This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Xuan Ninh - Emergency Department - Vinmec Central Park International Hospital
The kidney is the main organ that controls the correct level of potassium in the blood. Depending on what your doctor prescribes, people who take certain medications or have chronic kidney disease may need to limit the amount of potassium in their diet to help keep potassium levels within normal limits.
1. What is blood potassium?
Potassium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs potassium to help keep the heart beating, to help maintain fluid balance, and to allow nerves and muscles to function properly.
Normally, the potassium level in your body will be balanced by consuming foods containing potassium and at the same time eliminating excess potassium in the urine. However, people who have lost more than half of their kidney function are often unable to excrete enough potassium in the urine. In these people, potassium levels can become higher than normal, causing a condition known as hyperkalemia.
Potassium levels are measured by taking a blood sample from a vein. A normal blood potassium level is 3.8 to 5 mEq L. A blood potassium level greater than 6 mEq/L or less than 3 mEq/L is considered dangerous. In humans, blood potassium must be regulated to prevent serious complications.
Hyperkalemia usually does not cause noticeable symptoms, even at very high levels. At serum potassium levels above 6 mEq/L, ECG changes are common and the patient may feel unwell - a nonspecific symptom. At this level of blood potassium, dangerous complications can occur such as cardiac arrhythmias, severe muscle weakness, paralysis, even sudden death.
2. Diet to help lower blood potassium
For people with normal kidney function, experts recommend eating a diet with at least 4700 mg of potassium per day. People with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease should eat less than 3000 mg of potassium per day. Other restrictions should be made based on test results and the recommendations of the treating physician. Dietary hypokalemia is defined as 2000-3000 mg/day.
Dietitians can help you develop a low-potassium meal plan. Example 1 sample diet plan (tables 1 and 2):
Table 1. Low-potassium diet plan
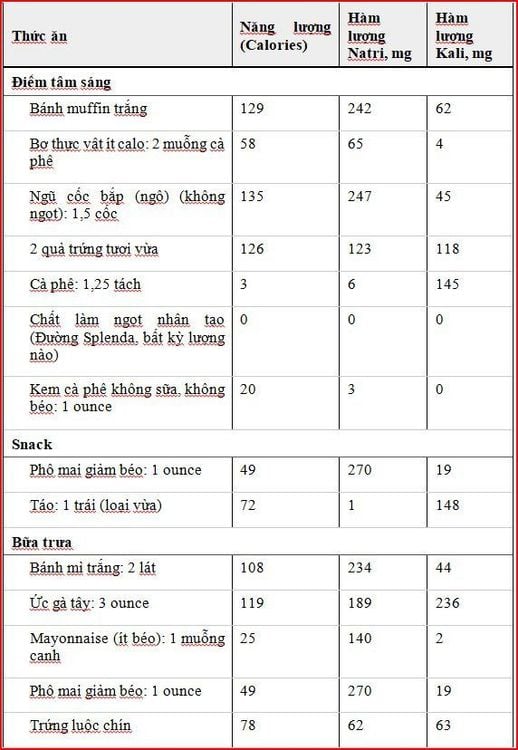
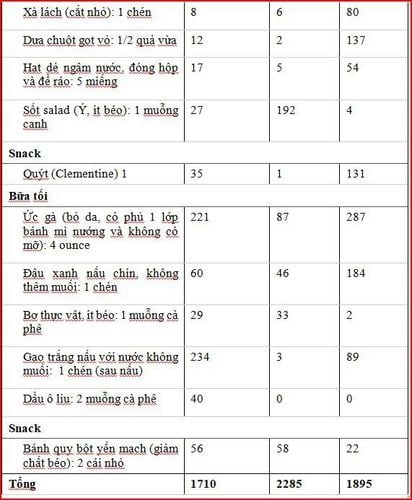
Note: This sample diet is calorie enough for people of small stature and low activity level. People who are active or older may need additional nutrients and calories. This diet contains less than 7% calories from saturated fat, which meets the American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines for nutrients.
