This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thanh Hai - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
A herniated disc is a condition in which a disc due to degeneration or trauma comes out of its place, compressing the nerves of the spinal cord. To diagnose a herniated disc, it is necessary to have information from imaging methods such as X-ray, CT-scan or MRI. This not only enhances the diagnostic ability, but also provides information for the treatment process.
1. What is herniated disc disease?
Herniated disc is a condition in which the mucous nucleus of the disc for some reason (possibly due to trauma or degeneration) comes out of its normal position. The herniated mass can move to the back, sides of the spine or to the front, pressing on the spinal cord. Therefore, patients with disc herniation often have chronic back pain.
Herniated discs can originate from areas of the spine with pre-existing degeneration, when traumatized slowly or suddenly, it can cause rupture or damage to ligaments causing disc herniation. Disc herniation can also occur in patients with perfectly normal discs but due to sudden spinal trauma with enough force to damage the spine and cause disc herniation.
Some of the factors that promote disc herniation include the following:
Age: The older the patient, the higher the risk of spondylolisthesis and is the leading cause of herniated disc. cushion. Cell death: Cells in the body will be programmed to die according to an existing program. This increase in cyclic death in the disc also contributes to disc herniation. Abnormalities in collagen. Abnormal blood vessels. Carry heavy objects frequently. Abnormal proteoglycans. Fat. Sedentary lifestyle. Poor fitness. The clinical manifestations of disc herniation include 2 main syndromes, spinal syndrome and nerve root syndrome.
Spine syndrome: Including signs of scoliosis, spastic paraspinal muscles, patients with limited range of spine motion, occurrence of spinal pain points, Schober index reduction below 13/10 , measure finger distance – ground rise. Nerve radiculopathy: Patient has paravertebral pain points, may have positive "ringing" sign, positive Valleix pain points, positive Lasègue test. Patients may also have motor and sensory disturbances under the control of the compressed nerve root.
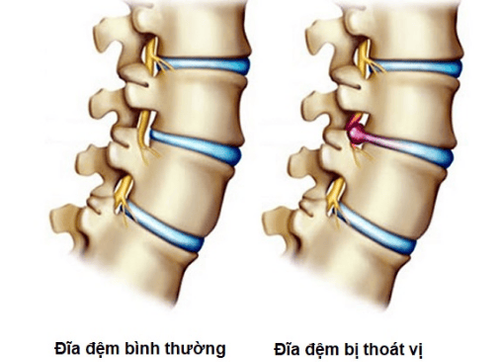
2. Imaging diagnostic methods for spinal disc herniation
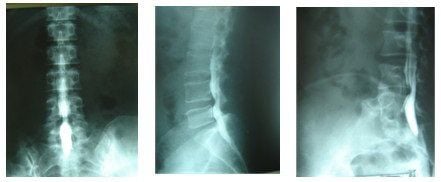
2.1. Routine X-ray
In patients with disc herniation, X-rays of the spine must be taken in both straight and lateral positions to be able to see Barr's triad:
Scoliosis on straight film. Decreased intervertebral height. The curvature of the spine on tilt film is reduced. The disc is an organ that is not contrasted on X-ray, so it cannot be seen directly. Herniation on X-ray can only be evaluated indirectly through the change of characteristics such as vertebral dilatation distance, adjacent vertebrae and spine curve.
2.2. Nerve root capsule
By using contrast material injected into the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord, then the patient is radiographed in two upright positions – tilted and 3⁄4 right and left. Disc herniation will be diagnosed based on seeing the image of nerve root amputation, the concave impression of the contrast column, (also known as the hourglass sign), the image may also be a column disruption. drug or complete amputation of the contrast column. Nerve capsule is a method to provide doctors with indirect images of disc herniation through images of spinal stenosis, synaptic foramen. However, the limitation is that because direct image of the disc cannot be obtained, there are some cases where compression cannot be distinguished from other causes. Currently, there are many advances in the field of imaging, the introduction of resonance imaging brings many benefits in the diagnosis of disc herniation, so nerve sheath imaging is rarely applied.
2.3. Computed tomography (CT) scan
Computed tomography is very valuable in cases of disc herniation accompanied by degenerative conditions of the components of the spine such as: bones, ligaments, joints... Signs of degeneration may be present. Visible calcification of the posterior longitudinal ligament, thickening of the yellow ligament and the beak. However, computed tomography has limitations in evaluating soft tissue structures such as disc tissue and the extent of herniation.2.4. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
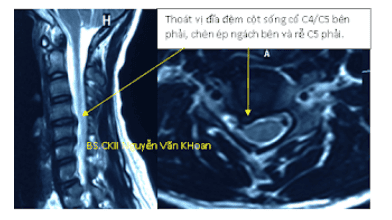
Thanks to the principle of magnetic resonance, on the magnetic resonance effect of organizations with many countries, there will be a decrease in signal on T1 image and an increase in signal on T2 image. The normal disc tissue is well demarcated, the signal on T1 is decreased and the signal on T2 is increased due to excess water. In discs that begin to degrade, because of the absence of water, the signal on T2 is not increased when compared to surrounding discs. The images of herniated disc masses are concentric with the disc and protrude posteriorly to the posterior border of the vertebral body. The hernia mass can be clearly seen on T1W and T2W images. The most common hernia location is posterior, based on longitudinal or transverse views to evaluate hernias. To accurately determine the position of the herniated disc compared to the location of the canal and the degree of spinal cord and nerve root compression.
Magnetic resonance imaging is considered a valuable test as a "gold standard" in the diagnosis of disc herniation. MRI imaging allows to exclude lesions within the spinal cord. The advantage of magnetic resonance imaging shows the image of the canal, the disc image with high resolution, observed in many different directions. Besides, MRI is a safe and non-toxic method for patients.
For accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, patients need to go to a reputable hospital to conduct examination and treatment as soon as there are signs of spinal disc herniation. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading prestigious hospitals in the country, trusted by a large number of patients for medical examination and treatment. Not only the physical system, modern equipment: 6 ultrasound rooms, 4 DR X-ray rooms (1 full-axis machine, 1 light machine, 1 general machine and 1 mammography machine) , 2 DR portable X-ray machines, 2 multi-row CT scanner rooms (1 128 rows and 1 16 arrays), 2 Magnetic resonance imaging rooms (1 3 Tesla and 1 1.5 Tesla), 1 room for 2 levels of interventional angiography and 1 room to measure bone mineral density.... Vinmec is also the place to gather a team of experienced doctors and nurses who will greatly assist in diagnosis and detection. early signs of abnormality in the patient's body. In particular, with a space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec ensures to bring the patient the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.