This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Master, Doctor Nguyen Nhu Thu Truc - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
Pregnant women are diagnosed with anemia when Hb is less than 11g/dl. Anemia during pregnancy will adversely affect not only the mother but also the fetus.
1. What is the problem of anemia in pregnant women?
Like normal people, to determine whether or not anemia is required by testing the hemoglobin (Hb) level in the blood. Pregnant women are diagnosed with anemia when Hb is less than 11g/dl.
Although there are many causes of anemia, in pregnant women, the most common cause of anemia is iron deficiency. This is the result of the body not being supplied with enough iron needed to make hemoglobin, a protein-based component responsible for the main function of red blood cells.
Women of reproductive age are inherently subject to a very high risk of anemia, during pregnancy, the need for iron increases many times to supply the fetus. At this time, anemia is further promoted. Therefore, women who are malnourished before pregnancy with poor nutrition and lack of proper rest will cause anemia even more.
2. How dangerous is anemia in pregnancy?
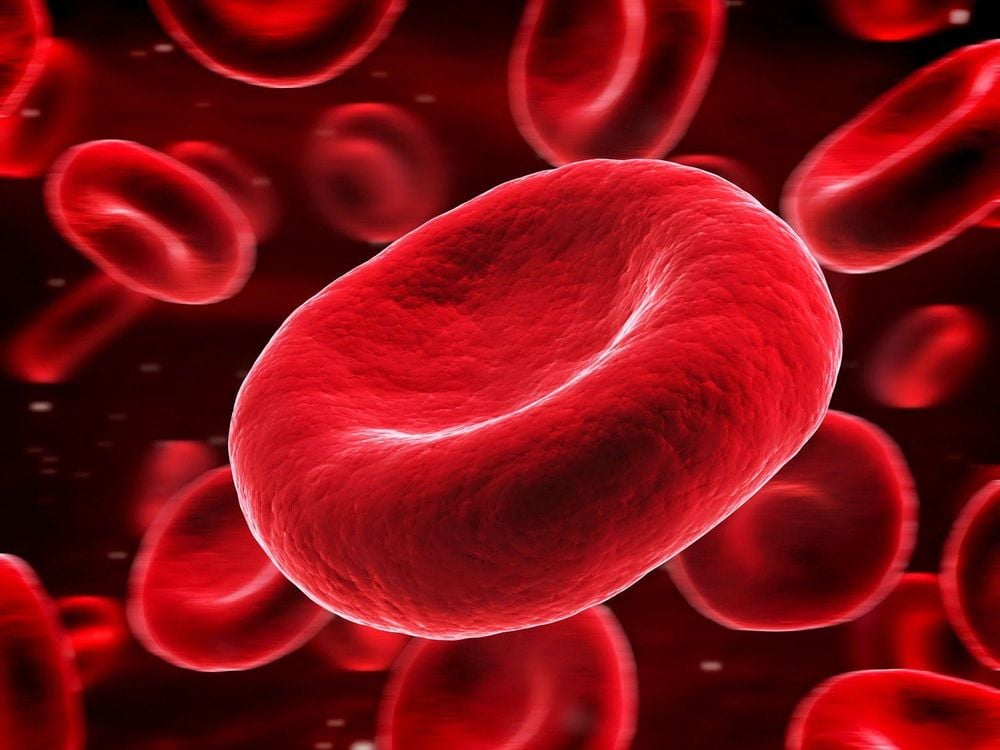
The role of hemoglobin is to carry oxygen with the blood stream to provide energy-generating metabolism in each cell, especially in important organs such as the brain and heart. Therefore, in normal people, anemia will make the body weak, tired, reduce the ability to exercise, poor concentration. If anemia progresses for a long time, it will increase the risk of malnutrition, cardiovascular diseases, and recurrent infections. However, anemia in pregnant women will adversely affect not only the mother but also the fetus.
For women, miscarriage is likely to happen in the first trimester or stillbirth or premature rupture of membranes, placental abruption, premature birth in the last trimester. At the same time, the pregnancy period also faces a high risk of gestational hypertension, preeclampsia - eclampsia, amniotic infection, premature rupture of membranes; the labor period is prone to prolonged labor, postpartum hemorrhage, postpartum infection. When the baby is born, the mother may have a lack of milk to feed the baby, easily exhausted...
For the fetus, chronic fetal distress due to malnutrition is common. Babies born with low birth weight, premature birth, jaundice after birth, prolonged nursing treatment time. Besides, children of mothers with anemia during pregnancy will have an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases than other children later in life. On the other hand, if the diet lacks folic acid, it can cause neural tube defects in the fetus such as craniofacial defects, split spine; Iodine deficiency causes children to be born with congenital hypothyroidism, mental retardation, mental retardation...
Therefore, maintaining hemoglobin within physiological limits is very important in the general population. pregnant women in particular. At the same time, a pregnancy with iron deficiency anemia would be considered a high-risk pregnancy.
3. How to choose food for pregnant women with anemia?

Nutrition is always the first concern of pregnant mothers, but when pregnant women with anemia should eat what to eat, they need specific instructions.
In which, a prerequisite is a menu that must meet the requirements of providing adequate energy in accordance with each stage of pregnancy and must be rich in ingredients. At the same time, pregnant women should focus more on iron-rich food sources.
Iron is observed to be abundant in foods with dark red and dark green colors, such as red meat (beef, pork, lamb... the darker the meat, the more iron it contains), fatty fish. , molluscs (scallops, snails, mussels...), liver, egg yolks, beans and other vegetables (watercress, broccoli, spinach, linden,...). Iron from foods of animal origin will be better absorbed than iron from plant sources. Specifically from animal protein such as meat, fish and especially poultry eggs. Eggs of chickens, ducks or poultry in general are a rich source of iron as well as other nutrients such as protein, calcium, phosphorus, minerals and many vitamins that are beneficial for the development of the fetus as well as the health of the fetus. health of pregnant women. In it, most of the nutrients in the egg are concentrated in the yolk while the white contains only protein. Therefore, the simplest source of nutrition that doctors often recommend is that every week pregnant women should eat three to four eggs to both increase the mother's physical strength and provide nutrients for the fetus.
The absorption of iron will become more effective if pregnant women also consume foods rich in vitamin C after meals. At this time, the source of fresh tropical fruit will allow a variety of choices for pregnant women. Those are acidic fruits such as guava, orange, tangerine, grapefruit, strawberry, tomato, kiwi, papaya, acerola... Should eat whole fruit instead of squeezing to get juice, because fruit also provides quantity High in fiber, helping pregnant women to defecate easily, preventing constipation.
Besides, the supply of iron will be limited if the mother accidentally takes it with substances that inhibit iron absorption. It is the tannin found in tea or the phytate in raw grains. Also, limit your intake of dairy products because dairy products block the absorption of iron from food, especially for women; If used, should be taken away from the main meal. Similarly, caffeine also inhibits the absorption of iron from food; Therefore, do not drink coffee, coke or carbonated soft drinks during meals but only drink 2 hours after eating.
4. Other sources of iron for pregnant women with anemia
To control iron deficiency anemia in particular or micronutrient deficiency during pregnancy in general, in addition to the daily diet, pregnant women need to actively supplement with special multivitamins. for pregnant women.
Particularly for pregnant women who have problems with small red blood cell anemia due to prominent iron deficiency, they must also take an iron pill in combination with folic acid. This should be maintained regularly from the time the pregnancy is discovered until at least one month postpartum, because the newborn is still at risk of iron-deficiency anemia when the mother's milk supply is not guaranteed.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.