This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Vo Cong Hien - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. BSCK I Vo Cong Hien has many years of experience in the field of imaging, especially in diagnosing kidney cysts with ultrasound, MRI, and CT.Kidney cysts are usually diagnosed with imaging tests but mostly with ultrasound. If in case the doctor suspects a malignancy, the methods of MRI, CT scan may be indicated to find the cause and have appropriate treatment.
1. What is a kidney cyst?
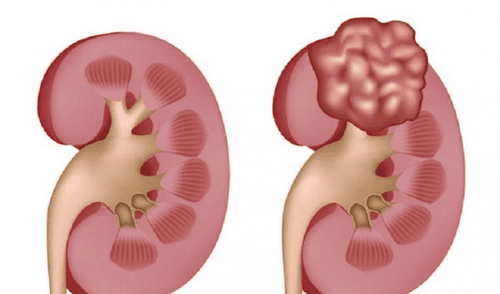
Kidney cysts are fluid sacs that form in the kidney. Most renal cysts are monocystic, thin-walled, and have a water-like fluid. It is more common in the elderly and usually does not cause any symptoms or harm.In rare cases, kidney cysts may require treatment due to infection, bleeding, or increase in size. When such complications occur, kidney cysts can cause the following symptoms:
Fever Rib or hip pain Epigastric abdominal pain Change in urination habits Blood in the urine (hematuria) Causes Renal cyst has not been identified. Age is believed to be the main risk factor. An estimated one-third of people over the age of 70 have at least one single kidney cyst. It is normal to have more than one single cyst in each kidney in the elderly.
Renal cysts that appear in large numbers in the kidneys can cause another medical condition called polycystic kidney disease (PKD). Polycystic kidney disease is an inherited disorder characterized by the development of clusters of cysts, which can cause impaired kidney function.
Hiện nay nguyên nhân gây u nang thận vẫn chưa được tìm ra
2. Diagnosis of kidney cysts with ultrasound, MRI, CT
Most cases of kidney cysts have no symptoms, so they are often discovered incidentally by imaging tests when examining other conditions. In the absence of any symptoms, kidney cysts usually do not require any further intervention or testing. However, with complex renal cysts with thick walls, solid tumors instead of liquid, additional tests are needed to monitor and determine whether it is a cyst or another malignancy. The diagnosis of kidney cysts is usually made by several types of imaging tests, including:2.1. Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound help to visualize the kidneys, thereby determining the nature of kidney cysts (number, size and wall of renal cysts). A convenient test that can be used to monitor kidney cysts when it detects any changes over time.
On ultrasound, if the renal cyst is round or oval in shape, with regular margins, clear fluid, negative void space, no posterior shadow, no communication with the pyelonephritis, the renal cyst is benign. Suspect malignancy for renal cysts with heterogeneous or dense echogenicity.
2.2. Abdominal and pelvic CT CT is an additional indication when there is a suspicion of complex renal cyst on ultrasound. It helps to differentiate benign renal cysts from renal tumours. A CT scan should be performed with contrast injection.
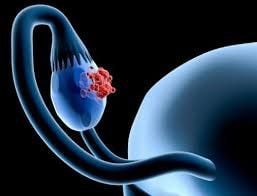
2.3. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Through MRI images, it is possible to determine in detail the structure of the kidney, helping to accurately diagnose the nature of the cyst. An MRI scan also needs to be done with contrast injection.
Chụp cộng hưởng từ (MRI) giúp chẩn đoán u nang thận
3. How are kidney cysts treated?
Renal cysts usually do not need to be treated unless symptoms are present or damage is caused to kidney function. Treatment of kidney cysts is done by the following methods:Sclerotherapy: Sclerotherapy is also known as aspiration of renal cysts. It is done by inserting a long needle through the skin and into the cyst under ultrasound guidance. This is followed by aspiration of the fluid and filling it with an alcohol-based solution that causes the cyst to harden and shrink, which reduces the chance of recurrence. The procedure is usually performed on an outpatient basis with local anesthesia. Surgery: For larger cysts, your doctor will make a small incision and access the cyst with laparoscopic surgery. Then, the fluid will be aspirated and the outer wall of the cyst will be burned or cut away. Laparoscopic surgery requires general anesthesia. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals with the function of examining, treating and screening many diseases, including kidney and urinary diseases. Especially to bring high efficiency in disease examination and treatment, Vinmec is now fully equipped with modern imaging equipment such as ultrasound machine, CT machine, MRI machine, endoscope.
When accurate results are available and the cause of the disease is found, doctors will coordinate with many different specialties to advise on the most effective treatment regimen to ensure the health of customers.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org