Table 2. Low Potassium Foods
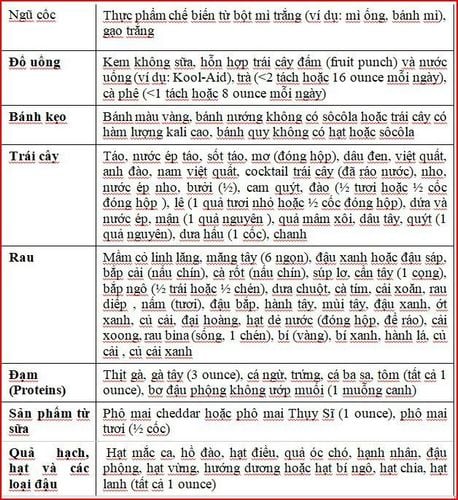
Note, one serving is 1⁄2 cups (4 ounces). These foods are low in potassium (average less than 200 mg of potassium per serving). Be sure to measure portions for each food and calculate the total amount at each meal to maintain a low potassium diet (e.g., an average of 2000 mg of potassium per day):
Fruit: 1 to 3 servings of low fruit potassium per day; Vegetables: 2 to 3 servings of low-potassium vegetables per day; Calcium and dairy foods: 1 to 2 low-potassium servings per day; Meat and meat alternatives: 3 to 7 low-potassium servings per day (about 15% of calories); Cereals: 4 to 7 servings of low-potassium cereals per day.

3. How to choose low-potassium foods?
To choose low-potassium foods for a hypokalemic diet, each person needs to:
Read food labels carefully: Almost all foods contain some amount of potassium. Therefore, it is important to choose low-potassium foods for your diet through food labels. Measure and note portion sizes when calculating potassium in foods: A large serving of foods that are low in sodium can have a high total potassium content. Using a smartphone with an online calculator can be very helpful in monitoring this situation. Be aware of low-potassium foods: You can eat low-potassium foods regularly. However, be mindful of portion sizes as your blood potassium can quickly rise if you eat a large serving. Reducing the potassium content of vegetables: Potassium in some high-potassium vegetables can be removed by a "washout" process. “Wrinkling” is the process of soaking raw or frozen vegetables in water for at least 2 hours before cooking to “pull” some of the potassium out of foods. Know which foods are high in potassium: Foods with the highest potassium content include: Cantaloupe, watermelon, grapefruit, all dried fruits, fruit juices, avocados, tomatoes sour cream, potatoes (smooth and sweet), Brussels sprouts, milk, yogurt, lentils and most nuts (except peanuts). Table 3. High Potassium Foods
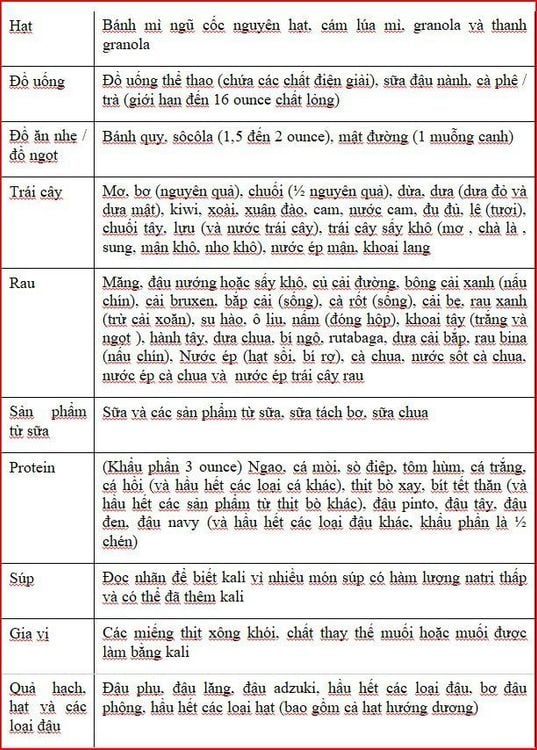
Note: 1 serving is 1/2 cup (4 ounces). These foods have more than 200 mg of potassium per serving. Therefore, it should be avoided or eaten in very small amounts if you are on a hypokalemic diet.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Update - Patient education: Low-potassium diet (Beyond the Basics)