This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by BSCK I Nguyen Xuan Tinh - Anesthesiologist - Resuscitation - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.The uterus is a part of the female body, where the fetus develops. Hysterectomy is a surgery indicated in some cases due to acute or chronic disease. Endotracheal anesthesia is an anesthetic method used in hysterectomy.
1. Endotracheal anesthesia in uterine surgery
Hysterectomy is indicated in pathologies such as bleeding, intrauterine tumor, genital prolapse... When a hysterectomy is performed, the patient is evaluated and the appropriate anesthesia method is selected. In which endotracheal anesthesia is a method of general anesthesia that the patient will sleep during the surgery.
Endotracheal anesthesia in hysterectomy is a method of general anesthesia, with endotracheal intubation for the purpose of breathing control during surgery and the recovery process after surgery.
2. Indications and contraindications
2.1 Designation
In hysterectomy due to causes such as fibroids with large size or abnormal bleeding, endometrial cancer ... or in emergency obstetrics. When controlling breathing for patients with masks, it is difficult. The patient is maintained under anesthesia with an inhalation anesthetic.

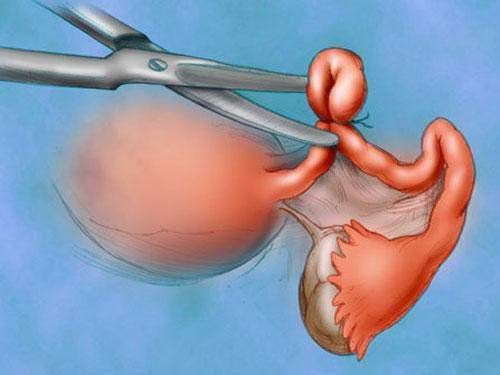
Bệnh nhân u xơ tử cung được chỉ định phẫu thuật cắt tử cung
2.2 Contraindications
Patient refuses to use endotracheal anesthesia. Insufficient facilities for anesthesia and resuscitation and technical incompetence.
3. Endotracheal anesthesia procedure in hysterectomy
3.1 Preparation
Performer: Doctor, nurse specializing in anesthesiology and resuscitation. Facilities: Anesthesia machine system with ventilator; hand squeeze oxygen source; monitor vital functions including electrocardiogram, arterial blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, temperature, breathing rate; defibrillator, phlegm aspirator. Laryngoscope, endotracheal tube of different sizes, suction tube, mask, squeeze balloon, oropharyngeal cannula, Magill pliers, soft mandrin. Medicines: Prepare drugs used in anesthesia resuscitation and handling of accidents. Other means for prevention in case of difficult intubation: Cook tube, laryngeal mask, tracheostomy kit, flexible bronchoscope, mouth opener... Patient: Full anesthesia examination before surgery, detection and prevention of the risks of possible complications. Advice and explanation of possible complications during hysterectomy anesthesia. Evaluation of cases at risk of difficult intubation. Use sedation the night before surgery if the patient is too nervous.
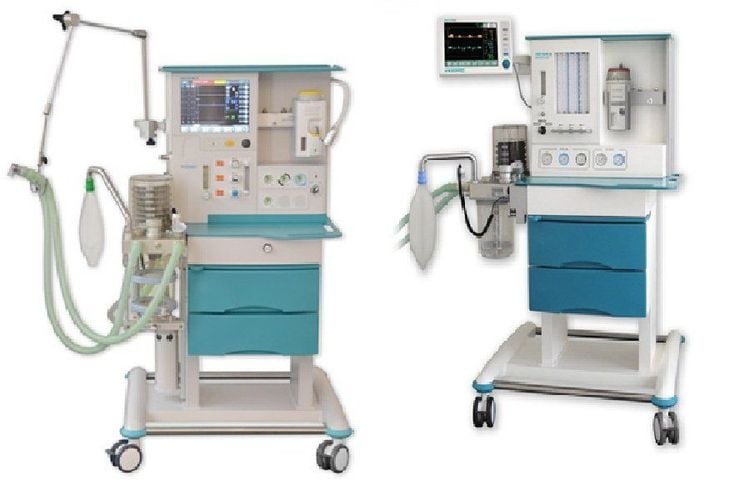
Hình ảnh máy gây mê kèm máy thở
3.2 Steps to take
Patient:
Patient position: Lie on your back, give 100% oxygen 3-6 l/min at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia. Install a tracker to monitor vital signs. Establish effective communication. Pre-medication. Anesthesia:
Can induce anesthesia with intravenous anesthetics such as propofol, etomidate... inhalation anesthetics or a combination. Combine some drugs to increase the effect of anesthetics such as: Opioid pain relievers, muscle relaxants if needed. Prophylaxis of reflux with H2-receptor antagonists and metoclopramide. Oral intubation: Conditions for endotracheal intubation when the patient is in deep sleep, with sufficient muscle relaxation in the vast majority of cases.
Open the patient's mouth, put one hand under the neck to help straighten the neck, put the laryngoscope to the right of the mouth, push the patient's tongue to the left, push the lamp deep down, coordinate with the right hand to press the cricoid cartilage and find epiglottis, orifice. Perform rapid induction of anesthesia and the Sellick maneuver in cases of full stomach.
