This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Ngo Thi Oanh - Pediatrician - Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Children with abnormal breathing and airways often have signs of slow or sudden onset, maybe the child has had signs of difficulty breathing before, but parents are often subjective. Children with a history of diseases such as persistent cough, upper respiratory infection, foreign body, congenital or acquired dyspnea, HIV infection, family history of asthma often have breathing abnormalities and airway.
1. Diagnosis of breathing and airway abnormalities
Parents can diagnose a child with abnormal breathing and airways through the following specific ways:1.1 Counting breaths A child's breathing changes are a typical sign of respiratory dysfunction. Counting breaths is a way to diagnose some airway abnormalities, as well as respiratory diseases in general.
However, parents also need to know that the breathing rate of young children is easily changed, especially when there are external stimuli and changes with certain age. A newborn's breathing rate can vary during the first week from 40 to 50 breaths per minute, if less than 60 breaths per minute is perfectly normal. Children may increase their breathing rate after short pauses in breathing, and at the same time contract their chest and inflate their nostrils at certain times. Children with restrictive lung diseases have faster and shallower breathing rates than normal children.
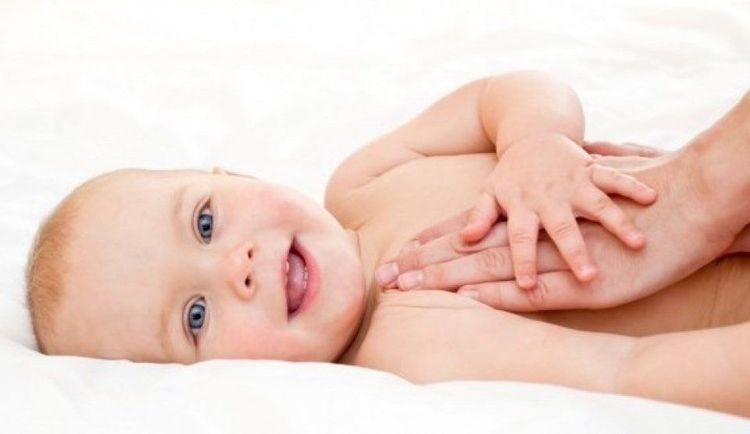

Đếm nhịp thở của trẻ cũng là cách giúp cha mẹ phát hiện những bất thường về thở
1.2 Listen to breathing sounds through the ears Children with respiratory disease have breathing abnormalities and the airways will have abnormal breathing sounds, easily recognized with normal headphones such as:
Whisper: The child breathes short, emits During expiration, close to the ear can be heard in children with severe pneumonia. In this condition, the child's lungs tend to collapse, and to prevent collapse, the child must try to retain functional residual volume by closing the epiglottis at the end of expiration. Whispering sound: a sound made during inspiration, can be heard when the baby breathes. Detecting stridor in children, can diagnose most likely the child has diseases related to narrowing of the upper airway, or in the thoracic segment causing respiratory diseases such as laryngitis, laryngitis, laryngitis, anomalies. airway object... Wheezing sound: emitted during expiration due to obstruction in the lower airways, from the bronchi down, especially in children with bronchiolitis, asthma, or tumors , large vascular malformations cause bronchial compression. However, the mother also needs to distinguish the sound of snorting caused by nasal obstruction, sputum sputum in the nasopharynx. 1.3 Listening to the lungs with a stethoscope This is a method of diagnosing abnormalities of the airways in children, which is a way to clinically examine and evaluate the sound of breathing in and out in children. Through listening to the lungs, it is possible to diagnose dyspnea, whether breathing is prolonged, and assess the flow of air into the lungs. Children with the trait of prolonging breathing when listening to the lungs often will have some problems such as obstructive lung diseases such as bronchial asthma, bronchiolitis.
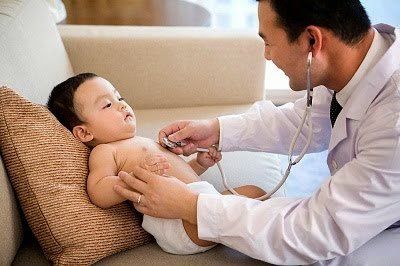
Nghe phổi bằng ống nghe để chẩn đoán các bất thường về đường thở của trẻ
Children's breathing sounds reduce or lose alveolar murmur when listening to the lungs, often due to pneumothorax, pleural effusion, atelectasis, even severe disease conditions, the patient is about to stop breathing..
Besides, when listening to the lungs, there is a hissing sound, snoring, shortness of breath, common in cases of pneumonia, bronchiolitis, asthma. The sound of stridor due to upper airway obstruction echoes down often not clearly audible to the ear, brought close to the ear near the child's mouth.
1.4 Pulmonary percussion As diagnostic in restrictive lung diseases, percussion in obstructive pulmonary disease. Percussion of the lungs is difficult to assess if the infant is low birth weight because the echoes echoing from the diseased lung will be mixed with the surrounding areas, making it difficult to diagnose.
2. Diagnosis of respiratory condition through breathing and airway abnormalities
| Chẩn đoán bệnh | Bất thường về thở, đường thở |
| Viêm phổi – Ho kèm thở nhanh và sốt |
– Thở rên hoặc khó thở – Diễn tiến nặng dần lên nếu không điều trị – Nghe phổi có ran nổ – Triệu chứng đông đặc hoặc có dịch ở phổi |
| Suyễn |
– Tiền sử khò khè trước đây – Thì thở ra kéo dài – Khò khè, thì hít vào ngắn – Đáp ứng với thuốc dãn phế quản |
| Dị vật đường thở |
– Bệnh sử đột ngột ho sặc sụa – Đột ngột thở rít hay suy hô hấp – Giảm phế âm khu trú hoặc khò khè |
| Áp-xe thành sau hầu |
– Diễn tiến chậm nhưng nặng dần – Khó nuốt, không nuốt được – Sốt cao |
| Viêm thanh khí phế quản |
– Ho như “sủa” – Khàn tiếng – Liên quan đến nhiễm trùng hô hấp trên – Thở rít thì hít vào – Dấu hiệu suy hô hấp |
| Bạch hầu |
Bạch hầu – ‘Bull neck’ do sự phì đại hạch lympho – Triệu chứng tắc nghẽn đường hô hấp với thở rít và thở rút lõm – Giả mạc màu xám ở họng |
In addition to zinc, parents also need to supplement their children with other important vitamins and minerals such as lysine, chromium, B vitamins,... errands.
Please regularly visit Vinmec.com website and update useful information to take care of your baby and family.