This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist Doctor II Pham Thi Van Hanh - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Currently, diphtheria drugs are mainly made from horse serum, diphtheria antitoxin made from human serum is very rare. Early detection and treatment of diphtheria is key, which requires hospitalization for treatment and isolation as soon as possible.
1. Diphtheria progression and prognosis
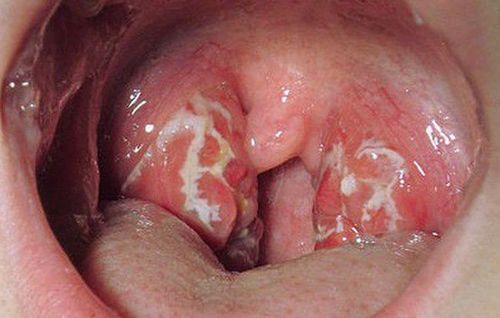
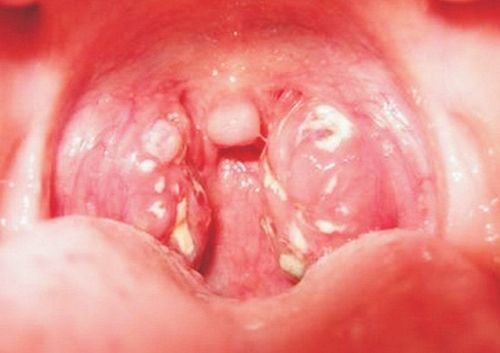
Pseudocyst lasts 3-4 days in mild form, about 1 week in severe form if antitoxin is not used. With antitoxin, pharyngeal lesions still develop during the first 24 hours. then the pseudomembrane softens, gradually peels off, does not bleed, and disappears.
Prognosis depends on:
Early diagnosis and treatment. Mortality before SAD: 20-30% of moderate cases. 80-90% in the larynx. When there is SAD, mortality is reduced to 3.5 - 22%, of which the highest rate is still found in laryngeal diphtheria. If diagnosed and treated late after 4 days, the mortality rate increases up to 20 times (according to FEIGIN) Immune status: The malignant form of diphtheria increases 15 times in cases of immunosuppression. Prognosis is severe when leukocytes are over 25,000, platelets decrease, atrioventricular dissociation, ventricular arrhythmias.
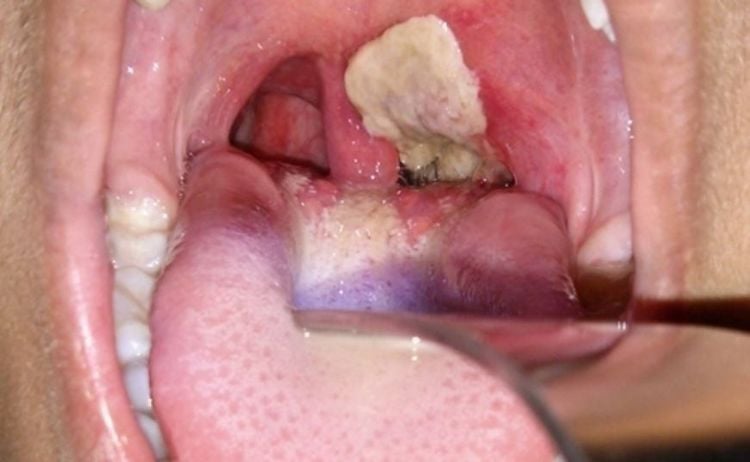
Bạch hầu thanh quản vẫn là thể thường gặp nhất
2. Diagnosing diphtheria
2.1. Definite diagnosis Based on clinical + epidemiological + laboratory tests:
Clinical: Signs of severe toxicity/slight fever. throat, white blood cells increased + Pseudomembranous specific for diphtheria bacteria Epidemiology: Surrounded by children with the same disease, in contact with patients, outbreaks, outbreaks. Tests: Fresh scan, culture with diphtheria bacteria in throat, culture on potassium Terullit medium or cause disease in guinea pigs. 2.2 Differential diagnosis Differential diagnosis with diseases with pseudomembranous membranes: Pharyngitis caused by staphylococci, streptococci. Vincent pharyngitis, viral pharyngitis, Herpes , Candida, necrotizing pharyngitis. Infectious mononucleosis Differentiate from diseases that cause laryngeal dyspnea: Acute laryngitis, caused by measles virus, abscess in the back of the pharynx, foreign body in the larynx
3. Treatment of diphtheria
Early detection and treatment of diphtheria is key, which requires hospitalization for treatment and isolation as soon as possible. Before SAD 30-50% TV due to asphyxiation. Currently 5% of TV due to myocarditis (most common laryngeal diphtheria)
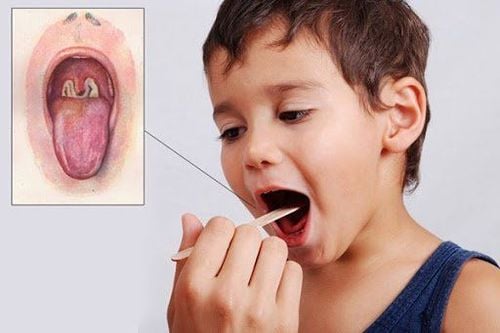
Cần phát hiện và điều trị bệnh bạch hầu sớm để cho kết quả tốt nhất
3.1 Principles of treatment: Early detection - early diagnosis Timely bactericidal antibiotic treatment Isolation for 10 -14 days, absolute bed rest Drugs neutralize toxins as soon as possible Early detection of complications , timely treatment Anti-relapse and superinfection. Adequate nutrition, if swallowing is difficult to eat through the tube 3.2 Specific treatment Diphtheria antitoxin (SAD- Serum Antitoxin Diphtheriae):
The drug is mainly made from horse serum. Diphtheria antitoxins made from human serum are rare. SAD needs to be started as soon as the disease is suspected. Mortality rate decreased by less than 1% if SAD was treated on the first day and increased 20 times if treated late on day 4. SAD only neutralized circulating toxins, but not already established toxins. attached to the organization.
