This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Hemorrhagic ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting the colon with an unclear pathogenesis. Treatment of ulcerative colitis has two phases: attack and maintenance. After the end of the offensive phase (clinical symptoms may have improved), the patient can gradually reduce the dose to the maintenance dose. So, which drug should be chosen for the maintenance treatment of bleeding ulcerative colitis?
1. Definitive diagnosis of bleeding ulcerative colitis
Definitive diagnosis of bleeding ulcerative colitis is based on many factors including clinical symptoms, laboratory tests, endoscopic imaging features and histopathology:Clinical symptoms (symptoms present at least 4 times) weeks): Diarrhea, small or large amount of blood in the stool, abdominal pain during or around the time of defecation. Gastrointestinal tract infections should be excluded. Laboratory tests: Iron-deficiency anemia, thrombocytopenia, hypoalbuminemia, autoantibodies (DANCA), increased fecal calprotectin. Colonoscopy imaging features: Characteristic diffuse inflammatory lesions in the rectum. Then, gradually spread to the upper segments of the colon with features such as loss of capillary network, loss of colonic folds, mucosal edema, congestion, secretions, many erosions, upper ulcers. surface, easy to bleed when inflated or touched with lights, real bleeding. In cases of long-term chronic inflammation, a pseudo-polyp may be seen.
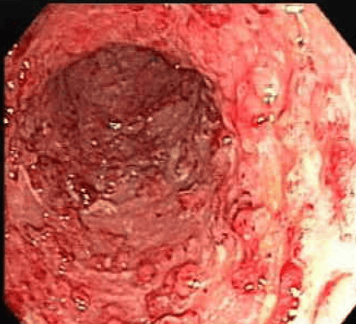
Hình ảnh giả polyp và sẹo loét cũ trong viêm loét đại tràng chảy máu.
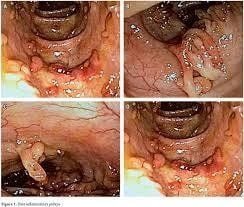
Hình ảnh giả polyp và sẹo loét cũ trong viêm loét đại tràng chảy máu.
2. Principles of treatment and assessment of treatment response
The choice of treatment modality depends on the severity and extent of the lesion and the individual characteristics of each patient such as frequency of recurrence, course of disease, response to previous treatments, effects of side during treatment. Age of onset, extra-gastrointestinal manifestations, and duration of disease are also important factors. The sum of these factors helps to group patients into patients with severe disease requiring inpatient treatment and patients with mild to moderate disease who can be managed as an outpatient.Use of Truelove and Witts classifications in clinical practice has been proven and is now a widely used indicator. In some settings, erythrocyte sedimentation rate > 30 mm/hr can be replaced by a CRP > 30 mg/l. To assess disease activity, some guidelines for the use of the Mayo Scale are developed based on the frequency of bowel movements, rectal bleeding, endoscopic imaging, and general assessment. Where, in the absence of endoscopic findings, the use of an incomplete Mayo score remains clinically relevant. During follow-up, the definition of treatment response, remission as well as resistance is important in optimizing and modifying treatment regimens.
3. Drug of choice for maintenance treatment of bleeding ulcerative colitis
3.1. Objectives of maintenance therapy and predictors of recurrence The goal of maintenance therapy is to prolong remission without steroids both on clinical and endoscopic findings. Clinical recurrence was defined as an increase in bowel frequency or a return of bloody stools and subsequently confirmed by endoscopic findings.Choice of maintenance drug depends on the extent of disease, disease progression (frequency and severity of flares), medications used, response and adverse effects. desire. Several factors have been shown to be associated with recurrence in patients with bleeding ulcerative colitis, including: Shorter duration of remission from previous treatment, faster frequency of flare-ups, patient have extra-gastrointestinal symptoms, low-fiber diet, young age, histopathological results show plasma cell infiltration in the basement membrane.
Adherence to treatment is also an important factor to be exploited. Patients who received <80% of the 5-ASA dose prescribed during maintenance therapy had a 5-fold increased risk of relapse. A meta-analysis also identified several prognostic factors for a higher risk of colectomy in male patients, with diffuse disease of the entire colon, the need for corticosteroid therapy, and the need for inpatient treatment. . Healing of colorectal mucosal lesions reduces the risk of surgery, increases clinical remission, and steroid-free remission.
Mục tiêu của điều trị duy trì là kéo dài thời gian lui bệnh mà không cần sử dụng steroid
Aminosalicylate: Mesalamine is the first-line choice for maintenance therapy in patients who achieve a response to mesalamine or topical oral steroids. Topical mesalamine is the first-line regimen for the maintenance treatment of focal proctitis or spreading colitis. A combination of oral and topical mesalamine may be selected as a second-line regimen for maintenance therapy. Dosage: 2g/day orally, 3g/week in the rectum. Although sulphasalazine is equally or slightly more efficacious, oral mesalamine preparations are preferred because of their reduced adverse effects.
Thiopurine: Used for patients with mild to moderate disease activity who have had an episode of mesalamine optimized dose but have failed to respond to or are intolerant of mesalamine. For steroid-resistant or dependent advanced-stage patients who require treatment with cyclosporin or tacrolimus, once remission is achieved, discontinuation of these agents should be within 6 months to minimize adverse effects. want. This is also the time to introduce immunomodulatory drugs and is necessary for these drugs to start working. Azathioprine or mercaptopurine is started while the patient is still on cyclosporine or tacrolimus and the steroid is reduced in dose,
Anti-TNF or Vedolizumab: The patient responds to advanced anti-TNF, which can be maintained with anti-TNF. TNF with or without thiopurine combination or maintenance use of thiopurine alone. Anti-TNF or vedolizumab can be used as first-line biologic therapy, Vedolizumab is effective in cases of failure of anti-TNF and, if the patient responds, can be maintained with vedolizumab. Thiopurine-nave patients with severe colitis who have responded to steroids, cyclosporin, or tacrolimus, may choose thiopurine for maintenance of remission.
Probiotics: Several clinical trial studies have demonstrated E.coli Nissle (ECN) at a dose of 100mg/day equivalent to 25 x 10° bacteria X4 days. Thereafter, increased to 200 mg/day was as effective as 5-ASA in maintaining remission. However, only ECN has positive data, other probiotics do not currently have much data.

Probiotic là một trong những loại thuốc được lựa chọn để điều trị bệnh viêm loét đại tràng chảy máu
Methotrexate : Studies involving Methotrexate have shown mixed results because the patient population selection is not truly homogenous. Therefore, to date, there is insufficient evidence to recommend the use of methotrexate in the maintenance treatment of bleeding ulcerative colitis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.