This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Doctor Nguyen Ngoc Phuong Nam - Emergency Medicine Doctor, Emergency Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Acute hemodynamic pulmonary edema is an urgent emergency, causing acute respiratory failure if detected, diagnosed early, treated promptly, the disease has the ability to recover quickly. If not treated promptly, it will quickly lead to severe acute respiratory failure, high risk of death.
1. Causes of acute hemodynamic pulmonary edema
A sudden increase in intraluminal fluid pressure that allows plasma to escape into the interstitial and alveolar spaces without anatomically damaging the alveoli. Usually the following causes lead to this acute pulmonary edema:Cardiovascular disease Valve disease, especially mitral and aortic valve disease. Hypertensive crisis (especially due to adrenal myeloma). Myocardial infarction Myocarditis Severe heart failure Noncardiac disease Renal disease, most commonly glomerulonephritis: Acute glomerulonephritis in children (due to increased blood volume). Chronic glomerulonephritis in adults: end-stage renal failure or hypertension. Procedures: too fast pleural puncture, too much fluid and too fast
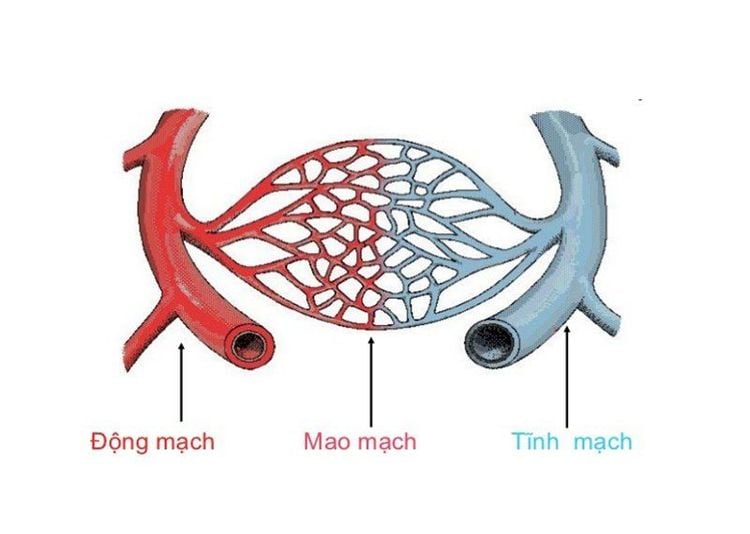
Phù phổi cấp huyết động là do sự tăng đột ngột áp lực dịch trong lòng mao mạch
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để có một lá phổi khỏe mạnh?
Để nhận biết phổi của bạn có thật sự khỏe mạnh hay không và làm cách nào để có một lá phổi khỏe mạnh, bạn có thể thực hiện bài trắc nghiệm sau đây.2. Identification signs
Shortness of breath Irritated, struggling, perspiring Patient sits and breathes. Rapid breathing rate, nose flaps, breathing effort, respiratory muscle contractions. If the progression is severe, you may be lethargic, slow breathing. Cardiovascular manifestations Initially, the patient showed a lot of cough, dry cough, then spit out a lot of pink foam. When the doctor listened to the lungs, there was a small grainy crackle at the bottom of the lung, later on a loud crackle throughout both lung fields.
3. Subclinical
Patients need to do some tests including:
Complete blood count X-ray Cardiopulmonary Blood Gases Electrocardiogram (ECG) Echocardiogram to diagnose heart disease, evaluate myocardial contractile function Urinalysis if acute glomerulonephritis is suspected Tests to evaluate heart failure, kidney function...

Bệnh nhân thực hiện các xét nghiệm cận lâm sàng để chẩn đoán tình trạng bệnh
4. Handling
Initial supportive measures
Provide adequate oxygen Keep patient in semi-sitting position Drug administration
Morphine sulphate : Morphine is given intravenously 2-5mg each time and repeated after 10-25 minutes if until it takes effect. Furosemide: Initial dose of 20-40 mg IV, then may be increased and repeated after a few minutes until an adequate response is obtained. The dose may be increased to a maximum of 2000mg. Nitroglycerin: An intravenous infusion is recommended at a starting dose of 10 mg/min and gradually increased according to response. Nitroprusside: The starting dose is 0.25 mg/kg/min. Inotropic agents are indicated after the above initial measures and in patients with low blood pressure or cardiogenic shock.
Mechanical ventilation
Non-invasive mechanical ventilation (breathing mask) is used immediately if acute dyspnea develops rapidly. Non-invasive mechanical ventilation improves dyspnea and reduces the risk of intubation. Closely monitor the patient's shortness of breath. Mechanical ventilation intubation (Invasive mechanical ventilation): Will be done immediately if the initial state is lethargic, comatose, cyanotic. Or non-invasive mechanical ventilation fails to improve respiratory failure and clinical course worsens.
Đặt nội khí quản thở máy khi bệnh nhân có tiến triển xấu đi
Acute hemodialysis or ultrafiltration
Indicated in patients with kidney disease or unresponsive to diuretics, medical drugs. Hemodynamic monitoring
For severe and critical conditions and patient monitoring, hemodynamic indicators must be monitored by more modern machines to promptly correct disorders. Notice and address possible causes of hemodynamic pulmonary edema. Common causes of acute hemodynamic pulmonary edema are:
Hypertension. Acute myocardial infarction or acute coronary artery disease. Acute valvular regurgitation (due to myocardial infarction, endocarditis ...) Myocarditis, cardiomyopathy... Newly occurring cardiac arrhythmias or volume overload (excessive fluid infusion) in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. Acute pulmonary edema is a life-threatening medical emergency if not detected early and treated promptly. Therefore, when seeing abnormal signs, especially for patients with cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease,... It is necessary for the patient to immediately go to a medical facility for examination and treatment. timely treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.