About 8-10% of patients are sensitive to horse serum, so endodermal testing must be done before injection. Dilute 0.1 ml of SAD with 0.9% Nacl, concentration 1/1000. (Test 0.1 ml injected in the skin, after 20 minutes read the results). If there is a reaction, it must be treated with Besredka method of desensitization: inject SAD several times with a diluted solution, inject with increasing concentration, 20 minutes apart.
The dose of SAD varies from 20,000 to 100,000 units, depending on the degree of intoxication, the location and size of the pseudomembranous membrane, and the timing of early or late administration. The drug is given as a single intravenous infusion over 30 to 60 minutes (or intramuscularly). SAD has little effect on dermatophytosis but is still recommended due to its toxic effect.
Mild form, pseudomembranous skin only in throat and skin, no complications, early treatment before 48 hours: 20,000 to 40,000 IU Moderate form, pseudomembranous spread to nose: 40,000 to 60,000 Severe cases, complications, late treatment after 72 hours: 80,000 to 100,000IU

Cần phải test nội bì trước khi tiêm để phòng bệnh nhân bị mẫn cảm với huyết thanh ngựa trong thuốc
Antibiotics
Indicated to kill diphtheria bacteria, limit exotoxin production, antibiotics can prevent disease transmission but cannot replace SAD.
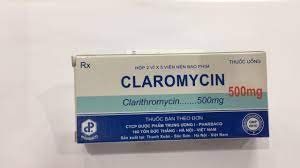
Penicillin G; 100,000 - 150,000 UI/kg/day, IV divided into 4 times x 7 days or Procaine penicillin: 25 - 50,000 UI/kg/day, divided into 2 deep intramuscular injections or Erythromycin 1.5g/24 hours, children 40-50 mg /kg/24h (maximum 2g/24h) - oral or: Clarithromycin, Azithromycin, Rifamicin. X 14 days 3.3 Treatment of complications Tracheostomy: When laryngotracheal dyspnea grade 2, TD close to dyspnea China grade I Severe Diphtheria: Prednisolone 0.5 -1mg/kg/24h x 2 weeks (Controversial - not yet there is clear evidence of the benefit of the drug in the prevention of complications) Myocarditis: Absolute rest: 55 days (minimum 2-3 weeks) Cardiac drugs (disputed), diuretics, anti-tumor Cardiac arrhythmia 3.5 Discharge criteria No clinical symptoms Complications gone, pseudomembranous diathesis gone Sufficient time for treatment and isolation Throat cultures 2 times negative, 7 days apart Need to be monitored for complications even after discharge
4. Diphtheria prevention
Early detection, timely isolation, localization of the outbreak and thorough treatment
4.1. Non-specific: Mandatory declaration Contact person: Should be closely monitored for 7 days, throat culture cultured Healthy carrier (the most important source of infection): Take Erythromycin for 10 days. Usually diphtheria bacteria will disappear after 2-4 weeks if antibiotics are not used

Cần phát hiện sớm để cách ly và khử trùng vùng ổ dịch kịp thời
4.2. Specifics: Administer diphtheria toxoid vaccine (generate toxin-neutralizing antibodies). IgM is produced 7 to 14 days after diphtheria vaccination. IgG appears after 5 to 8 weeks
Primary: 3 doses in 3 divided doses: 2,3,4 months of age (30 days apart) Repeat: 1 year old, 2 years old, 4-7 years old, 9-12 years old and every 10 years Others (during epidemics) Health workers working in environments with risk of diphtheria exposure Adults who have not been vaccinated or do not remember People who live in diphtheria-endemic areas Elderly, people with underlying medical conditions, Chronic diseases Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital offers a variety of diphtheria vaccination services for children and adults with 5 combinations, including:
Infanrix 6-in-1 vaccine Hexa from GSK (Belgium) 6-in-1 vaccine Hexaxim from Sanofi (France) 5-in-1 vaccine Pentaxim from Sanofi (France) Adacel 0.5 ml from Sanofi - France Tetraxim 0.5 ml from Sanofi - France To ensure To ensure vaccination effectiveness and safety, before injecting, customers will be examined by specialized doctors, fully screened for physical and health problems, and advised on preventive vaccines and regimens. vaccination, how to monitor and care after previous vaccination c when ordering vaccination according to the latest recommendations of the Ministry of Health & World Health Organization.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.