This is an automatically translated article.
Gastrointestinal bleeding is a very dangerous complication of portal hypertension. Depending on the patient's condition and the professional ability of the medical facility, the mortality rate of this disease can range from 20 to 80%.
1. What is gastrointestinal bleeding due to portal hypertension?
Gastrointestinal bleeding is a condition in which blood in the blood vessels of the gastrointestinal tract escapes out of the lumen, causing vomiting or bloody stools. This is a disease that requires emergency treatment including surgical and medical treatment.
Before starting treatment, the patient first needs to be identified with upper or lower gastrointestinal bleeding, then the doctor will evaluate the level of gastrointestinal bleeding, in order to give appropriate treatment. Based on the evaluation indicators, gastrointestinal bleeding is classified into 3 levels:
Grade I (Mild): Pulse <100l/min, blood loss <500ml (10%), HC >30%, Hct > 3 million/mm3, systolic blood pressure >90 mmHg. The patient is alert and only slightly tired. Grade II (Moderate): Pulse > 100 - 120l/min, blood loss <1500ml (30%), HC <20-30%, Hct 2 - 3 million/mm3, systolic blood pressure between 80 - 90mmHg . Patients present with symptoms of dizziness, excessive sweating, blue skin, pale mucous membranes, little urine. Grade III (Severe): Pulse >120l/min, blood loss >1500ml (30%), HC <20%, Hct 2 million/mm3, systolic blood pressure <80mmHg. Patients present with fainting, lethargy, or panic attacks. Accordingly, gastrointestinal bleeding due to portal hypertension is the rupture of varicose veins of the stomach or esophagus causing bleeding. This is a medical-surgical emergency that ranks first in terms of severe bleeding.
2. Causes of portal hypertension
There are many causes of portal hypertension leading to gastrointestinal bleeding, but mainly related to the liver:
Pre-hepatic causes: due to compression or narrowing such as congenital portal atrophy; portal vein thrombosis (accounting for 1⁄2 of all cases of portal hypertension in children); portal vein cavernous change; portal vein stenosis due to obstruction or tumor compression. In addition, portal hypertension can also occur due to the source from the spleen (tropical splenomegaly, visceral arteriovenous fistula,...) Intra-liver causes: mostly due to cirrhosis (in addition to cirrhosis). The biggest cause is alcohol, other causes leading to cirrhosis can be mentioned as viral hepatitis, long-term cholestasis, schistosomiasis, protein deficiency malnutrition). Post-hepatic causes: Budd-Chiari syndrome (Budd-Chiari Syndrome/BCS), diseases caused by right heart failure; malignant tumors in the liver or on the liver pressing on the hepatic veins, constrictive pericarditis, ...
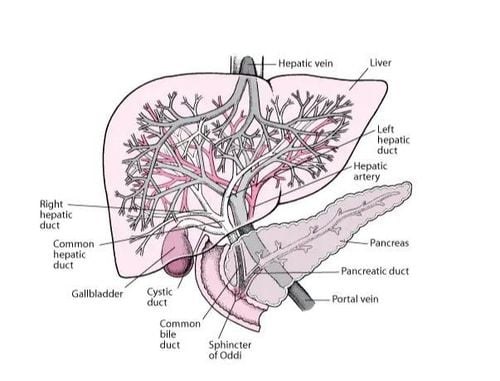
Có nhiều nguyên nhân gây tăng áp lực tĩnh mạch cửa
3. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal bleeding due to portal hypertension
3.1. Clinical diagnosis Patient has a history of cirrhosis, gastrointestinal bleeding; There are symptoms of vomiting blood, passing black stools; Appearance of clinical symptoms of cirrhosis; Clinical symptoms such as acute anemia, hypovolemic shock. 3.2. Laboratory tests: baseline Coagulation level: PT% (Prothrombin Time); Blood biochemistry: AST, ALT, Bilirubin TP, urea, creatinine, glucose, electrolytes; Peripheral blood count: TC, BC, Hb, HC; Gastroesophageal endoscopy. 3.3. Definitive diagnosis Conduct esophagogastroduodenoscopy to detect ruptured varicose veins of the stomach and esophagus.
3.4. Differential diagnosis Differential diagnosis is required from other causes of gastrointestinal bleeding, including:
Peptic ulcer; Vascular malformations; Hemorrhagic laceration (Mallory-Weiss syndrome); Bleeding of the biliary tract; Gastroesophageal polyp bleeding; Hemoptisi . SEE ALSO: Surgical treatment of portal hypertension

Ho ra máu là dấu hiệu xuất huyết tiêu hóa do tăng áp lực tĩnh mạch cửa
4. Treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding due to portal hypertension
Treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding due to portal hypertension is as follows:
4.1. Principles of treatment Restore circulating volume and prevent shock; Gastroesophageal endoscopy (with hemostatic intervention); Prevention of complications: hepatic pre-coma, hepatorenal syndrome, ascites infection. 4.2. Specific treatment Place an intravenous line, place the patient's head low and give oxygen; Perform endoscopic hemostasis as soon as possible; Transfusion of red blood cells if anemia; Drugs to reduce portal pressure; Continuous intravenous infusion from 2 days to 5 days: If the patient's stool is yellow, stop the infusion. If after 5 days there is still bleeding, you should also stop the infusion because it is not effective; Intestinal antibiotics: Flagyl, Ciprobay 0.5g x 2 tablets / day (7 consecutive days), neomycin oral tablet (if the patient can take it). In case it is not possible to drink, use prophylactic antibiotics by injection; Oral lactulose: dosage is 20 to 50g/24 hours or enema; Use fluids to maintain blood pressure; Monitor urine, hemodynamics, mental; If medical treatment fails, TIPS intervention or portal-host connection surgery. Portal hypertension is easy to cause gastrointestinal bleeding, dangerous complications and is the leading cause of death. In the process of treating gastrointestinal bleeding due to portal hypertension, hemostatic treatment is a very important step. Therefore, when performing this procedure, patients need to choose a reputable medical facility with full facilities and modern machinery to avoid dangerous complications during the procedure.
Tăng áp lực tĩnh mạch cửa dễ gây xuất huyết tiêu hóa
The Department of Gastroenterology of Vinmec International General Hospital always receives satisfaction and high appreciation from customers by the quality of treatment, medical equipment and patient care services. In particular, at Vinmec, there are:
Vietnam's leading modern equipment: High-resolution flexible gastrointestinal endoscope to help detect cancer at an early stage and accurate digestive diseases. American surgical robot has high precision, less invasive, fast patient recovery time. Team of highly qualified doctors: The doctors are well-trained at the leading surgical centers of Vietnam, Korea, Singapore, Japan, with high professional qualifications. Participate in short-term training courses abroad, update the latest techniques and treatment regimens in the world. Diagnosing and treating digestive diseases with the latest technology: Robotic endoscopic surgery with a success rate of up to 95%. Gastrointestinal endoscopy is painless and painless. Comprehensive patient care: Being the first hospital in Vietnam to apply the program of early recovery after surgery (ERAS), which shortens the hospital stay to only 3 - 5. Complication rate, cost of patients is reduced, bringing many benefits to customers. To examine and treat with leading doctors of Gastroenterology - Vinmec International General Hospital, please register on the website, or register online.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.