This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalThe most common symptoms of esophageal motility disorder (EMD) include difficulty swallowing and chest pain. However, to evaluate the criteria, it is necessary to perform upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, barium esophagography and esophageal manometry.
1. Overview of esophageal motility disorders
The esophagus acts as a tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach. Esophageal motility disorders (EMDs) are rare disorders of esophageal and lower esophageal sphincter movement. Esophageal motility disorders (EMD) represent a diverse group of conditions that alter the normal movement and movement of food from the esophagus into the stomach.The most common symptoms include difficulty swallowing and chest pain. Difficult to distinguish from other common diseases such as coronary artery disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease and malignancy. Standard evaluation included upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, barium esophagography, and esophageal manometry. The most well-described and most complete esophageal motility disorder is achalasia, which causes increased esophageal motility and poor relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (lower esophageal sphincter). Treatment for achalasia focuses on reducing the pressure of the lower esophageal sphincter to allow gravity to allow food to pass through the stomach. Balloon dilation and laparoscopic Heller myotomy (LHM) with angioplasty are standard treatments for achalasia.
1.2 Pathogenesis Esophageal dyskinesia is a disorder of the muscle lining the esophagus. In achalasia, the neurons of the myocardium are destroyed by chronic inflammation leading to esophageal motility disorders and poor dilation of the lower esophageal sphincter. The cause of chronic inflammation is unknown but may be an infectious agent in a genetically susceptible person. In South America, an achalasia-like disorder called Chaga disease is caused by infection with the protozoan T. cruzi bacteria. Similar to idiopathic achalasia, this disorder causes inflammation of the esophageal plexus with consequent dysfunction of esophageal motility and non-dilation of the lower esophageal sphincter (lower esophageal sphincter). However, patients with spastic esophagitis have a normal myocardial plexus. The etiology of these motor disorders may be due to fragmentation of vagus and mitochondrial nerve endings, esophageal muscle hypertrophy, and anxiety.
2. Diagnosis of esophageal motility disorders
2.1 Clinical Diagnosis The classic presenting symptom of achalasia is difficulty swallowing larger solids than liquids, often occurring for many years before diagnosis. Patients often learn to adapt to dysphagia by changing their diet or performing exercises that improve swallowing. Dysphagia is often accompanied by easy regurgitation of poorly digested food or liquids and is often worse in the supine position or after eating several meals. Sometimes regurgitation can lead to aspiration pneumonia.In addition, with poor nutrition, weight loss is inevitable. Patients with low back pain or spastic dyskinesia may complain of chest pain, which may or may not be worse with swallowing.
Chest pain, often incorrectly identified as being due to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is rare in patients with lower esophageal sphincter pressure.
2.2 Differential diagnosis When middle-aged patients report chest pain as part of their symptom complex, coronary artery disease and GERD must be considered initially. Difficulty distinguishing movement disorders from coronary artery disease is particularly difficult in patients who may have other risk factors for coronary artery disease such as diabetes, hypertension, tobacco use, or family history. However, chest pain associated with esophageal motility disorders is often accompanied by food intake and is often sharp, non-radiating, and rarely lasts more than a few minutes. This is in contrast to angina pectoris which is often associated with exercise and exertion and is a persistent, dull, or severe chest pain that may radiate to the jaw or left arm.
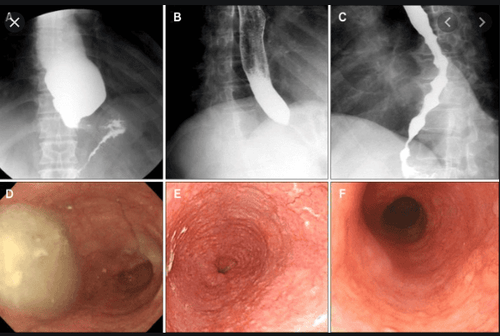
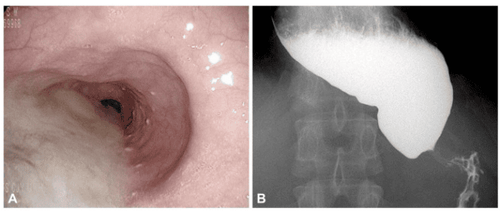
Other motility disorders such as esophageal spasm or jackhammer's esophagus often present with random, disordered esophageal contractions seen on endoscopy or radiographs of the esophagus with contrast.
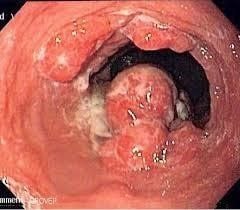
2.5 Role of High Resolution Esophageal Manometry (HRM) The most important test for diagnosing esophageal motility disorders is high resolution esophageal manometry (HRM). This test requires inserting a soft flexible catheter through the nose and into the upper part of the stomach. The catheter has a pressure sensor every 1-2 cm. In a high-resolution esophageal manometry, the patient is asked to swallow approximately 10 liquid swallows. Machine software generates maps showing time, length, and pressure that are used to further classify these disorders. The most commonly used classification system is called the Chicago Classification 3.0.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: John Dewitt, update in the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal motility disorders, Dispatches from the guild conference, series20, practicalgastro, march 2019 • volume XLIII, issue 3