This is an automatically translated article.
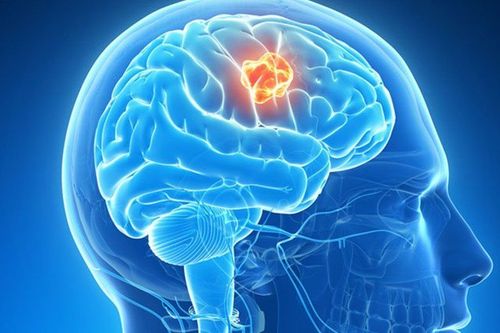
Craniopharyngioma is one of the rare benign tumors among craniofacial diseases. The most common treatment for craniopharyngeal tumors is craniopharyngeal surgery to remove the tumor from the patient's skull. This is not only a treatment measure but also must be combined with a number of other methods to have the most optimal treatment effect.
1. Is craniopharyngioma dangerous?
Craniopharyngioma, also known scientifically as Craniopharyngiomas, is a benign tumor in the cranium, with a very low rate of cranial diseases, about 2-%- 4%. Craniopharyngioma belongs to the type of squamous epithelial tumor, the growth rate in the patient is very slow and localized along the hypothalamic pituitary gland, around the nerve and vascular organization of the anterior skull base. Benign craniopharynx is located very close to the skull and the structure of the tumor is a solid structure, consisting of calcium fragments, possibly containing fluid within the tumor. Benign craniopharynx is most common in children, accounting for about 50% of all cases, and can be found in both boys and girls. Some cases of craniopharyngioma may also occur in elderly people with signs of decline or memory loss.Craniopharyngioma includes 2 main clinical forms as follows:
Craniopharyngeal tumor in enamel: The tumor has two main parts, solid and cystic. The solid part is calcified and the cystic part is the presence of cholesterol crystals. Enamel craniopharyngioma is more common in children than in adults. Papillary craniopharyngioma: This is a benign tumor of the cranial cavity that is common in adults. The structure is similar to craniopharyngioma of the enamel body, but the part is more dense and less calcified than the enamel body. Because the disease develops quite slowly, in the early stages of the disease, about 1-2 years, there are no obvious clinical symptoms. After this time, the tumor grows gradually, so some symptoms of craniopharyngeal tumor appear. The symptoms of the disease depend on the location of the tumor, but there are still some common symptoms such as:
Headache that does not respond to pain relievers. Vision is partially lost. Change in personality, sudden mood, easy to express emotions such as irritability, anger... Difficulty sleeping or insomnia, leading to a state of weakness, body fatigue. Nausea, especially early in the morning. Urinating frequently and frequently. For infants with craniopharyngioma, there may be signs of an abnormally large head. Constantly losing balance when moving, so it is easy to fall. Signs of depression Coma Although considered a benign pathology, the location of craniopharyngeal tumors is usually near the thalamus, pituitary gland, and important blood vessels and nerves of the brain, so the tumor is benign. Pharyngitis is considered a rather dangerous disease, although it progresses slowly, there is still a risk of recurrence and dangerous complications if not thoroughly treated.
2. Craniopharyngiary surgery
Phẫu thuật để điều trị u sọ hầu hoặc kết hợp giữa xạ trị và tiểu phẫu cần thiết
There are many ways to treat craniopharyngioma such as craniopharyngioma surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy, or a combination of radiation therapy and necessary minor surgery. In particular, craniopharyngioma surgery is one of the methods to treat craniopharyngeal tumors with a very high cure rate, preventing recurrence after treatment.
However, because craniopharyngeal tumors are often located in dangerous locations such as near the pituitary gland, the carotid artery, and around the tumor, there is optic interference and other important nerves, so surgery Craniopharyngioma requires extensive expertise in this field as well as adequate operating room equipment.
A very important note when treating craniopharyngioma by surgical method is that it is necessary to survey the endocrine system indicators of the patient before and after surgery to closely monitor the disease status. such as adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism caused by craniopharyngioma. After surgery, it is necessary to appoint magnetic resonance imaging of the skull to assess whether surgery has completely removed the tumor, if necessary, there will be indications for continued treatment with radiation therapy.
Indications of craniopharyngioma surgery include the following cases:
Craniopharyngeal tumor at the pituitary fossa location, above the pituitary gland, Craniopharyngeal tumor at a position above the pituitary gland and the lower half of the 3rd ventricle so that the entrance can be wide enough to reach the tumor. Contraindications of surgical methods are:
Craniopharyngeal tumors located outside the carotid artery at a distance of 10 mm. Craniopharyngioma in the position of the frontal horn. Craniopharyngioma is located in the lateral ventricles, or distant from the sphenoid sinus of the skull. Steps to perform craniopharyngioma surgery include:
Place the patient in a supine position, with the head straight and the chin tilted to the right, and at the same time maximally supine and fixed on the Mayfield frame. Administer anesthesia with endotracheal anesthesia on the patient. Install nerve locator Clean the nasal area and put Meche impregnated with Naphazolin solution to help the nasal tip to be more elastic. Disinfect the surgical area on the patient. Place the optic and expose the anterior sphenoid sinus. Use a drill and trigger to open the sinus wall. Sinus mucosal burning. Open the floor of the pituitary, dura and arachnoid. Practice removing the tumor from the patient's skull using Curette, Pince and a straw. Care should be taken to remove tumor sections one at a time and be careful with adjacent sensitive sites such as the pituitary stalk, basilar artery, or optic nerve. Stop bleeding. Use thigh fat to fill the surgical site. Use a thigh scale to fill the dura. Using nasal septum, septal bone... and bio-glue to reconstruct the pituitary floor. Fill the surgical site by covering the nasal mucosal flap. Use diluted Betadine with saline serum to wash the surgical site. Use 2 Meche Merocel to place 2 stitches. After surgery, patients need to be aware of a number of issues such as:

Sau phẫu thuật bệnh nhân cần lưu ý một số vấn đề theo chỉ dẫn của bác sĩ
Monitor vital signs closely, including pulse, breathing rate, blood pressure and temperature. Monitor consciousness, pupils, and urine as well as electrolytes regularly. Apply 3rd generation antibiotics at 1 week after surgery. In case the patient has signs of hypopituitarism, it is necessary to prescribe corticosteroids and endocrine therapy drugs. If the patient has signs of bleeding, it is necessary to stop the bleeding and operate to remove the hematoma. In the case of ventricular dilatation after surgery, apply ventricular drainage through the abdomen or out as soon as possible. If cerebrospinal fluid leak, it is necessary to drain, re-operate and suture the fistula. Patients with signs of infection should be treated with appropriate antibiotics. Craniopharyngioma is a benign disease, but because the location of the tumor is quite dangerous and involves sensitive parts such as blood vessels and cranial nerves, surgery for craniopharyngeal tumors is very difficult. Ask the operator to have a lot of experience. In addition, this method of treating craniopharyngeal tumors also requires necessary equipment and should be performed in reputable medical facilities to be able to promptly handle complications that occur during and after surgery. surgical procedure, providing the highest therapeutic effect.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
MORE
Is mediastinal tumor dangerous? Mediastinal tumor removal by open surgery How to treat mediastinal tumor?