This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Phan - Head of Interventional Imaging Unit - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. Doctor Nguyen Van Phan is an interventional radiologist and radiologist.Cavernous carotid artery catheterization is a condition in which there is a direct flow from the carotid artery into the wild sinus. The cause is usually traumatic or spontaneous after pathology on the artery wall. Regardless of the cause, the current treatment with digital angiography and cavernous carotid artery embolization is commonly performed with certain advantages.
1. What is cavernous carotid artery catheterization?
A cavernous carotid artery shunt is an abnormal connection between the carotid artery and/or its branches and a large vein in the skull called the cavernous sinus. The cavernous sinuses are located behind the eyes and receive confluent blood from the brain to follow the jugular vein back to the heart.Cavernous carotid artery catheterization can develop after trauma or spontaneously. Trauma that causes cavernous carotid artery dissection can occur after head trauma and results in rupture of the internal carotid artery. At this time, the patient will have "classic" manifestations with signs of conjunctival redness, bulging eyeball and arteriovenous fistula in the eyeball; When the condition is severe, some patients will have double vision or progress to loss of vision.
Besides, cavernous carotid artery catheterization can also be a complication in intracranial vascular intervention. Spontaneous cavernous carotid artery dissections are often the result of ruptured carotid aneurysms; However, these openings may be due to arterial diseases such as collagen vascular disease, atherosclerotic disease or hypertension.

In surgery, the patient is removed a part of the skull cap and then occluded the internal carotid artery and the segment. distal to the stoma with a surgical clip. In this position, the opening will be blocked with bio-glue to prevent blood flow into the vein. At the same time, a branch of the external carotid artery may also need to be connected to the middle cerebral artery to supplement blood flow to the brain, to prevent a secondary stroke event in the future. In endovascular intervention , the stoma site will be accessed and occlusion is performed by inserting instruments through the vascular line . At this time, the preservation of the internal carotid artery will be achieved to the maximum extent. Compared with craniotomy, endovascular intervention is preferred due to its low invasiveness, early patient recovery, shorter hospital stay and better long-term prognosis.
2. What is endovascular intervention in the treatment of cavernous carotid artery catheterization?
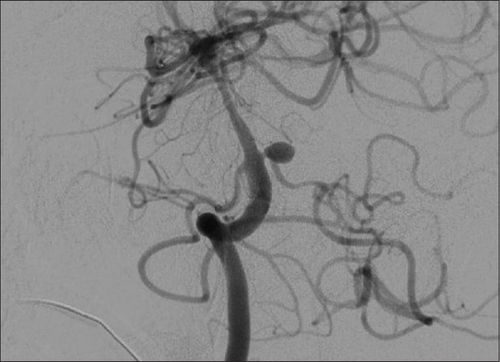
Recent advances in endovascular techniques have provided a number of different treatment options for cavernous carotid artery dissection. From these achievements, the endovascular approach has evolved as the mainstay of treatment in clinical emergencies and if conservative therapy fails. Since the manifestations of cavernous carotid artery catheterization are different in each case, the features of the foramen need to be fully investigated on digital angiograms with background erasure in order to determine the intervention methods and instruments. optimal cavernous carotid artery occlusion.For direct cavernous carotid artery catheterization occurring from a cavernous tear of the internal carotid artery or, less commonly, from an intracranial rupture of an aneurysm, the goal of treatment is to prevent the tear. between the carotid artery and the cavernous sinus while maintaining an intravascular anastomosis. Instruments used were removable silicone balloon occlusion, metal spiral occlusion, stenting or, finally, internal carotid occlusion.
For indirect cavernous carotid artery catheterization due to small dural artery shunts between the meningeal branches of the internal carotid artery, the external carotid artery, or both, and the cavernous sinus. The goal of treatment in this condition is to both plug the catheter and reduce the pressure in the cavernous sinus. This can be accomplished by blocking the arterial branches supplying the orifice by percutaneous embolization or, more commonly, by venous embolization.

3. Digital imaging procedure to erase background and cavernosal carotid artery shunt
Intervention for cavernous carotid artery embolization is indicated for treatment in cases of direct cavernous carotid artery catheterization, not for indirect catheterization.Because it is a sophisticated and very specialized technique, patients and their relatives need to be thoroughly explained about the procedure, as well as the associated risks, in order to coordinate between patients, relatives and doctors . Next, the patient needs to fast, drink ~6 hours, can drink water but not more than 50ml, change into appropriate clothes and in the supine position on the intervention table, place an intravenous line.
Means of monitoring breathing, pulse, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, SpO2 are mounted on the patient and the indicators are displayed on the screen for easy observation. After cleaning the inguinal and genital areas, the doctor will cover the area with a sterile tissue to prepare for intervention. In case the patient is overstimulated or poorly cooperated, it is necessary to consider appointing sedation to facilitate the procedure.
At the intervention site, usually the femoral artery, unless this entrance cannot be done, using other routes, the doctor will conduct local anesthesia,. Once the anesthetic takes effect, the doctor inserts a needle and places the opener into the femoral artery. Under the guidance of digitized angiography and contrast media, the physician adjusted and inserted the catheter up to the internal carotid artery and observed the fistula into the desert.
When accessing the location and determining the necessary features of the cavernous carotid artery septal defect, the use of which tools to plug the catheter in the intervention will depend on the available means and the skill and experience of the patient. surgeons. The following cavernous carotid artery catheterization kits are available:
Balloon occlusion: Once a 6F size catheter is inserted into the internal carotid artery, the balloon is attached to the tip of the microcatheter and pass the ball to the vent. Once the balloon position is correct as seen on the DSA image, the balloon will be inflated until the passage is completely blocked. Multiple bulbs can be used if the throughput size is large.

Otherwise, it is necessary to make a bridge or scaffold first to ensure adequate blood flow to the brain after the occlusion. Once that is guaranteed, a ball stopper or a metal coil can be used... but the plug material must meet the condition that it is covered through the opening to avoid re-circulation of the backflow from the top down. .
Metal spiral catheter occlusion: When the catheter is too small in size or does not have a balloon device, the doctor will choose a metal spiral catheter. Under the guidance of digitized angiography, the microcatheter was inserted into the stoma and then released the metal helix until the catheter was completely blocked. This intervention can choose an arterial or venous approach.
After ensuring that the flux image has been thoroughly resolved on the digitized angiogram, remove the background; At the same time, the cerebral circulatory system and the rest of the body still circulate normally, the interventional instruments will be withdrawn. The puncture artery site will be directly pressed by hand for about 15 minutes to stop bleeding and then bandaged for 8 hours. During this time, the patient is limited to bed movement.
4. Complications that may be encountered in digital background erasure and cavernosal carotid artery catheterization
Because this is a delicate technique, any manipulation during the procedure carries the risk of tearing an intracranial artery, leading to cerebral hemorrhage or dissection. In addition, other complications are also related to the intervention such as stimulation of thrombosis, vasospasm response or displacement of embolization material...After the end of the procedure, the location of the intervention if not If the bandage is good to stop bleeding, there will be a risk of hematoma or subcutaneous bleeding. However, this risk is similar to that of other transarterial endovascular interventions.
In summary, with advances in endovascular interventions, digital angiography with background erasure and cavernosal carotid artery embolization has become the mainstay of treatment for this pathology. However, the endovascular approach and the type of instrument used need to be carefully examined and considered depending on the patient's orifice characteristics. Moreover, the factors of supporting equipment and human resources also need to be ensured for optimal results of the procedure.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.