This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Cong Trinh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
And Master, Doctor Tong Diu Huong - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) is a vascular angiography method based on the principle of image exclusion through a digital image processor to help capture blood circulation, identify pulmonary artery abnormalities and thereby identify common pulmonary artery diseases.
1. Overview of digitized imaging techniques of pulmonary vascular intervention
Digital erasure scan helps doctors have enough data to determine the appropriate pulmonary vascular intervention (embolization, fibrinolysis, pulmonary embolism...). These techniques help minimally invasive, treat from within the blood vessel without the need for open surgery, thereby minimizing the associated risks.Indication cases: The need to identify pulmonary artery abnormalities: Congenital abnormalities, pulmonary aneurysms, pulmonary artery thrombosis... Pulmonary artery intervention: The need to resolve embolism, recurrence pulmonary artery bypass. Cases of contraindications:
Note: No absolute contraindications Relative contraindications: Patients with severe organ failure (liver failure, kidney failure ..), thrombosis in the right atrium, Patients with an allergy to contrast agents, pregnant women
Bệnh nhân suy gan chống chỉ định thực hiện thủ thuật này
2. Process of digital background removal and pulmonary vascular intervention
2.1 Preparation for the procedure
In order to perform digital scan to erase the background and intervene with pulmonary vessels, it is necessary to prepare:Implementation team:
Radiology specialist, auxiliary doctor. Optical technician. Nursing. Anesthesiologist/technologist (if patient is difficult to cooperate) Means of use:
Digital angiography eraser (DSA): ceiling or floor mounted
One or two batteries.
Lead vest, apron for shielding from X-rays. Film, film printer and image storage system. Drugs:
Local anesthetics General anesthetics (depending on the case) Non-ionizing water-soluble contrast agents (Ultravist, Xenetic, Iopamiro, Pamiray) Anticoagulants Neutralizing anticoagulants Skin antiseptic solutions and mucosa. Common medical supplies:
Syringe 1,3,5,10ml Distilled water (physiological saline) Surgical clothes Medicine box and accident first aid box. Aseptic interventional kits (knife, scissors, forceps, tool trays..v.), Cotton gauze, medical bandages for surgery. Special medical supplies:
Intravascular needle Set of catheters Guide Micro-interventional catheter Diagnostic catheter Interventional catheter Micro-interventional catheter Embolization material:
Bio-foam to help stop bleeding (Gelatin) Synthetic resin beads (PVA) Bio-glue (Histoacryl, Onyx) Temporary embolizers (Spongel, Gelfoam) Metallic spirals (Coils) of all sizes. Patients need to prepare:
Be explained specifically about how to take pictures and how to intervene to effectively coordinate with the doctor. Perform a pre-procedure clinical examination. Fasting, drinking before 6 hours. Limit drinking more than 50ml of water. If the patient cannot lie still, sedation will be prescribed.

Trước khi làm thủ thuật, bệnh nhân không uống quá 50ml nước.
2.2 Implementation process
Anesthesia methodIn the intervention room: The patient lies supine on the imaging table. The doctor placed an intravenous line, installed a monitor to monitor breathing, pulse, electrocardiogram, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation in the peripheral blood. Disinfect and cover with a sterile, perforated cover. Conduct pre-anesthesia or anesthesia if necessary (if patient is uncooperative, young child...) Select technique and route of catheterization: Based on Seldinger method, access can be from femoral vein (most common) ), internal jugular vein, superior vena cava, right atrium to right ventricle and pulmonary artery. Procedure:
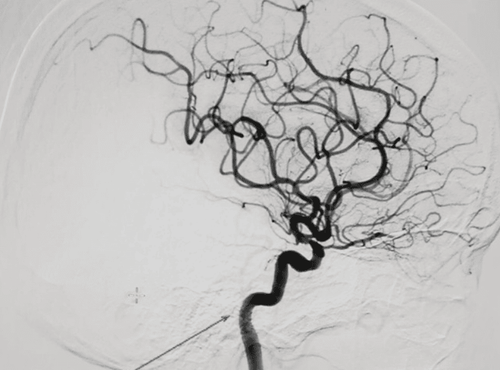
The nurse disinfects the groin area on both sides of the thigh (the way to the femoral vein). Cover the entire patient with canvas, leaving only the puncture site and the catheter insertion site open. Conduct local anesthesia at the site of insertion of the catheter into the lumen. Needle puncture, insert the tube set into the femoral vein. Through the catheter, the angiogram leads and catheters are inserted into the inferior vena cava, up the right atrium, into the right ventricle, and up into the pulmonary artery. Through a syringe pump and under the effect of contrast agents, the entire system of the right and left pulmonary arteries can be seen, identifying pulmonary artery abnormalities: aneurysms, pulmonary artery malformations, pulmonary artery thrombosis... and capture these markers. Determine the method of pulmonary intervention: Release the embolus, recanalize the abnormal pulmonary artery with embolization material, open the artery, remove the pulmonary artery thrombus (if any). Withdraw the catheter and tube into the lumen after satisfactory pulmonary angiography and intervention. Gently apply pressure by hand to stop bleeding for 15 minutes, then apply pressure to the intervention site for 6 hours. Evaluation of results:
After the end of the intervention, put the patient to rest and monitor the dorsal pulse, bleeding, hematoma at the puncture site. Combined with monitoring of the whole body (pulse, temperature, blood pressure, patient's reactions).
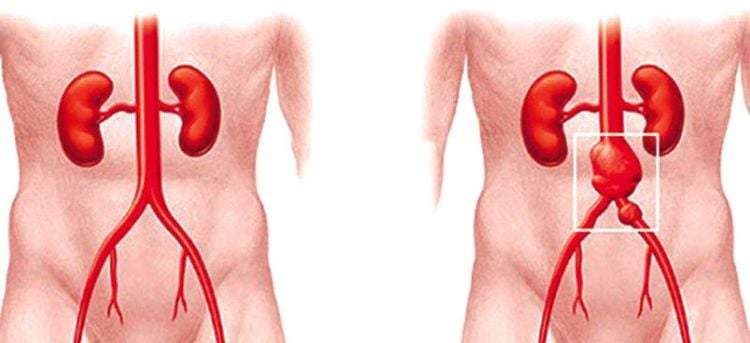
Tai biến có thể xảy ra sau thủ thuật như phình động mạch
3. Complications after the procedure and treatment direction
During the intervention: Bleeding due to puncture of the artery: apply compression until the bleeding stops. Thrombosis from the femoral vein, inferior vena cava to the right atrium and pulmonary artery causes pulmonary infarction, which should be quickly detected and promptly treated by a specialist. Aneurysm: Conduct arteriovenous catheterization or rupture of catheter or wire, then endovascular or surgical intervention. Always monitor the patient's hemodynamic and respiratory status (especially emergency patients due to gastrointestinal bleeding). Immediately after the intervention:Monitor bleeding at the puncture site: The patient needs to be immobile at the hospital bed, immobilize the leg on the side of the puncture for at least 6 hours. Monitor pulse, temperature, blood pressure, abdominal condition after intervention. Background digitized angiography is an important technique in the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary artery disease in particular and many vascular diseases in general. When performing the technique, the patient should follow all instructions of the doctor to achieve high therapeutic effect and reduce the risk of complications.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Master. Doctor. Tong Diu Huong has more than 10 years of experience in the field of specialized imaging in diseases on images Ultrasound, X-ray, multi-slice CT, Magnetic resonance in diseases of the nervous system, digestive system , urology, cardiology, musculoskeletal... Besides, there are interventional imaging techniques, fine needle aspiration cells under the guidance of ultrasound and computed tomography.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.