This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Tong Van Hoan - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.Emergency pleural ultrasound is an imaging technique with high sensitivity and specificity, which plays a very important role in the diagnosis and treatment of pleural diseases today.
1. What is an emergency pleural ultrasound?
Pleural ultrasound is an imaging technique with the aim of detecting and evaluating the properties of pleural fluid, estimating the amount of fluid, guiding thoracentesis, pleural biopsy, and evaluating nodular lesions. or pleural mass. This method has long been applied in examining the chest wall, pleura, mediastinum, lung parenchyma,... In addition, pleural ultrasound is also used to diagnose early cases of pneumothorax. without a chest X-ray.Advantages of pleural ultrasound are: No radiation dose, compact equipment, can be performed at the bedside in critically ill patients, emergency patients, can be repeated many times, time fast examination time and low cost. However, this method also has the limitation that the image resolution depends on the device; The images are not objective, are operator dependent and can make analysis of some ultrasound images difficult.
Siêu âm màng phổi giúp phát hiện bất thường
2. Indications/contraindications
Detect and evaluate pleural effusion, especially in case of suspected purulent, hemothorax due to pathology or after procedures with risk of effusion; Clarifying the nature of opacities in chest wall or pleura such as tumor, fluid; Differential diagnosis of pleural effusion or localized subdiaphragmatic fluid, assessment of diaphragm mobility; Detection and assessment of pleural thickness, pleural tumor, lung tumor invading the chest wall; Guidelines for puncture, drainage and pleural biopsy; Detect, monitor complications, progress of pneumothorax.
Siêu âm giúp đánh giá tình trạng tràn dịch màng phổi
3. Perform emergency pleural ultrasound technique
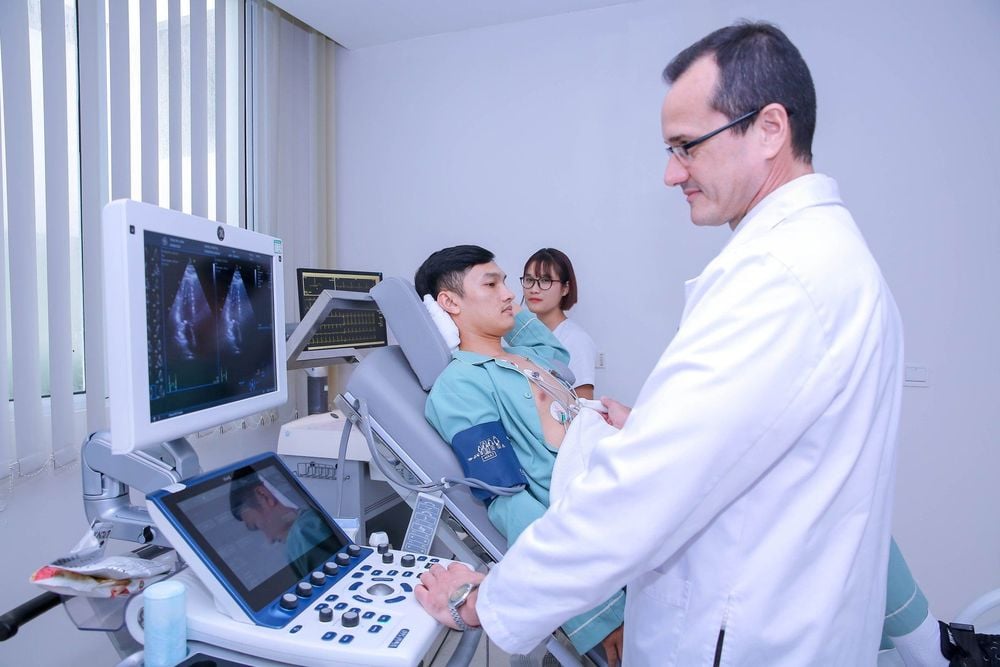
3.1 Preparations Performers: Radiologists; Means of use: 2D ultrasound machine with 3.5 MHz frequency probe and acoustic gel; Patient: Have a standard posture, expose the area to be ultrasound. The patient should have his/her record checked (history, medical history, invasive procedures performed) and physical examination. Sitting position: Place the ultrasound probe in the intercostal spaces, helping to examine the pathology of the chest wall, pleura and detect small pleural effusion. Lying position: Examine the pleura at the lateral and posterior costal angles, the basal lung parenchyma and take the liver as an ultrasound window, evaluate the diaphragm and pleura.
Máy siêu âm
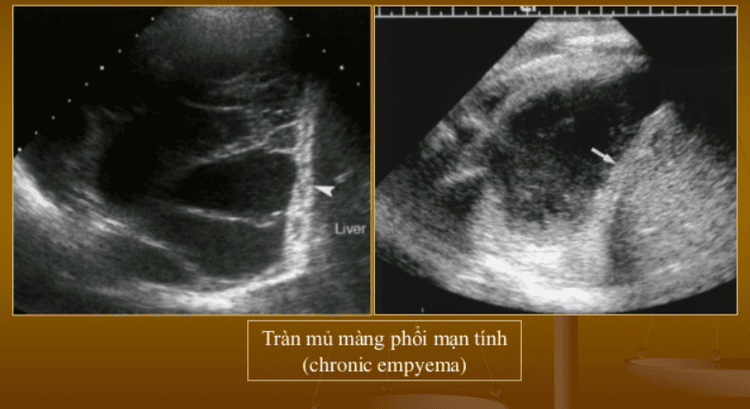
Siêu âm màng phổi
Emergency pleural ultrasound is a method capable of diagnosing chest wall pathology, pleural effusion, pleural thickening, pleural tumor, pneumothorax, assisting in locating and orienting puncture, biopsy , drainage,... Patients who are assigned to perform pleural ultrasound need to coordinate well with their doctors to obtain accurate diagnosis results, which will provide good support for future treatment.
Master. Doctor Tong Van Hoan has 10 years of experience in the field of Emergency Resuscitation, is capable of performing difficult techniques in Emergency Resuscitation such as advanced mechanical ventilation, continuous and intermittent dialysis, plasma exchange. , difficult airway intervention, hemodynamic monitoring by PiCCO, advanced cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ACLS), emergency bedside ultrasound, echocardiography...
Customers can go directly to the Health system Vinmec nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
MORE:
Diagnosing septic shock Diagnostic tests for pleural effusion When does septic shock occur?