This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Le Thi Minh Huong - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Hepatobiliary disease is closely related to the patient's diet and living habits. Therefore, in order for the disease not to progress seriously, and at the same time to prevent recurrence, patients with hepatobiliary disease need to have a scientific and healthy diet, and limit foods that are not good for the liver and bile.
1. Overview of liver and biliary diseases
The liver is an organ with many important functions such as: metabolism of glucide, metabolism of protein, metabolism of lipids, metabolism of minerals, metabolism of vitamins and detoxification (endogenous toxins, bacterial toxins, toxins). of alcohol and drugs, etc.).Bile has an important role in digestion, absorption of fats in food, absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, K,... However, the functions of the liver and bile have can be affected when liver cells are damaged or the diet is not reasonable.
Hepatobiliary disease can occur in any subject, regardless of age and sex. Irregular living habits, abuse of drugs and harmful stimulants, lack of periodic health check-ups,... are the causes of hepatobiliary diseases increasing strongly.
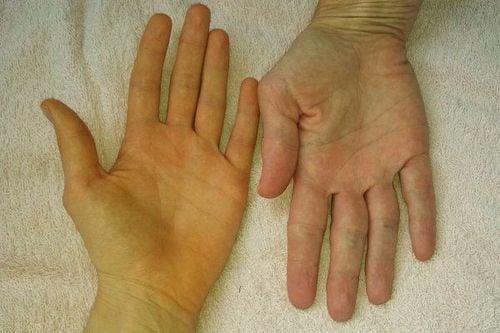
When suffering from hepatobiliary diseases, patients often have symptoms such as fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, jaundice, dark urine, flatulence, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, ascites, hepatomegaly, edema, bleeding,... Some hepatobiliary diseases such as liver dysfunction, fatty liver, cirrhosis, liver cancer, cholecystitis, gallstones,... not only affect daily activities but also It can also endanger the patient's life.
2. Principles of nutrition for patients with hepatobiliary disease
What do liver disease patients eat? Some of the principles of nutrition patients need to keep in mind include:Reduce dietary lipids: When liver cells are damaged, their cytoplasm will produce fat droplets that can kill cells - a phenomenon fatty degeneration of the liver. Therefore, people with hepatobiliary disease should limit lipids in the diet; Increase dietary glucose: Normally, some of the glucose from food is stored in the liver as glycogen. The function of metabolism and glycogen storage helps the liver to take on the role of detoxifying the body. When the liver is damaged, glycogen in the liver is reduced, so the diet needs to be fortified with more glucose to create more glycogen in the liver; Increase protein in the diet: The regeneration of liver cells requires a large amount of protein. The diet needs to be fortified with protein to help the liver fight poisoning due to arsenic, chloroform and carbon tetrachloride.
3. Proper nutrition for hepatobiliary diseases
3.1 Diet for hepatitis patients Acute hepatitis
In the early stages of acute hepatitis, when the patient is feverish, nauseated or vomiting: Should drink sugar water, fruit juice, vegetable broth. People with anorexia or vomiting can add 20% glucose intravenous drip; When the patient has no fever, nausea or vomiting: Skimmed milk, sweetened condensed milk, soup, porridge, pho and fruits of all kinds should be used; Resuscitation phase: Give the patient milk to drink because milk contains a lot of good protein and methionine helps to protect the liver. At the same time, the patient should eat more eggs, meat, fish, tofu to supplement protein. At this stage, because the progression of the disease cannot be predicted, it is necessary to apply a hepatoprotective diet for at least 3 consecutive months in combination with careful monitoring of the disease.

When the acute phase and resuscitation have passed, patients with chronic hepatitis have liver weakness for a long time, even for a lifetime, so it is necessary to monitor the patient for many years, ensuring the correct diet according to the principles of nutrition. nursing. Some important notes:
Eat many meals for the best absorption of nutrients by the body; Avoid shrimp, snails, crabs, ... because seafood can cause allergies; Only fresh fish and eggs should be eaten; do not eat rotten fish and eggs for a long time; Fat: Only butter and vegetable oil should be used and avoid frying and stir-frying dishes. At the same time, limit the use of animal fat; Make sure to eat enough carbohydrates found in rice, noodles, corn, potatoes,... In the progression of chronic hepatitis: Patients should be given a diet similar to acute hepatitis.
3.2 Diet for cirrhosis patients Diet therapy has the effect of supporting, improving and restoring the function of weakened liver cells, avoiding complications of hepatic encephalopathy. The patient's diet is as follows:
Compensated cirrhosis (stage without ascites)
It is necessary to maintain a reasonable and almost normal diet, including adequate protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and minerals. minerals, avoid excessive abstinence. At the same time, it is recommended to divide meals and change the way of food preparation to create palatability for the patient.
Protein: Should use proteins with high biological value, low in fat such as lean chicken, lean fish, and pork. lean, eggs, skimmed milk, beans and bean products; Fat: Should reduce animal fat, limit fried foods, prioritize using vegetable oil and butter, do not cook at high temperature; Powdered sugar: Should increase easily absorbed starch such as rice, potatoes, honey, sweet fruits; avoid eating confectionery with lots of buttermilk, jam, soft drinks;

