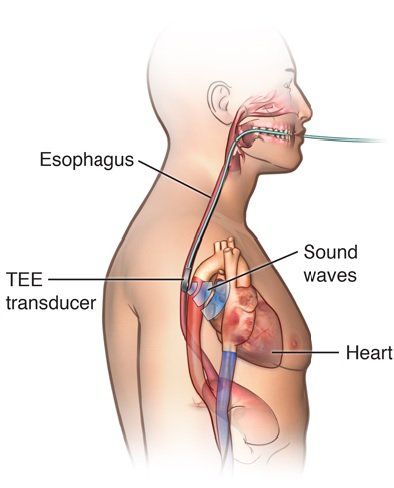
This is an automatically translated article.
Ultrasound assessment of diastolic function is an integral part of the routine evaluation of patients with symptoms of heart failure or dyspnea. The Echocardiographic Society generally recommends a comprehensive evaluation of diastolic function, including multiple Doppler-based parameters and two-dimensional echocardiography to grade diastolic dysfunction.
1. Function of diastole
Diastolic function is the ability to fill the left ventricle adequately to produce the required ejection volume without increasing diastolic pressure. Diastole consists of four successive phases, beginning with aortic valve closure at the end of systole and ending with mitral valve closure:
Isovolumetric dilation Fast filling Slow atrial filling Fluid return The epidemiology of diastolic dysfunction is extremely common in critically ill patients, occurring in 20-57% of patients with sepsis. In the community, diastolic dysfunction is a major pathophysiological mechanism in grade 2 heart failure.
Rối loạn chức năng tâm trương cực kỳ phổ biến ở những bệnh nhân nặng
2. Causes of diastolic dysfunction
Factors affecting diastolic function include:
Abnormal left ventricular muscle elasticity Due to increased myocardial mass Increased stiffness of the left ventricular wall due to increased collagen fibers and decreased myocardial cells Abnormalities of the aorta and major arteries
3.Characteristics of clinical symptoms of diastolic dysfunction
In patients with heart failure due to impaired diastolic function, there is often a history of exercise syndrome: fatigue, dyspnea due to cardiac output restriction and pulmonary capillary hypertension.
When listening to the heart, if the galloping sound appears in young people (usually under 20 years old) and the 4th sound (usually in people over 50 years old), this is considered a suggestive sign of diastolic dysfunction, sometimes when accompanied by systolic dysfunction.
4. Technique to probe left ventricular diastolic function by ultrasound
There are many techniques to investigate diastolic function such as ultrasound, radiographic angiography, hemodynamic exploration. Echocardiography is a technique that plays an important role in the exploration and evaluation of diastolic function.
Pulsed tissue Doppler ultrasound: is used to measure the maximum velocity of the myocardium and is very suitable for measuring the longitudinal velocity of the ventricular muscle.
To measure the longitudinal velocity of the myocardium, a Doppler window is placed in the ventricular muscle immediately adjacent to the mitral annulus. The cardiac cycle is represented by 3 waves:
Sa: systolic myocardial velocity Ea: myocardial relaxation rate at the beginning of diastole Aa: velocity of myocardium due to atrial contraction. The symbols a for the annulus, m for the myocardium, and E' are often used to distinguish ultrasonic velocities. Pulsed tissue Doppler ultrasound has high temporal resolution but does not allow simultaneous exploration of multiple myocardial regions.
One-dimensional color ultrasound (ColorTM): The principle of the method is to study the propagation speed of left ventricular outflow on one-dimensional color ultrasound images. The technique is performed in a 3-chamber or 4-chamber view of the heart at the apex so that the maximum view of the left ventricular chamber can be seen starting from the mitral valve. The observed filling flow has the form of a solid red mass, originating from the open mitral position to the apex of the heart, its velocity recorded along the locating line between the colored line from the origin to the end point. near or close to the apex of the heart.
Siêu âm tim là kỹ thuật đóng vài trò quan trọng trong thăm dò và đánh giá chức năng tâm trương
5. Evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by ultrasound
An important influencing factor for Doppler echocardiography of left ventricular filling is the degree of transmural gradient. Left ventricular blood-receiving capacity and left ventricular diastolic dilation are the two parameters that mainly influence this gradient. Because they reflect the pressure gradient between the left atrium and the left ventricle, mitral velocities are directly correlated with left atrial (preload) pressure and are negatively and independently correlated with left ventricular relaxation. Ea reflects the initial myocardial relaxation rate as the mitral annulus ascends at the beginning of the rapid filling period. Peak velocity Ea can be measured at any point on the mitral annulus at apical views, with the lateral mitral annulus being the most commonly used.
Because of the difference in the direction of the myocardium itself, the velocity Ea measured in the wall is slightly lower than the Ea measured in the lateral wall.
Velocity Ea measured at the lateral wall ≥ 20cm/s in healthy children and young adults, this parameter decreases with age. In adults over 30 years of age, Ea measured in the lateral wall >12 cm/s corresponds to normal left ventricular diastolic function. Ea decreases of ≤8cm/s in middle-aged and elderly people indicate impaired left ventricular relaxation and may help distinguish normal from pseudonormal pattern of mitral flow. Simultaneous echocardiographic and catheterization studies have shown that left ventricular filling pressure is correlated with the ratio between:
E-wave velocity of mitral flow on pulse Doppler. The Ea wave velocity of tissue Doppler ultrasound recorded at the mitral annulus (E/Ea). E/Ea can be used to estimate left ventricular filling pressure as follows:
E/Ea lateral wall > 10 or septal E/Ea > 15 corresponds to increased left ventricular end-diastolic pressure E/Ea < 8 respectively equivalent to normal left ventricular end-diastolic pressure.
6. Evaluation of right ventricular diastolic function by ultrasound
Doppler echocardiography has made the study, exploration and evaluation of right ventricular diastolic function much more convenient, especially in cases of pathology that directly affects the functioning of the heart. This ventricular chamber such as myocardial infarction in the lower wall spreading to the right ventricle, pulmonary embolism ... or in diseases that are generally assumed to be affected only by the left ventricle (hypertension, disease, etc.) primary or ischemic cardiomyopathy).
The impact of hypertension on right ventricular diastolic function is not fully understood until now. Increased right ventricular pressure, right ventricular systolic dysfunction, and right ventricular hypertrophy have been reported in hypertensive patients in several studies using Doppler echocardiography.
Technically, Doppler imaging of tricuspid flow is performed in the same way as for the mitral valve, and the Doppler spectrum of the two flows is usually the same. Thus, we can also obtain the Doppler parameters of the tricuspid valve similar to the Doppler parameters of the mitral valve that we have shown. The accuracy of Doppler indices to assess right ventricular diastolic function has been proven through a number of radionuclide comparison studies, but in clinical practice, the method is still considered too new. to confirm its feasibility.
In summary, ultrasound is a non-bleeding method with high sensitivity and specificity in the assessment of diastolic function.
Phương pháp siêu âm tim Doppler đã làm cho công tác nghiên cứu, thăm dò và đánh giá chức năng tâm trương thất phải thuận lợi hơn
To protect cardiovascular health in general and detect early signs of cardiovascular disease, customers can sign up for the Cardiovascular Screening Package of Vinmec International General Hospital. The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Why should you choose Cardiovascular Screening Package at Vinmec International General Hospital?
Simple and quick procedure. Enthusiastic advice and support, reasonable and convenient examination process. Comprehensive facilities, including a system of clinics and consultations, blood collection rooms, dining rooms, waiting areas for customers... Professional, caring way of working.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.