This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Vu Duy Dung - Department of General Internal Medicine - Vinmec Times City International HospitalBecause of the scarcity of TB bacteria in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), the diagnosis of CNS TB can be difficult. There are many diagnostic tests that can be used; This article presents groups of tests and provides an approach to the diagnosis of CNS TB infection. Hyponatremia occurs in nearly 45% of patients with tuberculous meningitis and is largely due to cerebral salt loss.
1.Test sensitivity and specificity
The diagnostic sensitivity of a test for a CNS infection is defined as the proportion of people with a CNS infection who test positive, while specificity is the proportion People without central nervous system infections have negative test results.
Although optimal CSF testing will identify CNS infection in all individuals with infection and rule out infection in all individuals without infection (100% sensitivity and specificity). 100%), most tests have either high sensitivity or high specificity, but not both.
If diagnostic sensitivity is low, a high percentage of tests will not detect an infection if present (many false negatives), whereas if specificity is low, a high percentage of tests will result infection even though it is practically absent (many false positives). Since most CNS infections are severe and many are treatable, it is often more important to have a highly sensitive CSF test so as not to miss the diagnosis of a CNS infection.
2. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
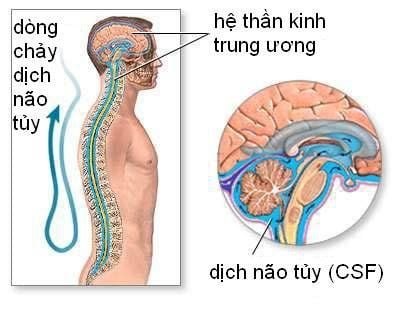
One of the first descriptions of lumbar puncture was by Wynter in 1891 when he used a trocar to alleviate hydrocephalus from tuberculous meningitis in four patients. Compared with other CNS infections, tuberculous meningitis typically causes mild leukocytosis similar to viral or fungal meningitis but with higher protein elevation than most other CNS infections. .
In a study of 84 patients with tuberculous meningitis, CSF leukocytes in 253 samples ranged from 5 cells/mm3 to 2021 cells/mm3, with 85% of samples ranging from 50 cells/mm3 to 500 cells/ mm3. CSF protein is often elevated in tuberculous meningitis, and if CSF is left upright at room temperature for 6 to 12 hours, the protein can form a fine fibrin clot (also called a pellicle or network) spider [spiderweb]).
Longitudinal studies of CSF abnormalities have found delayed normalization of protein levels and cell counts; In only 2 (4%) of 45 patients, protein levels were normalized at 6 months, and in 6 patients (13%) normalization took more than 1 year.
Average time for protein to return to normal is 8 months. With CSF cell counts, although cell counts decreased by 50% at 1 month in 96% of patients, 36% had CSF cell abnormalities at 6 months and 16% at 24 months. Normalization of CSF glucose levels occurred more rapidly, with 58% returning to normal by 1 month and 88% to normal by 2 months.
3.Adenosine Deaminase
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) is an enzyme in purine metabolism involved in the reproduction and differentiation of lymphocytes. ADA is produced by the cerebral cortex and lymphatic tissue, with increased concentrations reflecting nonspecific CNS damage and increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier.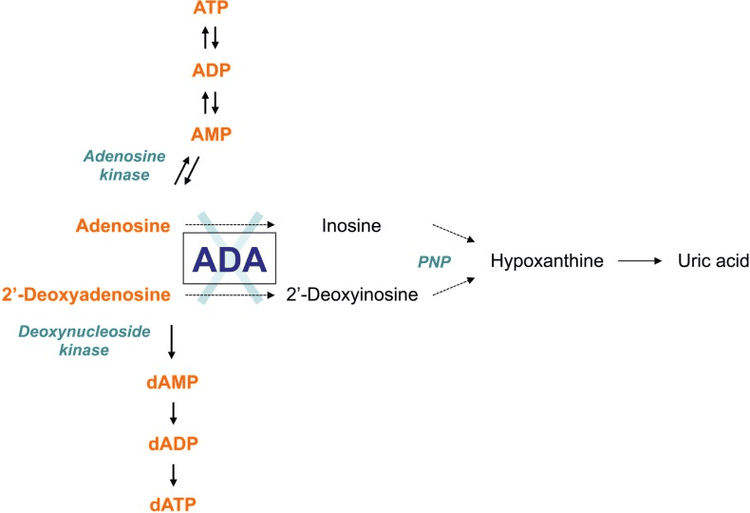
Elevated CSF ADA is associated with most forms of meningitis and is closely correlated with CSF protein levels. In many parts of the world, culture and PCR of CSF mycobacteria are not available, and the ADA test is commonly used to help differentiate between meningitis caused by M. tuberculosis and meningitis caused by other bacteria or viruses.
