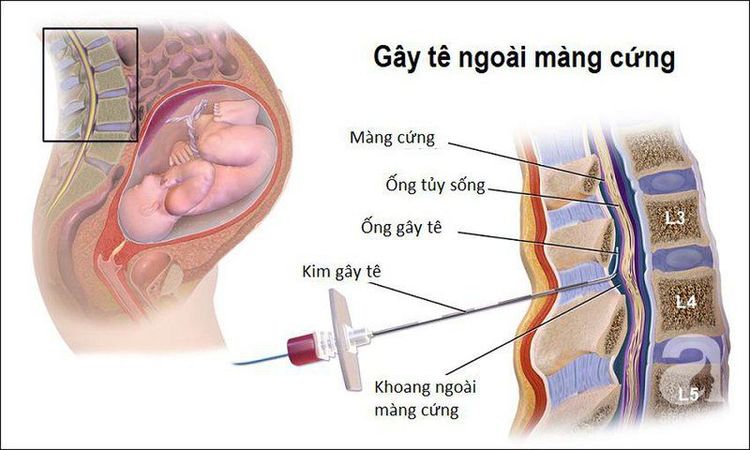
Epidural anesthesia is a technique that uses local anesthetics or drugs of the morphine family to be injected into the epidural space. The goal is to provide pain relief when the drug penetrates directly into the nerve root or specific receptor.
1. Method of epidural anesthesia
1.1. Advantages Create favorable conditions for surgery to take place; Provide additional anesthetic for prolonged surgery; Pain relief after surgery ; Recovery of bowel movements faster than anesthesia; Patients can breathe on their own, so there are fewer pulmonary complications, and less complications of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. 1.2. Cons There is a risk of failure; Slow onset of action; Possible neurological complications; Epidural catheters cannot be used in the absence of adequate monitoring facilities; High risk of infection.2. When is epidural anesthesia needed?
Absolutely contraindicated if:
The patient refuses to perform; Infection in the area of the skin that needs to be numbed with needles; Systemic infections, including blood or bacteremia; Blood clotting disorders; Increased intracranial pressure; Have an allergy to the anesthetic; Cardiovascular disease; Insufficient tools and means of resuscitation. There are also some relative contraindications, for example:
Infection near the area to be anesthetized; Lack of circulating volume; There are diseases of the central nervous system; Chronic back pain, or kyphosis.
3. Preparation steps
3.1. Performer Specialist Anesthesiologist and Resuscitation Officer. Physicians performing the procedure should wash their hands, wear gowns and gloves as they do during surgery.3.2. Kim Tuohy 18G media has a curved tip (which enables easy identification of the epidural space without perforating the dura); Standard epidural equipment kit: 15G primer needle, 20G medication needle, syringe, gauze, alcohol cup, hole punch,... all must be sterile. 3.3. Patient Sitting position: Back bent, chin resting in front of chest, arms crossed in front, legs stretched out on the table. This position is easy to do, but should not be chosen when hemodynamically unstable and local anesthetic is low; Lying on the side with a curved back: The spine is parallel to the table, the shoulders and pelvis are perpendicular to the operating table, the legs are bent, the thighs are bent in front of the abdomen, the head and neck are bent forward; Install a secure IV line and pre-infuse crystalloids.
4. Procedure
5. Monitoring and handling of accidents
Nerve damage Common if the anesthetic is above L1 due to the wrong puncture of the spinal cord, in rare cases, damage to the nerve roots.
Hypotension May be accompanied by bradycardia because local anesthetic paralyzes the sympathetic ganglia. Treatment is by intravenous fluid replacement and intravenous ephedrine 5 - 10 mg each time, repeated until blood pressure is normal. This is less common with drugs from the morphine family.
Intravenous injection Causes convulsions, coma, even stopping cough medicine benzodiazepines, midazolam or thiopental.
General spinal anesthesia Due to wrong puncture or wrong catheter placement in the spinal cord. Symptoms are hypotension, respiratory arrest, inhibition of cardiac nerve conduction, especially when using bupivacaine. This case needs to be detected early and treated quickly as emergency respiratory - circulatory arrest.
Catheter rupture in the dural space Care should be taken not to withdraw the catheter on the Tuohy needle or press the catheter excessively and suddenly to prevent the risk of catheter breakage, needle fracture.
Infection of the epidural space Must ensure that the entire technical procedure is absolutely sterile, especially when placing analgesia catheters after prolonged surgery.
Hematoma in the epidural space Blood vessel damage can cause severe back pain. This case requires MRI to diagnose and sometimes surgery to remove the hematoma.
Headache Occurs when a Tuohy needle is inserted through the dura or infected the epidural space. Treatment is by lowering the pillow, giving intravenous fluids, adding sedation or, if severe, sealing the perforation with autologous epidural blood pump.
Respiratory failure Need to monitor breathing, when less than 12 times / minute, treat with naloxone if using morphine or respiratory support.
Other complications: Vomiting, nausea, respiratory depression, cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest,... managed according to the protocol of the Ministry of Health.
In summary, epidural anesthesia is a regional method of anaesthesia, by introducing an appropriate amount of local anesthetic into the epidural space. The distribution of nerves in the epidural space divides into certain regions on the skin surface. Therefore, this technique will cause loss of sensation in some areas due to the nerves being absorbed by the anesthetic, creating favorable conditions for surgery and reducing postoperative pain.
Epidural anesthesia is the most effective pain relief method currently being applied, but in order to minimize the possible dangerous complications, pregnant women need to consider choosing a medical facility that ensures safety. guarantee, reputation to carry out this method of pain relief. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that strictly applies safe surgical anesthesia practice standards according to international guidelines. Vinmec has a team of experienced anesthesiologists and nurses, modern equipment such as: nerve detectors, ultrasound machines, Karl Storz's difficult airway control system, comprehensive anesthesia monitoring system GE's AoA (Adequate of Anesthesia) including monitoring of anesthesia, pain and muscle relaxation will provide high quality and safety, helping patients to have adequate anesthesia, not wake up, and do not have residual muscle relaxants after surgery.
Vinmec Health System is also proud to be the first hospital in Vietnam to sign with the World Anesthesiology Association (WFSA) towards the goal of becoming the safest hospital for surgical anesthesia in Southeast Asia.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.