This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Trinh Le Hong Minh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
1. What is digitized angiography?
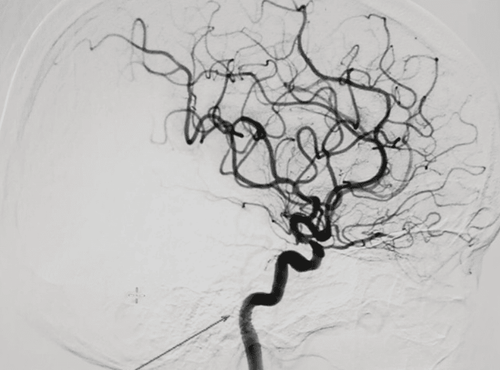
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) is also known as Digital Subtraction Angiography. This is an imaging method based on digitally processed angiograms. The resulting images will show the arteries to be studied, thereby making it easier for the doctor to diagnose the disease.2. Application of DSA
Diagnosis and treatment of malformations, brain aneurysms, arteriovenous shunt lesions, rich vascular tumors; Emergency intervention for stroke patients caused by cerebral artery thrombosis; Diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to blood vessels in the marrow; Diagnosis and intervention of abnormal aorta, renal artery, limb, carotid artery, peripheral artery; Cardiac catheterization and closure of the cardiac catheterization, angioplasty of the artery, or placement of an intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation; Place vena cava filters, place pacemakers or remove circulatory foreign bodies, echocardiography, cardiac chambers. DSA technology is applied in many fields of medicine.
3. What is an upper extremity arterial background digitization scan?
Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is an imaging method used to capture arteries when needed. This procedure can be applied to many parts of the body providing clear and accurate images of the arteries. This method is often used to diagnose arterial malformations or thrombophlebitis in the extremities.3.1 Indications Upper limb deformity; Check the connections; Upper extremity trauma with suspected vascular injury; Angiography for interventional radiology; Patients with congenital or acquired diseases of the arteries of the upper extremities. 3.2 Contraindications This procedure has no absolute contraindications. However, patients with coagulopathy, renal failure, a clear history of allergy to iodinated contrast agents or pregnant women should not use this procedure. In addition, the doctor can also decide whether or not to perform this procedure based on the patient's condition.
3.3 Procedures Preparation The digital background scan requires an intravenous line, so it usually requires local anesthesia and pre-anesthesia for children under 5 years old.
Carrying out the technique First, the patient will be disinfected and anesthetized at the needle puncture site and proceed to insert the tube into the vessel.
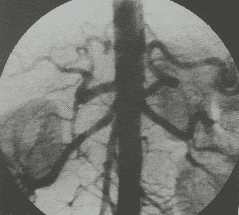
To image the subclavian and axillary arteries, the doctor will insert a 5F catheter to the base of the subclavian artery and then inject medication.
To take an angiogram of the brachial artery or the elbow or the radial artery, the doctor will also use a deeper catheter to bring it closer to the artery to be examined and inject medicine.
When injecting Iodine contrast, it is also important to note whether the patient is allergic or not? What is the speed and dosage? Normally, the drug volume and injection speed will vary depending on the method of segmentation or “Bolus tracing”. The usual volume of drug used is 30ml of drug injected with pressure of 500PSI, speed of 6ml/s with Bolus tracing or a volume of 12ml with pressure of 500PSI, speed of 5ml/s.
In the case of direct puncture, the needle will be inserted downstream from the axillary or brachial artery and then injected.
After the necessary satisfactory results are obtained, the doctor will remove the catheter and press the armband over the needle puncture site for 15 minutes to stop the bleeding. Finally, the patient was put on compression bandages for 6 hours after the procedure or used an instrument to close the lumen.
Evaluation of results The obtained images will clearly show the anatomical structures of the arteries of the upper extremities from the subclavian arteries to the axillary arteries, brachial arteries, radial - ulnar arteries and hands. Based on this image, the doctor can detect lesions or abnormalities if any.
4. Possible complications
Needle puncture and luminal catheterization can cause some complications for the patient, and iodinated contrast agents can also be a cause.During the procedure, the patient may have an artery tear, dissection of the artery at the puncture site, causing the bleeding to not stop. This case should be pressed and bandaged immediately, then move the puncture site to the opposite side.
In case the doctor suspects that the patient has an artery occlusion due to a blood clot, it is necessary to examine it promptly and under the guidance of a specialist. Patients may also receive thrombolytics or thrombectomy.
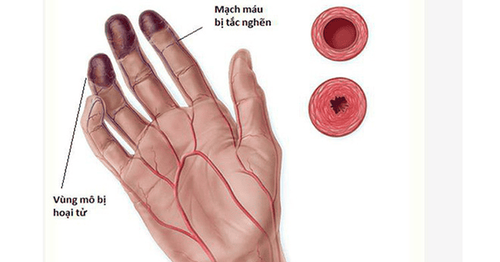
After the end of the procedure, the patient may have hematoma or bleeding, in this case the patient needs to be bandaged and rested until the bleeding stops. Another rare case is that the patient has a bulging or an arteriovenous catheter, which requires endovascular intervention or surgical measures to manage. In other cases, there may be an infection, which requires antibiotics to treat.
Digital imaging technique to erase the background of the upper extremities artery and the applications of this DSA technique has helped a lot in the examination and treatment of doctors. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is equipped with a high-tech DSA background scanning machine (Phillips - The Netherlands) to help:
Coronary angiography and intervention Peripheral artery imaging and intervention Congenital heart interventions percutaneous Aortic Valve Replacement Intervention (TAVI) Mitral valve clip (Mitra Clip) Pacemaker placement, CRT-d, ICD Liver Embolization Intervention (TOCE) Compared with previous generations, the DSA Allura Xper FD 20 has more outstanding advantages, helping to diagnose diseases quickly and achieve the best efficiency:
For clearer image quality during intervention Integrated 3D rendering in endovascular intervention skull, peripheral There are anti-collision modes of the beam head with the patient Integrating the latest technologies: StentBoost, XperCT, Allura 3D in coronary and vascular interventions Before taking a job at the International General Hospital Vinmec Central Park, the position of Doctor of Radiology since February 2018, Doctor Trinh Le Hong Minh used to work as a resident in the Radiology Department at various hospitals. Institutes: Cho Ray, University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Oncology, Gia Dinh People, Trung Vuong... from 2012-2015. Officially worked at Cho Ray Hospital from 2015-2016, City International Hospital from 2016-2018.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.