Although increases in ADA are not specific for tuberculous meningitis, elevations are associated with a poor prognosis of tuberculous meningitis in children. In a meta-analysis, an ADA higher than 8 U/L improved the diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis (sensitivity < 59% and specificity > 96%), but most experts agree that the causative organism Other diseases, especially bacterial, should be ruled out before being attributed to M. tuberculosis infection.
4.Staining and culture of acid-fast bacilli
Central nervous system tuberculosis is difficult to diagnose by Ziehl-Neelsen staining (acid-fast bacilli) and traditional cultures of mycobacteria and is most valuable when performed by a skilled technician.
When only one sample is tested for CSF, the sensitivities of smears and cultures are 37% and 52%, respectively, while if three CSF samples are tested, the values increase to 87% and 83%.
Unfortunately, CSF cultures usually take 2 to 4 weeks to become positive, so when CNS TB is suspected, empiric treatment for the follow-up diagnosis of CNS TB needs to be done. is initiated before the diagnosis is established.
HIV status should be firmly established at the time of diagnosis because co-infection reduces the sensitivity and specificity of the TB test as well as the differential diagnosis of CNS lesions, especially when there is only one central nervous system lesion.
5. PCR TB
Most PCR tests for the detection of M. tuberculosis amplify the MPB64 or IS6110 gene, a multiple-copy insertion in the M. tuberculosis genome. The sensitivity and specificity of PCR tests for M. tuberculosis is highly dependent on the diagnostic criteria used, the amount of CSF tested, and whether anti-tuberculosis drugs are prescribed prior to CSF collection.
Two PCR tests for the detection of M. tuberculosis have been licensed in the US for testing respiratory specimens: the direct amplified MTB test and the MTB Amplicor test. These tests can be performed on samples of cerebrospinal fluid.
PCR tests may be more sensitive than CSF cultures, but a diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis cannot be ruled out based on a negative PCR result. Where available, TB PCR tests may be a valuable additional tool for detecting TB infection.
6.Cartridge-based nucleic acid amplification assay
A cartridge-based nucleic acid amplification test that can detect M. tuberculosis in clinical specimens as well as mutations associated with rifampin resistance; The detection of rifampin-resistant bacteria can influence the decision to switch to second-line drugs. In 2013, WHO endorsed the MTB/RIF Xpert test as an appropriate initial test for the investigation of tuberculous meningitis.
Since WHO confirmation, a more improved test from the same manufacturer has been released, with early studies suggesting it is more sensitive and specific for the diagnosis of meningitis due to TB. The advanced test uses a larger chamber to amplify DNA and adds two more molecular targets to detect TB.
In a prospective cohort study of 129 patients with HIV infection and suspected TB meningitis, the test was more sensitive than culture or prior testing for the diagnosis of TB meningitis, with a higher degree of sensitivity. sensitive 95%, compared with 45% sensitivity of pre-assay or mycobacterial growth indicator tube culture.
Of the 21 cases detected by advanced testing, eight (38%) were not detected by prior tests. Although the value of the CSF test increases with these tests, none of them reach 100% sensitivity, so the clinician if there is a high suspicion of CNS TB (eg. , a patient with meningitis in the setting of hyponatremia and pulmonary lymphadenopathy) should still consider initiation of empiric anti-tuberculosis therapy.
7. Biopsy
Biopsy may be a useful adjunct test for patients with isolated lesions with enhanced enhancement or with chronic meningitis with negative repeated cultures.
Although the sensitivity of biopsy is unknown, in theory, treatment of an infected tissue with Ziehl-Neelsen (acid-fast bacilli) staining, culture, and PCR testing should increase the diagnostic value.
For cases of CNS tuberculosis that are not suspected at the time of biopsy, healthcare professionals should consider sending formalin-fixed or paraffin-coated tissue for PCR testing despite its low sensitivity than fresh tissue.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, a system of modern equipment and technology. The hospital provides comprehensive and professional medical examination, consultation and treatment services, with a civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to the source:
Zunt JR. Tuberculosis of the Central Nervous System. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2018;24(5, Neuroinfectious Disease):1422–1438