This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Phan - Head of Interventional Imaging Unit - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. Doctor Nguyen Van Phan is an interventional radiologist and radiologist.Nasopharyngeal fibroids are benign tumors (essentially vascular fibers are concentrated) but have the ability to grow and spread, destroy strong bones, and can spread into the skull, affecting even health. life threatening if not detected and treated promptly. There are many effective treatment methods. Currently, digitized angiography erasing the background and treating nasopharyngeal fibroids by embolization method brings good results, reducing the tumor's spread and invasion.
1. Overview of nasopharyngeal fibroids
Nasopharyngeal fibroid is a benign fibrous tumor that adheres to the skull base in the nasopharyngeal region and splenic into adjacent structures. The tumor is firm, has many lobes and has a stalk, the size is different depending on the time of detection. When removing the tumor and observing it under the microscope, there are many blood vessels or blood pools scattered in the tumor along with fibrous tissue, forming a network that covers the entire tumor.Nasopharyngeal fibroids progress silently with increasing obstruction and stuffiness in one side of the nose. In the late stage, the patient has stuffy nose, blocked nose on both sides, runny nose continuously and more. Occasionally, patients have nosebleeds, which can initially stop the bleeding on their own, and then require medical intervention to stop the bleeding. Other symptoms include tinnitus, hearing loss due to the tumor pressing on the pinna, fatigue, weakness, pale skin.
If left to grow naturally, nasopharyngeal fibroids will fill the nasal cavity, sphenoid sinus, maxillary sinus, eye socket, break the cleft palate, reduce the upper jaw bone and swell under the skin. When the tumor penetrates into the skull, it will damage the intracranial nerves, causing difficulty swallowing, blindness, and inability to smell. Patients with untreated nasopharyngeal cysts will die from bleeding or intracranial complications that cause increased intracranial pressure.
Surgery is the main treatment for nasopharyngeal fibroids. In addition, radiation therapy combined with endocrine therapy may be indicated to shrink the tumor. Treatment of nasopharyngeal fibroids by digital embolization is a minimally invasive and highly effective procedure with low complications.

2. Digital imaging method to erase the background and embolize the treatment of nasopharyngeal fibroids
2.1 Related concepts
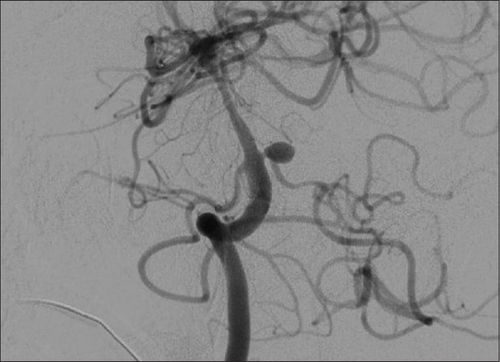
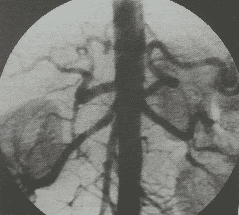
Digital subtraction angiography: Also known as digital subtraction angiography (DSA). This is a fluorescein technique that uses X-rays to make clear images of blood vessels. On the principle of digital angiography erasing the background: Using fluorescent light and X-rays to take pictures of blood vessels in the area to be examined before and after injecting contrast material into the blood vessels to be taken. Finally, the computer will blur the background image, clarifying the vascular system. Embolization: A minimally invasive procedure, used to slow tumor growth by blocking its blood supply, blocking oxygen and nutrients from feeding the tumor. The embolization agent will be injected into the tumor through a flexible tube that follows the artery that supplies blood to the tumor. Embolization can be used alone or in combination with other treatment methods such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy,... This method is applied to embolize tumors of the head, face and neck, cancer. liver cancer, uterine fibroids, prostate enlargement,... With nasopharyngeal fibroids, the doctor will first take an angiogram of the head, face and neck to find the arterial branches that supply blood to the tumor. u. Then, perform occlusion of the vascular peduncles supplying blood to the tumor through a small catheter placed in the artery, thereby reducing the blood supply to the tumor, reducing the amount of blood to the tumor, thereby reducing the risk of cancer. Bleeding status during surgery to remove nasopharyngeal fibroids.
2.2 Indications and contraindications
IndicationCases of nosebleeds due to nasopharyngeal fibroids while waiting for surgery. Preoperative embolization to reduce bleeding in nasopharyngeal fibroid surgery. Contraindications
No absolute contraindications Relative contraindications for cases of renal failure, blood clotting disorders, pregnant women or clear allergy history.

