This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc, BS. Dang Manh Cuong - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has over 18 years of experience in the field of ultrasound - diagnostic imaging.1. What is Endoscopic Ultrasound?
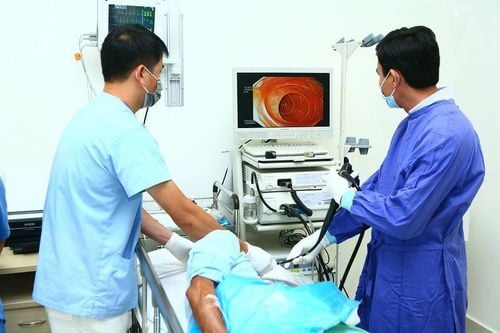
Endoscopic ultrasound is a technique that combines both endoscopic and ultrasound procedures at the same time, in which the ultrasound probe is applied to the lesions arising when the doctor needs to explore through the endoscope such as: Injury to the wall of the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas and biliary tract.Endoscopic ultrasound is considered as one of the most important achievements in the digestive field in recent years.
Endoscopic ultrasound differs from conventional flexible bronchoscopes in that: Conventional flexible bronchoscopy helps doctors to observe and evaluate the surface of the patient's gastrointestinal tract, but it does not allow identification of the invasion of lesions as well as abnormalities located below the epithelial lining. Therefore, with the endoscopic method, the technique has attached to the end of the endoscope a probe that can conduct ultrasound examination from within the gastrointestinal tract.

2. When is the patient indicated for endoscopic ultrasound?
2.1 Diagnose abnormalities in the submucosa of the gastrointestinal tract Differentiate a lesion from the gastrointestinal tract wall or from the outside Assess the size and structure of the tumor Assess the size of the gastric mucosal folds Diagnose varices in the esophagus and stomach Staging of gastrointestinal tumors Diagnose some pathologies of the pancreas and biliary tract Evaluate the stages of cancer Determine the location of endocrine tumors Find stones and worms in the common bile duct 2.2 Other indications Evaluation of treatment outcomes for varices Inflammatory bowel disease Esophageal motility pathology Benign healing ulcer Assessment of ulcer bleeding risk Pseudocyst drainage pancreatitis under the guidance of SANS Chronic pancreatitis Fine needle aspiration under the guidance of SANS Diagnosis and classification of cancer Destruction of the visceral plexus for pain relief Esophageal spasms .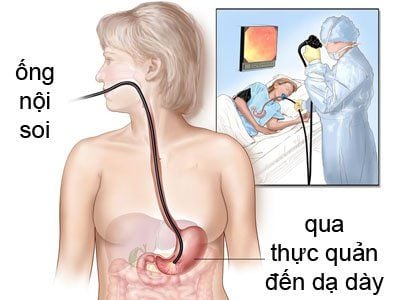
3. Instruments to prepare for endoscopic ultrasound indication
Endoscopic ultrasound machine, suction machine, light source, monitor, mouthpiece Pulse monitor, blood pressure monitor, spO2 Medication Seduxen, buscopan, midazolam, fentanyl or propofol 01 gastroenterologist, 1 nurse, 1 Anesthesiologist Endoscopic ultrasound machine used in gastrointestinal diagnosis with Radian transducer with frequencies of 7.5MHz, 10MHz, 12MHz.4. Endoscopic ultrasound procedure
Before performing ultrasound endoscopy, the patient is required to fast for 6 hours before the procedure, the patient will be seen by the anesthesiologist first to explain the benefits and risks of the procedure and agree.Give the patient an anti-foam Simethicone 30 minutes before the test.
Steps to take
The nurse needs to prepare and check the scope. After anesthesia, place the patient on the left side and place the mouthpiece between the two dental arches. Anesthesia method: Use anesthesia with seduxen or midazolam/fentanyl for intravenous or endotracheal anesthesia depending on the case. Must monitor pulse, blood pressure, temperature, breathing rate.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
LEARN MORE
Value of endoscopic biliary ultrasound Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatitis (ERCP): What you need to know Endoscopic ultrasound for gastrointestinal cancer screening