This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Duc Thong - Anesthesiologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital. The doctor has 14 years of experience in the field of Anesthesia.Endotracheal anesthesia is an anesthetic method that involves placing an endotracheal tube for controlled breathing during surgery. Endotracheal anesthesia is indicated in endoscopic surgery to remove brain tumors under the tentacle, ventriculomegaly, craniocervical brain tumors or support brain tumor removal. Anesthesia - resuscitation should ensure against cerebral edema and avoid increased intracranial pressure.
1. Endoscopic surgery to remove brain tumor
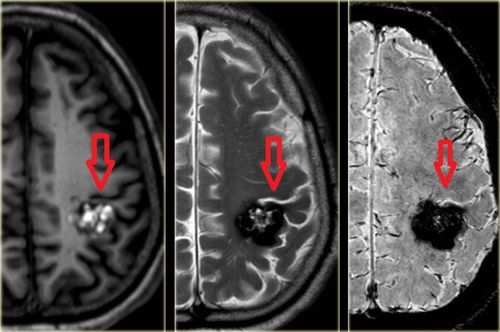
A brain tumor is a condition in which abnormal cells grow in the brain. Both benign and malignant brain tumors cause brain cell damage and even death.There are many methods of treating brain tumors such as: Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, ... in which surgery to remove brain tumors is the most basic treatment method in the treatment strategy of brain tumors.
The purpose of surgery is to completely remove the tumor, take a surgical specimen to diagnose the tumor's nature. Surgery to remove brain tumors mainly uses microsurgery glasses, however, microsurgery lenses are difficult to observe and evaluate tumors and surrounding healthy structures in hidden corners. Pulling too much to the tumor, healthy structures, blood vessels, nerves will damage the healthy tissue. Therefore, endoscopic support in these cases will help the surgeon better control and cut the brain tumor better.
2. Indications for endoscopic surgery to remove brain tumors
Tumors of the pituitary region: pituitary tumors, craniopharyngeal tumors, meningiomas, germ cell tumors, Rathke cysts, Epidermoid tumor, cutaneous tumor, cord tumor II... Tumor of cerebellar pontine area: Tumor VIII, cutaneous tumor, epidermoid tumor, cyst, brain stem tumor, nerve tumor VII, IX, X, XI, XII... Tumor in the occipital foramen tumour, in the base of the skull in the temporal region, in the ventricles . 2.2 Contraindications Contraindicated endoscopic brain tumor removal surgery in the following cases: Brain tumors that cannot be supported by endoscopy without space, such as intraparenchymal tumors (glioma) located deep in the brain parenchyma, brain metastases (located deep in the parenchyma), large brain tumors, extensive cerebral edema.
Contraindications to the use of assisted laparoscopy are relative. Large tumor, much edema, no space will be difficult to drill using endoscopic.
3. Endotracheal anesthesia endotracheal surgery to remove brain tumors
Indications for endotracheal anesthesia in endoscopic surgery to remove brain tumors under the tentacle, ventriculomegaly, craniocervical brain tumors or support brain tumor removal.
Contraindicated in the following cases:
The patient disagrees The medical facility does not have enough anesthetic and resuscitation facilities The technician is not technically proficient.
4. Endotracheal anesthesia procedure endoscopic brain tumor removal

The patient is asked to lie on his back, breathe 100% oxygen 3-6 l/min at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia.
Pre-anesthesia (if necessary)
Initiation of anesthesia:
Sleeping pills: Intravenous anesthetics (propofol, etomidate), volatile anesthetics (sevofluran, desfluran...). Painkillers: fentanyl, sufentanil, remifentanyl... Muscle relaxants: Succinylcholine, rocuronium, vecuronium... Conditions for endotracheal intubation: The patient sleeps deeply, with sufficient muscle relaxation. Gently manipulate, avoid stimuli that increase intracranial pressure. 4.2 Endotracheal intubation There are two techniques for intubation: oral and nasal.
Oral intubation technique:
Open the mouth, insert the laryngoscope to the right side of the mouth, move the tongue to the left, push the lamp deep, coordinate with the right hand to press the cricoid cartilage to find the epiglottis and the larynx subject. Pass the endotracheal tube gently through the glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes 2-3 cm through the vocal cords.

Choose the side of the nasal passage and instill vasoconstrictor drops (naphazoline, otrivin...). Select an endotracheal tube size smaller than that of the oral route. Insert an endotracheal tube lubricated with lidocaine grease through the nostrils Open the mouth, insert the laryngoscope to the right side of the mouth, move the tongue to the left, push the lamp deeply, coordinate with the right hand to press the cricoid cartilage to find the rod cap. glottis and glottis. Favorable case: insert the endotracheal tube gently through the glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes through the vocal cords 2-3 cm. Use Magill pliers to guide the tip of the endotracheal tube into the correct glottis; The assistant pushes the endotracheal tube from the outside in difficult cases. Gently withdraw the laryngoscope. Endotracheal balloon pump. Check the correct position of the endotracheal tube with auscultation and EtCO2 results Fix the tube with adhesive tape. In case of difficult intubation: apply the procedure of difficult intubation with a flexible endoscope. 4.3 Maintenance of anesthesia Maintain anesthesia with intravenous or volatile anesthetics, analgesics and muscle relaxants (if necessary). If cerebral edema is present, it should be managed by rapid intravenous infusion of Mannitol or corticosteroids. Control breathing by ventilator, maintain EtCO2 33-35 mmHg. Monitoring the depth of anesthesia based on heart rate, blood pressure, sweat, tears (PRST); MAC, BIS and Entropy ... and vital signs: heart rate, blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, body temperature.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.