2.3 Preparatory work
Implementation personnel: Doctors, interventional radiology technicians, nurses; doctor, anesthesiologist (if necessary). Technical facilities: Digital angiography machine to erase background, image storage system, specialized contrast agent pump, shirt + skirt + X-ray shielding lead collar... Medicine: Local anesthetic, general anesthetic (in case of an indication for anesthesia), contrast agent containing water-soluble iodine, Heparin and neutralizing drug Heparin, PVP skin antiseptic solution. Common medical supplies: Syringes of all kinds 5ml, 10ml, 20ml, physiological saline, gloves, caps, gowns, surgical masks, sterile intervention kits (knives, scissors, forceps, needle bowls) type, instrument tray, bean tray), cotton, gauze, surgical tape, Etrolley vehicle. Special medical supplies: 5F - 6F vascular access kit, angiography needle, 0.035 inch standard lead, 4 - 5F angiography catheter, 1.9 - 2.7 F microcatheter, microlead 0.014 - 0.018 inches; Materials that cause embolism: Bio-foam, synthetic resin beads, bio-glue, metal spirals of all sizes; Patient: The procedure is thoroughly explained; fasting before 6 hours, can drink no more than 50ml of water; In the intervention room, the patient is in the supine position, fitted with a pulse monitor, breathing rate, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, SpO2 disinfecting the skin, covered with a sterile towel with holes; if the patient is too excited and cannot lie still, sedation should be used; Test sheet: Medical record, order of procedure, X-ray film, magnetic resonance, computed tomography (if any).2.4 Performing the trick
Anesthesia: Perform local anesthesia or general anesthesia. The patient lies supine on the background digitized angiogram table, intravenous line is placed, pre-anesthesia is injected. For children under 5 years old who do not have a sense of cooperation or people who are too excited or scared, they should be given general anesthesia; Selecting the technique of use and inlet of the catheter: Selection of the Seldinger technique. Catheter access may be from the femoral or radial artery. Usually, the inlet of choice is from the femoral artery. In case the entrance from the femoral artery cannot be interfered with, other entrances are selected; Diagnostic angiography: Perform antiseptic, anesthetize the puncture site, insert the needle and place the catheter into the artery. Next, perform selective internal carotid angiography, selective external carotid angiography, or selective vertebral artery angiography. Doctors can also conduct 3D scans depending on the pathology; Embolization: First, insert a guide catheter into the gill vessel (usually into the external carotid-mandibular artery). Next, the microcatheter is inserted into the malformed blood vessel or artery causing the bleeding. Then, inject embolization material (depending on the characteristics and location of the lesion to choose temporary or permanent embolization material). Finally, after a satisfactory scan, remove the catheter and catheter, apply pressure directly on the needle puncture site for about 15 minutes to stop bleeding and apply pressure for 8 hours. The procedure is successful when:The nasopharyngeal tumor and the arteries supplying the tumor are completely occluded; The arteries that supply blood to the normal organs are not blocked.
2.5 Complications and how to deal with them
During the procedureProcedural complications: Arterial tear causing bleeding or dissection of the artery. Treatment measures are to stop performing the procedure, apply pressure again, and follow up. If bleeding stops, embolization can be performed after 1-2 weeks; Contrast-induced: Includes acute reactions (nausea and vomiting, urticaria, laryngeal edema, bronchospasm, hypotension), anaphylaxis and complications due to extravasation of contrast. Treatment measures depend on each specific reaction according to the standard protocol; Vasospasm: Depending on the degree of vasospasm, a selective vasodilator pump can be used. After the procedure
Where the catheter may bleed or have hematoma: Apply pressure and keep the patient immobile until the bleeding stops; Arteriovenous bulge or catheterization, broken wire or catheter: Can be managed with surgical intervention; Suspicion of arterial occlusion due to blood clot or embolism due to detachment of atherosclerotic plaques: Need timely examination for treatment; There are signs of infection after the procedure: Antibiotics should be used for treatment; Other rare complications: Blindness, paralysis, embolization, tooth failure, oropharyngeal necrosis,... need specialist consultation for appropriate intervention measures. The technique of digital angiography to erase the background and embolize the treatment of nasopharyngeal fibroids helps control bleeding from the tumor and prevents the blood supply to nourish the tumor, thereby improving the treatment efficiency. When being assigned to perform this procedure, patients need to strictly follow the doctor's instructions before, during and after the treatment process.
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied digital angiography to remove background in examination and diagnosis of many diseases. Accordingly, the digitized angiography technique at Vinmec is performed methodically and in accordance with the process standards by a team of highly skilled medical doctors and modern machinery, thus giving accurate results. contribute significantly to the diagnosis and stage of the disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE
What is bone tumor? Types of benign tumors in bone Application of digital erasure angiography (DSA) in the field of neurology Digital angiography and embolization for treatment of uterine fibroids