The principles and goals of eating are the same as those of compensated cirrhosis, but attention should be paid to the following issues:
Reduce protein, reduce salt, increase fiber in green vegetables, fruits to laxative, make sure to go 2-3 times/day; Eat more green vegetables and fruits to increase the patient's potassium supply; Ensure the amount of water to drink 1 - 1.2 liters/day and prioritize drinks and foods with bile and liver laxative properties such as green tea leaves, bare kernels, artichoke flowers,... 3.3 Nutrition for the disease Hepatic coma Hepatic coma is the final stage of liver diseases. Nutrition for patients with hepatic coma should pay attention to the following:
Do not use protein through food and do not transmit amino acid solutions such as moriamin to the patient. However, if infusion of branched-chain amino acids in patients can be improved brain syndrome in hepatic coma; Provide about 1700 - 1800 calories/day of energy from glucid and lipid to limit protein degradation; Infuse 30% glucose solution and add insulin in appropriate amount; Supplementing with vitamin B1 and vitamin C by injection; Add a laxative. When there are signs of good disease progression, increase to 20g of protein/day, of which half is vegetable protein (from soy milk or mung bean powder).
3.4 Diet for patients with gallbladder and bile ducts Acute cholecystitis
For patients with acute cholecystitis, the treatment should pay attention to rest the gallbladder, so the diet should be eliminated or Reduce protein and fat (because they make the gallbladder contract more). Therefore, the patient's diet is mainly glucid such as sugar water, vegetable juice, fruit juice, adding cereal flour, mashed potatoes, reducing salt and eating more fiber to prevent constipation. Patients can also add skimmed milk.

Patients with chronic cholecystitis often have symptoms of digestive disorders, so the diet should ensure that there is no additional burden on the function of the biliary tract. Specifically:
Limit fat because fat makes bile go to the intestines irregularly, increasing toxins into the blood and affecting the liver; With foods rich in protein: Should eat less meat every day, should use white meat and lean meat, no fat, simple processing. Plant proteins such as beans and peas should be eaten in the form of simmered or crushed; With foods rich in glucid: Should use a lot of sugar because it is easy to digest and does not adversely affect bile. Patients with chronic cholecystitis should not use chocolate, cakes, ... because it causes indigestion. Gallstones
To avoid stagnation of bile and biliary tract infections, should limit foods that cause constipation because constipation will create an opportunity for intestinal bacteria to grow, leading to duodenitis, inflammation of the bile duct and gallbladder, makes bile more prone to deposition and stone formation.
To avoid the risk of forming cholesterol stones, should limit foods high in animal fat and cholesterol. Such foods are egg yolks and animal viscera.
People with hepatobiliary diseases need to maintain a reasonable and scientific diet to support disease treatment, control disease symptoms and prevent potentially dangerous complications.
In order to detect liver and biliary diseases at the earliest, you should have regular health checkups or perform a hepatobiliary screening as soon as your body has unusual symptoms related to hepatobiliary. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has Hepatobiliary Screening packages, which help detect Hepatitis Virus at an early stage even when there are no symptoms and other liver diseases. In addition, the comprehensive hepatobiliary screening package helps customers:
Assess the liver's ability to work through liver enzyme tests; Evaluation of bile function; vascular nutrition; Early screening for liver cancer; Perform tests such as Total blood cell analysis, blood clotting ability, screening for hepatitis B, C Assessment of hepatobiliary status through ultrasound images and diseases that have the potential to affect liver disease/cause liver disease. more severe liver disease In-depth analysis of parameters to evaluate hepatobiliary function through laboratory, subclinical; the risk of affecting the liver and early screening for hepatobiliary cancer.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.