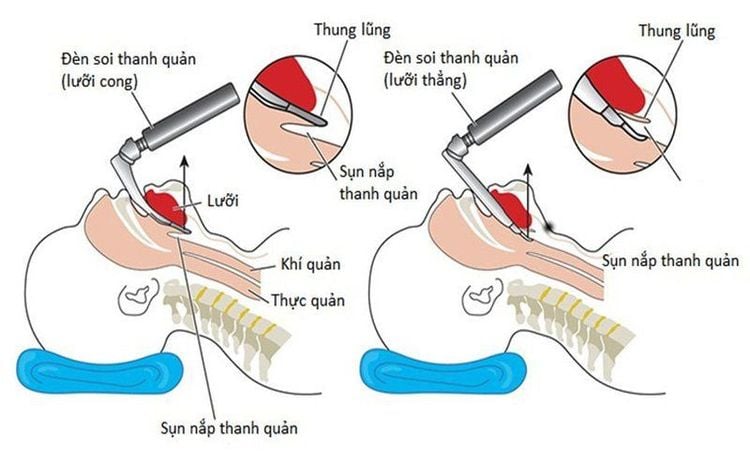
Kỹ thuật đặt nội khí quản từ đường miệng trong gây mê nội khí quản trong phẫu thuật cắt tử cung
Pass the endotracheal tube gently through the glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes about 2-3 cm across the vocal cords. Remove the laryngoscope and inflate the endotracheal balloon. Check after removal of the light for the correct position of the endotracheal tube by listening to the lungs and EtCO2 results. Fix the tube with adhesive tape and place the cannula in the mouth to avoid biting the tube (if necessary) In case the patient is intubated Difficulty in tracheal intubation, difficult endotracheal intubation procedure is required. Maintenance of anesthesia: Maintaining anesthesia can use intravenous or volatile anesthetics, analgesics and muscle relaxants (if necessary).
Monitor:
Need to control breathing with ventilator or hand squeeze. Monitor the depth of anesthesia based on heart rate, arterial blood pressure, sweating, tearing... Preventing cases of endotracheal intubation in the wrong position, folding, or obstruction.
3.3 Standards for extubation
When the surgery is completed, the endotracheal tube should be removed when the following criteria are met:
The patient is awake, following orders; Raise the head for more than 5 seconds, TOF > 0.9 if present; The patient can breathe on his own and the respiratory rate is within normal limits; Stable pulse and blood pressure; Body temperature > 35 degrees Celsius; There were no complications from anesthesia or surgery.

Khi huyết áp người bệnh ổn định có thể rút ống nội khí quản
4. Complications and management of complications due to intubation
4.1 Reflux of gastric juice into the airway
Signs: There is digestive fluid in the oral cavity and airways. Treatment: Drain the fluid, lie down with the head low, tilt the head to one side; Rapid endotracheal intubation and clear airway drainage; Monitoring and prevention of lung infections after surgery
4.2 Hemodynamic disorders
Hypotension or hypertension , arrhythmia (bradycardia, tachycardia, arrhythmia). Depends on the treatment.
4.3 Complications due to intubation
Unable to intubate the endotracheal tube; Re-intubate for difficult intubation or switch to another method of anesthesia. Misplaced in the stomach: Signs: Auscultation of the lungs without alveolar murmurs, no measurement of EtCO2. Treatment: Reinsert the endotracheal tube. Vocal, air, bronchospasm Difficult or no ventilation, auscultation with crackles or muted lungs Management: Provide adequate oxygen, add hypnotics and muscle relaxants, ensure ventilation and give bronchodilators and corticosteroids ; If breathing is not controlled, a difficult endotracheal intubation procedure should be used. Trauma during endotracheal intubation: Bleeding, tooth fracture, vocal cord injury, foreign body falling into the airway... Diagnosis and treatment on a case-by-case basis.
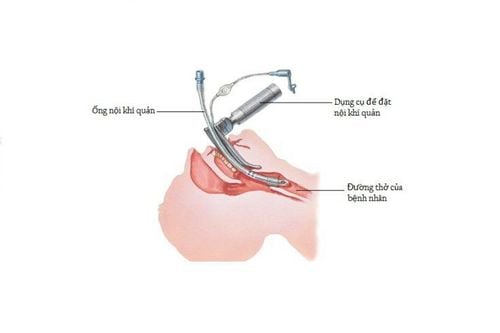
Bệnh nhân không đặt được ống nội khí quản phải chuyển sang phương pháp vô cảm khác.
4.4 Respiratory complications
Folding, retracting, causing the endotracheal tube to be pushed deep into one lung, lowering or opening the respiratory system, running out of oxygen...
Treatment: Need to immediately ensure ventilation and provide 100% oxygen, solve reason.
4.5 Complications after extubation
Respiratory failure after extubation due to many causes. Sore throat hoarse voice. Constriction of the vocal cords, trachea, and bronchi. Inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. Narrow larynx, trachea. Treat the patient on a case-by-case basis and on a case-by-case basis.
Hysterectomy has many surgical options such as laparoscopic surgery, transabdominal surgery or robotic surgery. The appropriate surgical method is indicated on a case-by-case basis.
During surgery and when endotracheal anesthesia in hysterectomy surgery can cause some complications, it is necessary to choose reputable sites to limit the risk of complications.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Doctor Nguyen Xuan Tinh has more than 18 years of experience studying and working in the field of Anesthesia - Resuscitation. Before working as an anesthesiologist at the Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital, Dr. Tinh worked for a long time at Cam Xuyen Tinh District General Hospital, Ha Tinh.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.