This is an automatically translated article.
Glossitis and tongue cancer are among the most common diseases in the oral cavity. Clinically, these are two completely different pathologies. However, because the presentation of each patient is different, sometimes there is still confusion in the diagnosis. So how to distinguish geographic glossitis from tongue cancer?1. Glossitis map
Glossitis is a disorder that occurs on the surface of the tongue, caused by a virus. This is a benign disease that does not pose a threat to the health of the child or the sick person. The disease is common in children, sometimes it can also be seen in adults.
Clinical manifestations:
Characteristic lesions appear on the surface of the tongue with alternating white streaks like a map, so the disease is called map glossitis, or may appear as clustered lesions, red patches surrounded by white border, clearly demarcated. The shape, location and even size of the lesion can vary from day to day. No tongue papillae. Location: common on the tip of the tongue or the tongue whiskers. The disease does not cause pain, does not cause discomfort to the child. Pain may appear when eating hot, salty foods. Clinically, glossitis is easily misdiagnosed with thrush, hairy tongue, sometimes mistaken for tongue cancer in the early stages.
Glossitis can persist from a few months to several years and then go away on its own without any treatment, or there are cases where the disease persists for a lifetime. However, in severe cases, it can cause ulcers in the tongue, leading to pain, affecting the activities of the oral cavity, especially eating. When the glossitis does not go away on its own within 7-10 days, the child should see a doctor for proper examination and treatment.
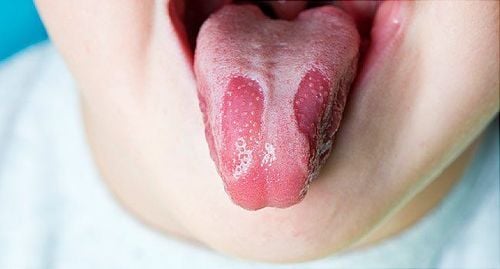
Viêm lưỡi bản đồ thường gặp ở trẻ nhỏ, đôi khi cũng có thể gặp viêm lưỡi bản đồ ở người lớn
Treatment of glossitis is mainly related to hygiene care:
Should clean the child's mouth regularly with 0.9% saline or mouthwash as prescribed by the doctor, can Brush your tongue with a soft brush. Provide adequate nutrients, give children enough water to drink. Treat other problems such as gingivitis, VA, tonsillitis... as prescribed by the doctor. For glossitis in adults, additional attention should be paid to lifestyle habits: do not drink alcohol, do not smoke.
2. Tongue Cancer
Tongue cancer is also a common disease in the oral cavity. But in terms of prevalence, glossitis is more common.
Different from glossitis, tongue cancer is classified as one of the malignant diseases with the ability to spread and metastasize to other parts, seriously affecting the patient's health.
Tongue cancer can also occur at any age, but mainly occurs in people over 40 years old, especially those who have a history of smoking, drinking alcohol regularly. From the study of clinical statistics, up to 70-80% of patients with tongue cancer are alcoholics.
In addition, the disease can also occur in people with genetic factors, or exposure to radiation or HPV infection.
Clinical manifestations of tongue cancer: in the early stages there are almost no signs, the disease often manifests when it is in the late stages:
Tongue pain: this is an early symptom of the disease, pain increases when chewing or tongue activity. Lesions: on the surface of the tongue, there are white patches attached to the tongue, this plaque shows signs of increasing over time. In severe cases, there may be signs of bleeding that are not related to the scratch or other injury. Location: commonly found on the side of the tongue. May be accompanied by a sore throat, unpleasant bad breath. In late-stage patients, when tongue cancer has metastasized to other parts, symptoms of other diseased organs can be seen.
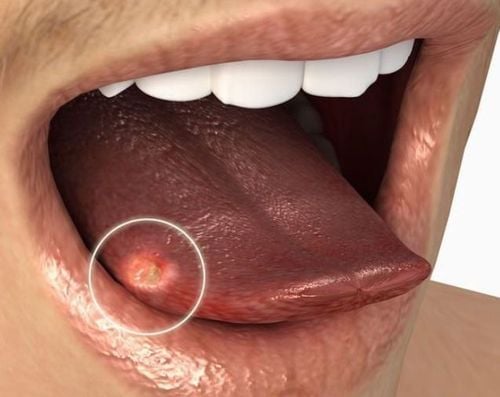
Ung thư lưỡi ở giai đoạn đầu gần như không có dấu hiệu gì và thường bị bỏ qua
Tongue cancer, if not treated and controlled, cannot go away on its own, but progresses gradually in 5 stages:
Tumor stage: is an early stage, clinical manifestations are not clear, can be intervened treatable. Lymphatic stage: In the early stages, there are no cancer cells in the lymphatic system, but gradually as the disease progresses, cancer cells will invade the lymphatic system and then spread faster. Metastatic stage: cancer cells grow and spread and spread to other parts of the body. Advanced cancer stage: high risk of death, difficult to treat. Tongue cancer is not like glossitis, the disease needs to be detected early and treated promptly to maintain the patient's health. Currently, there are 3 main methods to treat tongue cancer:
Surgery: apply treatment with early stage cancer. Radiation therapy: applied to patients who do not respond to surgical treatment or patients with advanced cancer. Chemotherapy: can be combined with the above 2 methods to treat cancer, applied to patients who do not have indications for surgery to remove the tumor. In summary, tongue cancer and glossitis are both common diseases. However, clinically, both these diseases are different in both clinical manifestations, causes as well as treatment methods. If you find that your body has abnormal symptoms, please see a specialist for an accurate diagnosis and timely treatment, to avoid affecting your health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.