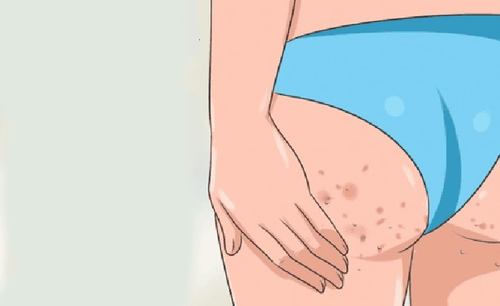
Both lumps and boils cause lumps under the skin. They are often similar in appearance, but their causes and treatment differ. This article will cover the differences between cysts and boils and abscesses.
1. Distinguishing features between cysts and boils, abscesses
It can be easy to confuse cysts with boils and abscesses because they can have similar symptoms.
A cyst is a fluid- or pus-filled sac that can form in or on the human body. There are different types of cysts, and some may appear related to cancer; however, most cysts are benign, meaning they are not cancerous. A cystic tumor is distinguished from a cancerous tumor by its characteristic outer sac.
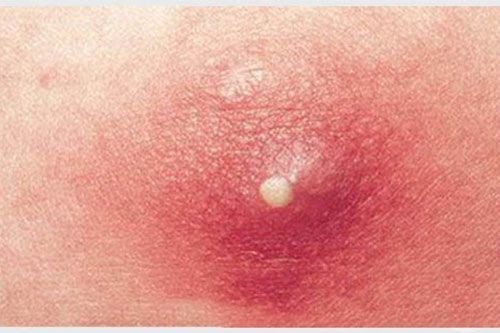
An abscess is a pus-filled infection in body tissue. Pus forms when the immune system fights an infection caused by bacteria. Additionally, abscesses are caused by viruses, parasites, etc. Abscesses may appear on the skin or inside the body. A small abscess on the skin may also be called a boil. The main differences in specific symptoms are: cysts grow slowly and are usually painless unless they become large. In contrast, an abscess is painful, uncomfortable, often red, and swollen. The infection can also cause symptoms elsewhere in the body. Both cysts and abscesses can form in various locations inside and outside the body. While an infected cyst can become an abscess, an abscess does not necessarily begin as a cyst.

2. Example difference between cyst and abscess
2.1. Difference Between Cyst and Abscess of Bartholin Gland Bartholin glands
Bartholin Gland Bartholin glands are two pea-sized structures, one on each side of the vaginal opening, that secrete vaginal lubrication.
In about 2 percent of women, the Bartholin gland can become blocked due to trauma or irritation. This can cause the fluid they secrete to back up, enlarging the gland; this condition is called a Bartholin's duct cyst. Usually, Bartholin's gland cysts are small and asymptomatic. However, if the cyst grows large, it can cause discomfort when walking, sitting, or having sex. A Bartholin gland abscess is an infection of the gland or its ducts. Abscesses may form or be initiated by an infected Bartholin's ductal cyst. Bartholin's gland abscesses are three times more common than Bartholin's gland cysts.
The most common bacteria that cause abscesses in the Bartholin's glands are anaerobes:
- Bacteroides fragilis
- Clostridium perfringens
- Peptostreptococcus species
- Fusobacterium species
- Sexually transmitted bacteria, such as *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* (which causes gonorrhea), and *Chlamydia trachomatis* (which causes chlamydial infection), can also cause Bartholin gland abscesses.
2.2. Dental Cysts and Abscesses
A dental cyst is a small sac that appears around a tooth, forming at the root of a dead tooth or around a crown, etc.
A tooth cyst may remain small and cause no symptoms. If they grow, they can cause pain. If a tooth cyst becomes infected, it will become an abscess.
A tooth abscess is an acute infection that causes swelling and pain. Sometimes, bacteria causing the infection will cause bad breath.
3. Common Types of Cysts and Abscesses
Some common types of cysts and abscesses include:
- Abdominal abscess
- Amoebic liver abscess
- Anorectal abscess
- Bartholin gland cyst or abscess
- Brain abscess
- Dental cyst or abscess
- Pancreatic abscess
- Peripheral kidney abscess
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Pilonidal cyst
- Pyogenic liver abscess
- Oropharyngeal abscess
- Skin abscess
- Spinal cord abscess
- Subvaginal (perianal) abscess.
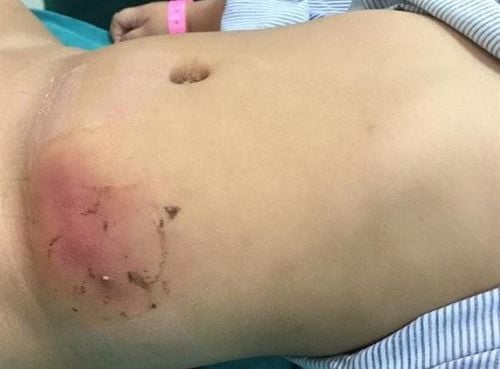
4. How to Treat Cysts and Boils, Abscesses?
Cysts and abscesses are treated differently depending on their extent and location. Some cysts may not require treatment, but if a cyst is causing pain or discomfort, it may need to be removed. Abscesses are often painful infections that need treatment to relieve pain and prevent the spread of infection. For cysts and abscesses in internal organs, blood tests should be performed to confirm infection. Imaging techniques include X-rays, CT scans, and MRI to determine the location. Treatment will vary depending on the type and location.
4.1. Bartholin's Gland Cyst or Abscess Bartholin's cysts
Bartholin's Gland Cyst or Abscess Bartholin's cysts may be asymptomatic and require no treatment. However, if the cyst has grown, causing discomfort, it should be drained. If an infected abscess is present and the area surrounding the abscess is swollen, red, and tender, it indicates cellulitis and should be treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics such as cefazolin, cefuroxime, ceftriaxone, nafcillin, or oxacillin. For large cysts or abscesses requiring drainage, a Word catheter is a safe method. First, a local anesthetic is administered; then, a small incision is made near the gland, and the Word catheter is inserted. The catheter has a small balloon that secures it; a small tube allows drainage.
4.2. Dental Cysts or Abscesses Dental
Dental Cysts or Abscesses Dental cysts may be asymptomatic, but abscesses are often painful and require immediate treatment. If a cyst occurs at the end of a dead root, root canal treatment may allow the cyst to heal. A small cyst may be removed with the affected tooth. Tooth abscesses often result from decay or a broken/chipped tooth, allowing bacteria to infect the pulp.
Antibiotics for tooth abscesses include amoxicillin, clindamycin, and metronidazole. Some cysts are small and asymptomatic; however, larger cysts can cause problems and sometimes lead to infection or an abscess. In contrast, an abscess is an acute infection requiring immediate medical attention.
Follow the Vinmec International General Hospital website for more health, nutrition, and beauty information to protect the health of yourself and your family.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.