This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Doctor of Radiology, Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Carotid stenosis is a narrowing of the large arteries on either side of the neck that carry blood to the head, face, and brain. This condition is often the result of a buildup of plaque in the arteries known as atherosclerosis. Carotid stenosis can worsen over time and can completely block the artery leading to a stroke.
1. What is carotid stenosis?
The carotid arteries are two large blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the large front part of the brain. This is responsible for thinking, speech, personality, and sensory and motor functions. You can feel the pulse of the carotid artery on each side of your neck, just below the angle of the jaw line.
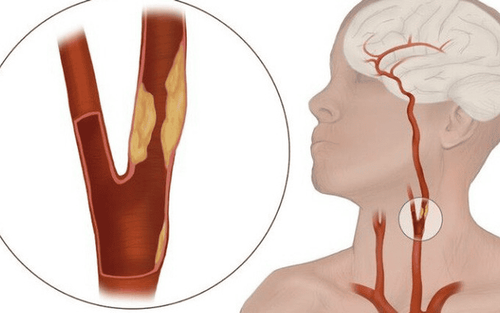
Like the arteries that supply blood to the heart (coronary arteries), carotid arteries can also develop atherosclerosis or harden on the inside of blood vessels.
Atherosclerosis is the accumulation of cholesterol, fats and other substances that travel in the blood stream, such as inflammatory cells, cellular waste products, proteins and calcium. These substances stick to the walls of blood vessels, over time these substances stick to the walls of blood vessels as people age and combine to form plaque. Over time, the accumulation of fats and cholesterol narrows the carotid arteries (Carotid artery disease or carotid artery stenosis). This reduces blood flow to the brain and increases the risk of stroke.

Bệnh nhân hẹp động mạch cảnh có thể tăng nguy cơ đột quỵ
A stroke is similar to a heart attack, a brain stroke occurs when blood flow is cut off from part of the brain. If the lack of blood flow persists for more than three to six hours, permanent brain damage can result. A stroke can happen if:
An artery becomes extremely narrow There is a tear or rupture in an artery that has atherosclerosis and travels to the brain Plaque breaks off and travels to smaller arteries in the brain Blood clots The formation and blockage of blood vessels Stroke can occur from many conditions other than carotid artery disease. For example, sudden bleeding in the brain, known as an intracerebral hemorrhage, can also cause a stroke. Other possible causes include:
Sudden bleeding in spinal fluid - subarachnoid hemorrhage Atrial fibrillation Cardiomyopathy High blood pressure Obstruction of small arteries inside the brain
2. Symptoms and risk factors of carotid stenosis
2.1. Symptoms of carotid artery stenosis
The patient may not have any symptoms of carotid artery disease. However, you may have warning signs of a stroke. A transient ischemic attack (also called a TIA or "mini-stroke") is one of the most important warning signs of a stroke. A TIA occurs when a blood clot suddenly blocks an artery that supplies blood to the brain. The following symptoms of TIA are temporary and may last for a few minutes or hours, and may occur alone or in combination:
Sudden loss of vision or blurred vision in one or both eyes Weakness and/or numbness on one side of the face, or an arm or leg, or one side of the body Speaks slowly, has trouble speaking, or has trouble understanding what others are saying Loss of coordination Dizziness or confusion Difficulty swallowing

Mất thị lực là triệu chứng thường gặp của TIA
A TIA is a medical emergency, as it is impossible to predict whether it will progress to a major stroke. If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, get emergency help. Immediate treatment can save a person's life or increase the chance of a full recovery.
TIAs are strong predictors of future stroke; a person who has undergone a TIA is 10 times more likely to have a stroke than a person who has not undergone a TIA.
2.2. Risk factors for carotid artery stenosis
Factors that increase the risk of carotid artery disease include:
High blood pressure: Excessive pressure on the artery walls can weaken the vessel walls and make them more susceptible to damage. Tobacco use: Nicotine can irritate the inner lining of the arteries, and smoking also increases heart rate and blood pressure. Diabetes: Diabetes reduces your ability to efficiently process fat, putting you at risk for high blood pressure and atherosclerosis. High levels of fat in the blood: High levels of LDL cholesterol (low density lipoprotein cholesterol) and high levels of triglycerides will facilitate the accumulation of plaque in the arteries. Family history: The risk of carotid artery disease is higher if a close relative has atherosclerosis or narrowing of the coronary arteries.

Hút thuốc là một yếu tố nguy cơ của bệnh hẹp động mạch cảnh
Age: Arteries become less flexible and more prone to injury with age. Obesity: Excess weight increases the likelihood of high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and diabetes. Sleep apnea can increase your risk of stroke. Lack of exercise: This factor contributes to diseases that damage the arteries, including high blood pressure, diabetes and obesity.
3. Diagnostic imaging in the carotid artery
Usually people have no symptoms of carotid artery disease until a TIA or stroke. That's why regular health checkups are so important. Your doctor can listen to the arteries in your neck with a stethoscope. If there is an abnormal sound, it is called a carotid murmur.
Listening to neck murmurs is a simple, safe, and inexpensive way to screen for carotid stenosis, although this technique may not detect all blockages. Some experts believe that a murmur may be a better predictor of atherosclerosis than stroke risk. However, you should let your doctor know if you have had any of the symptoms listed above.
Imaging techniques used to diagnose, locate and measure the severity of carotid stenosis include:
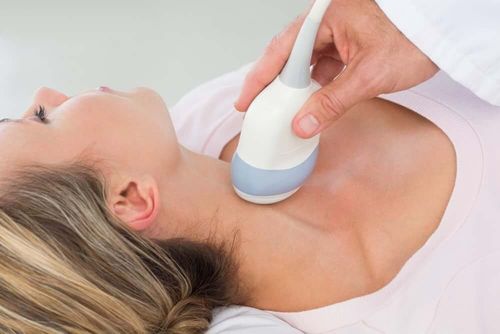
Carotid ultrasound (including Doppler ultrasound): This technique uses uses sound waves to create real-time images of the arteries and locate blockages. Doppler is a special ultrasound technique that can detect areas of reduced blood flow in the arteries.
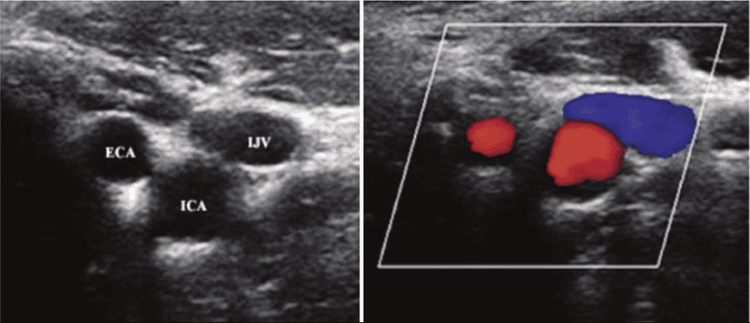
Siêu âm Doppler giúp chẩn đoán bệnh động mạch cảnh
Computed tomography angiography (CTA): CTA uses a CT scanner to create detailed images of arteries anywhere in the body - in the case of stenosis The carotid artery is in the neck. This technique is especially useful for patients with pacemakers or stents. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA): This noninvasive technique provides information similar to that of CTA but does not use ionizing radiation. Cerebral angiography: Cerebral angiography is a minimally invasive diagnostic technique in which a catheter is guided from an artery to the area to be examined. Contrast is injected through the tube and the image will be taken by X-ray. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of facilities, modern medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors for many years With experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured that they will be examined and treated at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: radiologyinfo.org, mayoclinic.org, my.clevelandclinic.org